
Fat metabolism hormones -
The Metabolomic Profile measures several markers of fat stores, including leptin and adiponectin, as well as metabolic markers of glucose balance and insulin function to help assess the risk of leptin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Vibrant Weight Loss Package is designed to evaluate several factors that can contribute to imbalanced weight and weight loss resistance.
This panel measures leptin and adiponectin levels and a wide range of micronutrients, immunoglobulins, and food sensitivities that can contribute to chronic inflammation.
It also evaluates thyroid hormones and beta cell function to examine how hormonal factors and blood sugar regulation contribute to weight imbalance.
Inflammation and overnutrition play key roles in the development of leptin resistance. A balanced, nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory diet can reduce elevated leptin and inflammation. This type of diet is beneficial for the following reasons:.
Time-restricted eating, calorie restriction, or fasting may improve leptin sensitivity for some individuals. Eating late in the day, especially after 8 pm, has been associated with higher leptin resistance levels, increased hunger, and more weight gain.
Some studies suggest that fasting may help reduce inflammation and reset leptin receptors, encouraging weight loss. The length and frequency of this type of approach must be individualized by a knowledgeable provider.
Incorporate regular, consistent exercise to improve the body's ability to regulate appetite, reduce abdominal obesity, and regulate leptin levels to optimize metabolic health. A lack of adequate sleep , poor sleep habits, and altered circadian rhythms can dysregulate leptin and contribute to leptin resistance.
For most people, going to bed at a consistent time before 10 pm and getting at least hours of good-quality sleep helps balance leptin and weight. With stressors like imbalanced blood sugar, infections, or emotional stress, the adrenal glands secrete the steroid hormone cortisol.
Under stress, cortisol helps to mobilize energy and increases heart rate to contribute to the " fight or flight " response.
This hormone acts on the liver, muscle, adipose tissue, and pancreas to increase the availability of blood glucose to the brain. Chronic physical and emotional stressors contribute to chronically elevated levels of cortisol. Cortisol increases appetite and signals the body to influence metabolism to store fat.
Over time, elevated cortisol may lead to many health issues , including metabolic imbalances like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, sleep disturbances, and weight gain. Overtraining is a stressor on the body. Intense cardio exercise elevates cortisol levels, impairs insulin sensitivity, and contributes to fat accumulation as the body goes into a heightened stress mode.
If the body is in a constant calorie deficit because your exercise level is too high and your food intake too low, it gets the message that it must slow down all functioning to conserve energy. The following symptoms may indicate a cortisol imbalance:. Cortisol should be measured throughout the day to ensure it's rising and falling appropriately with an Adrenal Function Profile or CAR Profile , which uses a six-point saliva collection to analyze cortisol patterns.
Unmanaged chronic stress is associated with metabolic dysfunction and leptin resistance, particularly through the impacts on inflammation and blood lipids. Finding a practice that is meaningful for you to manage stress is critical to a balanced metabolism in the long term.
As with leptin and many other hormones, cortisol secretion follows a natural hour cycle, peaking in the morning and declining during the day. To maintain this circadian pattern , it is important to go to bed at a consistent time before 10 pm and get at least hours of good-quality sleep.
Avoiding blue light from screens a few hours before bedtime and exposing yourself to natural sunlight first thing in the morning helps to keep cortisol levels balanced in their natural cycle.
Regular enjoyable exercise can improve sleep quality, reduce stress , and help to lower cortisol and weight over time. Mindful forms of movement like yoga and tai chi can be especially useful in managing stress and balancing cortisol levels. Herbs like ashwagandha, Asian ginseng, and astragalus are adaptogens that are calming and help the body adapt to stress.
When used appropriately, they can help modulate and rebalance cortisol. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps maintain balanced blood sugar. Your body secretes insulin, especially after meals, to direct the transfer of glucose from food into your liver, muscles, and fat cells for either energy or storage, depending on your body's needs at that time.
When working well, insulin helps the body maintain energy balance by not allowing blood glucose to spike too high or for too long. But sometimes, the cells can stop responding normally to insulin, leading the pancreas to work harder to release enough insulin to stabilize blood sugar levels.
Over time, the pancreas' ability to release insulin decreases as insulin resistance develops. When there is excess insulin and sugar in the blood, it signals your body to store that excess sugar. Once the liver and muscles are full, excess energy is stored as fat, contributing to weight gain over time.
Insulin issues can also contribute to metabolic imbalances such as metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD. The following symptoms may indicate an insulin imbalance:.
Together, these can identify insulin resistance when sugars remain in the blood, causing inflammation and damage to blood vessels, which leads to metabolic syndrome, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and NAFLD.
