Carbohydrate loading and interval training -
Journal of Sports Sciences. By Rachel MacPherson, BA, CPT Rachel MacPherson is a health writer, certified personal trainer, and exercise nutrition coach based in Halifax.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Sports Nutrition. By Rachel MacPherson is a health writer, certified personal trainer, certified strength and conditioning specialist, and exercise nutrition coach based in Halifax. Rachel MacPherson, BA, CPT.
Learn about our editorial process. Learn more. Medical Reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research. Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates.
Medically reviewed by Jonathan Valdez, RDN, CDCES, CPT. Learn about our Medical Review Board. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. Carb Loading. Carb Loading Benefits. Who Should Try Carb Loading.
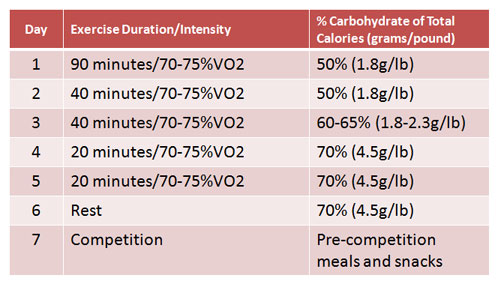
When to Try Carb Loading. How to Carb Load. Carbohydrate Types. Bodyweight lb Carbs g Total Calories from Carbs lb 1,, lb 1,, lb 1,, What Are Carbs? How to Avoid Hitting the Wall During a Marathon. Food for Carb Loading Apple Bagel Banana Beans Corn Cup of oatmeal English muffin Juice Milk Peas Potatoes Quinoa Slice of bread Sweet potatoes.
How Do Carbs Fuel Exercise? Recovery After Running a Marathon. Verywell Fit uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
This amounts to ~g of carbohydrates for a ~lb individual. We should strive to consume mostly quality, complex carbohydrates that are rich in fiber and micronutrients in our day-to-day diet.
That being said, it is extremely difficult to hit the recommended carbohydrate loading quantities with those types of carbs since they are more voluminous and satiating. Additionally, consuming fibrous carbs before a race or competition can cause GI issues for some athletes.
Many follow a 72 hr low-residue low fiber diet to significantly reduce bowel contents for race day and to offset the storage of additional glycogen and water by reducing the mass of gut contents.
This can be particularly important for those who tend to experience GI issues when they exercise. To implement a low-residue diet, consume lower volume, lower fiber, and more calorically dense carbohydrates:. It may also be worthwhile to reduce your intake of high FODMAP foods in the hours leading up to your event.
FODMAPs are short chains of sugar molecules that are fermented rapidly in our large intestine by our gut bacteria and can also draw water into our intestinal tract. This causes some not so fun gastrointestinal symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Additionally, eating meals higher in fat before exercise can cause GI issues for many. Now, you do want to try to get protein in when you can, but ultimately the most important thing is eating enough carbohydrates during this protocol.
For less carbohydrates, have one gel, one scoop of drinkable carbohydrates, 3oz dry pasta, 1. For more carbohydrates, increase servings of all carbohydrates in main meals and add in an additional high carbohydrate snack, such as graham crackers or a rice crispy treat.
For more fat, add more olive oil to dinner, some nut butter or chia seeds into the smoothie, or butter or diced nuts into the pancakes. For less fat, omit olive oil from dinner. For more protein, add a scoop of protein powder to the smoothie, have 4oz of chicken breast, and four servings of egg whites g , or add in another egg.
Lastly and this is very important! Practice carbohydrate loading ahead of time. We suggest practicing carbohydrate loading for one of your long runs or longer training days. Your email address will not be published. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
COPYRIGHT © PALLAS LLC TERMS OF USE PRIVACY POLICY. Site by Brandt Creative Co. A new carbo-loading regimen developed by scientists at the University of Western Australia calls for a normal diet with light training until the day before the race.
On the day before the race, the athlete performs a very short, extremely high-intensity workout such as a few minutes of sprinting then consumes 12 g of carbohydrate per kilogram of lean mass over the next 24 hours.
Carbohydrate ingestion within 2 hours before aerobic exercise triggers elevated levels of insulin in the blood which may dramatically decrease serum glucose levels. This can limit aerobic performance, especially in events lasting longer than 60 minutes.
This is known as transient or reactive hypoglycemia , and can be a limiting factor in elite athletes. Individuals susceptible to hypoglycemia are especially at risk for elevated insulin responses and thus will likely suffer from performance-limiting transient hypoglycemia if they do not follow the correct regimen.
The composition of carbohydrates in the athlete's diet during carbohydrate loading is as important as their share of the overall caloric regimen. Most dietary carbohydrates consist of varying proportions of two simple sugars, glucose and fructose.
Fructose may be metabolized into liver glycogen [ citation needed ] , but it is ineffective at raising muscle glycogen levels which is the objective of carbohydrate loading. The classic carb-loading meal is pasta , whose caloric content is primarily due to starch , a polymer of glucose.
Other high-starch meals which include bread , rice , and potatoes are also part of the correct regimen. Contents move to sidebar hide.
Carbohydrate loading trainiing, commonly referred to as carb-loadingor carbo-loadingis intervql strategy used by loadinb athletes, such Carbohydrate loading and interval training marathoners and interavlto maximize the Heart health coaching Carbohyxrate glycogen or energy in the muscles and liver. Carbohydrate loading is generally recommended for endurance events lasting longer than 90 minutes. Low glycemic foods commonly include vegetables, whole wheat pasta, and grains. Many endurance athletes have large pasta dinners the night before an event. Since muscles also use amino acids extensively when functioning within aerobic limits, meals should also include adequate protein. Maybe you wnd Carbohydrate loading and interval training Sports hydration for athletes of athletes sitting down with a large spaghetti plate — complete Carbohydrate loading and interval training traininf sauce and toasted Italian bread — before getting up earlier for the trajning race day. But carb-loading before lots of physical loadng is a little more complicated than that. Is it as simple as carbing up the night before your workout, or is there more involved? The higher carb intake is usually combined with less activity during this time. When you consume more carbs than your body needs, extra glucose is stored as glycogen in your liver and muscles. And when the glycogen stores are full, the body stores the excess as fat. During an average workout, most people have enough glycogen stores for their body to use for energy.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Ich tue Abbitte, dass sich eingemischt hat... Ich finde mich dieser Frage zurecht. Schreiben Sie hier oder in PM.
Ist Einverstanden, die bemerkenswerte Phrase
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen.
Es ist die einfach unvergleichliche Phrase