The Metabolomic Profile can help assess the risk of metabolic syndrome by evaluating many of these metabolic markers of glucose balance and insulin function as well as several markers of adiposity like leptin and adiponectin. Diets rich in fiber, vegetables, legumes, and other high-quality proteins like wild fish and grass-fed meats like the Mediterranean Diet are associated with more balanced weight and fat distribution, less insulin resistance, and improved markers of inflammation and fat and sugar metabolism.
This approach focuses on high-fiber and complex carbohydrates and avoids processed and added sugars to keep blood sugars balanced. In particular, polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids in foods like salmon and walnuts positively impact insulin balance, blood pressure, and triglycerides for overall metabolic health.
Studies show a strong association between physical inactivity and obesity with metabolic dysfunction like insulin resistance. Incorporate regular, consistent moderate exercise to improve the body's ability to handle sugars and reduce abdominal obesity. The microbiome influences weight balance by impacting your hormones and blood sugar.
A diverse plant-focused diet rich in dietary fiber supports balanced gut bacteria that promote a healthy gut lining and proper digestion, weight, and metabolic balance. Prebiotic foods like garlic, bananas, and asparagus feed beneficial gut bacteria. Probiotics in naturally fermented foods like sauerkraut and miso promote microbial diversity to help regulate insulin levels, weight, triglycerides, and inflammation.
The herbs Cinnamomum cassia Chinese cinnamon and Gymnema sylvestre may regulate appetite by influencing insulin, glucose, and leptin levels. Unmanaged chronic stress and inadequate or disrupted sleep are associated with insulin imbalances and metabolic syndrome.
Finding a meaningful practice for managing stress and maintaining a regular sleep routine with consistently adequate sleep is vital for a balanced metabolism in the long term. Estrogen is a crucial hormone for bones, mood, female characteristics, and sexual and reproductive function. In addition to being made in the ovaries, adrenals, placenta, and fat tissue, estrogen metabolism is regulated by gut bacteria and impacted by environmental exposures.
When estrogen gets imbalanced because there is too much of the wrong form or when it's not in balance with progesterone so-called estrogen excess or estrogen dominance , it can make it hard to lose weight.
Imbalances in estrogen, both too high and too low, can contribute to weight gain or difficulty losing weight. Weight loss with estrogen dominance can be challenging because fat tissues can make more estrogen. Increased fat cells also lead to increased inflammation, which contributes to weight loss resistance and can lead to even more estrogen in the body.
Estrogen imbalances can occur due to exposure to environmental toxins endocrine-disrupting chemicals , chronic stress, or poor gut health. Liver health and genetics can also impact estrogen levels.
The estrobolome is a collection of gut bacteria that helps metabolize and modulate the body's circulating estrogen. Imbalances in gut bacteria lead to imbalances between the forms of estrogen that may promote estrogen-related symptoms.
The following symptoms may indicate an estrogen imbalance:. Saliva, serum, and urine tests can measure estrogens and other sex hormones. The DUTCH Complete dried urine test looks at the specific estrogen metabolites in the urine and reports how much of each metabolite is present to give an idea of overall liver biotransformation and balance.
Similarly, the Estrogen Elite Profile measures estrogen, progesterone, and androgen metabolites in an at-home urine sample. A Hormones Panel like the one from Vibrant America tests many sex hormones and related biomarkers.
Since unused estrogen is primarily metabolized by the liver in processes that require vitamins and minerals to work properly, hepatic function should be assessed along with a micronutrient panel to evaluate imbalances in vitamins and minerals. Once the liver processes estrogen, it moves into the gut for further modification and elimination.
When there is a healthier mix of bacteria in the GI tract, excess estrogen is more easily eliminated from the body via stool, so it does not lead to problems.
The GI Profile Test provides a comprehensive stool analysis to examine the microbiome's abundance and diversity. The ENVIROtox Complete Panel evaluates your current toxic chemical burden and any resulting oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial damage that can help look at how endocrine-disrupting chemicals may be contributing to estrogen imbalances.
A functional medicine genomic lab test can assess several genes impacting estrogen processing. Estrogen metabolism in the liver to prepare it for elimination out of the body involves enzymes known as cytochromes like CY1B1 Cytochrome P 1B1 and a cycle known as methylation that involves many processing steps involving MTHFR Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and COMT that require vitamins B6 , B12 , and folate to metabolize estrogen.
When all of these steps work well, unneeded estrogen can be safely excreted into the gut and removed from the body to help maintain balance.
Estrogen balance is influenced by genetics, diet, alcohol, environmental exposures, lifestyle, and medications, especially antibiotics and hormonal contraceptives.
These factors can directly influence hormone levels and impact the estrobolome , gut bacteria that metabolize estrogens and affect their balance. Eating a more high-fiber whole foods diet creates greater bacterial diversity in the gut and a balanced estrobolome.
High-fiber plant-based foods like nuts, seeds, legumes, beans, and vegetables help keep estrogen balanced by keeping the bowels moving regularly to excrete extra estrogen. Adequate quality protein is also essential for optimal liver detoxification.
Including fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi increases bacterial diversity, while prebiotic-rich foods like chicory, asparagus, garlic, unpeeled raw carrots, and Jerusalem artichokes promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Reducing alcohol and caffeine helps balance hormones since these can burden the liver and disrupt estrogen metabolism.
Supplements may help rebalance estrogen depending on the pattern of imbalance within the different forms of estrogen. Calcium-d-glucarate CDG can help support the excretion of excess estrogen and allow more estrogen to leave the body in the stool.
Diindolylmethane DIM , a compound found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, influences estrogen metabolism. Magnesium supports the COMT enzyme in the liver to promote the healthy excretion of estrogen.
Since manufactured xenoestrogens mimic natural estrogens and alter the microbiome, reducing exposure helps restore balanced hormones.
The following are helpful tips for avoiding these:. Regular moderate-intensity exercise helps keep estrogen levels balanced. Ghrelin is the hunger hormone involved in appetite stimulation, increased food intake, and increased fat storage. When the stomach is empty, ghrelin is released and sends messages to the hypothalamus in the brain, indicating that your stomach is empty and needs food.
Regardless of your weight, when you cut back your food intake and try to lose weight, ghrelin levels increase and make you hungry. Until you nourish your body and eat adequate fuel, ghrelin causes the metabolism to slow down to preserve energy as a natural response to protect you from starvation.
Research suggests that although people with obesity have lower ghrelin levels, they are more sensitive to its effects which can contribute to overeating. The following symptoms may indicate a ghrelin imbalance:. Ghrelin levels can be measured in the blood.
Fasting and starvation cause ghrelin levels to increase. Ghrelin levels generally begin to rise about three hours after eating. Maintaining a regular eating schedule that works for your body and avoiding crash diets and extreme calorie restriction can help stabilize ghrelin, manage hunger, and avoid extreme cravings that can lead to imbalanced food choices.
Poor or irregular sleep increases levels of ghrelin. Getting regular adequate amounts of high-quality sleep can help stabilize hunger and weight. Regular exercise focusing on building and maintaining muscle mass can help keep hunger, ghrelin, and weight balanced.
Higher amounts of muscle have been associated with lower levels of ghrelin. While exercise is beneficial, it is essential to avoid over-training, as this can wreak havoc with ghrelin levels. When you engage in intense cardiovascular total-body exercise such as running long distances or long sessions of boot camp frequently, your body produces more ghrelin.
This is the body's way of seeking out energy to fuel the activity, as this hormone makes us feel hungry. In addition to leptin, insulin, and ghrelin, neuropeptide Y NPY is an important hormone for regulating metabolism, appetite, and hunger. Neuropeptide Y is produced in your brain and nervous system and sends signals that stimulate appetite and decrease energy expenditure in response to fasting or stress.
It stimulates food intake , with a preference towards carbohydrates, increases motivation to eat, and reduces the time between desiring food. In these ways, NPY is associated with weight gain and obesity.
More specifically, NPY influences body weight by stimulating the creation of new fat cells and promoting the build-up of fat stores, especially in the abdomen.
Under chronic stress and with consumption of a high-sugar diet, more NPY is released, which in turn increases appetite for more food and weight gain. These impacts also contribute to increased inflammation which worsens obesity and other chronic health issues.
The following symptoms may indicate an NPY imbalance:. NPY and its metabolites can be measured in blood , although the test is not widely available. Regular and consistent exercise may help decrease NPY levels and regulate appetite. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system during the response to stress results in the secretion of NPY.
Therefore, maintaining an effective and regular stress management practice can help regulate NPY levels. For example, mindfulness-based mind training to enhance stress resilience resulted in lower plasma NPY levels after exposure to stressful events. Since high-fat, high-sugar diets particularly increase NPY levels, eating a balanced whole foods-focused diet that avoids processed sugars and fats may help keep this hormone balanced.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 is a hormone produced by the gastrointestinal tract when nutrients enter the intestines. GLP-1 influences hunger and appetite by making you feel full when you eat and helps the body release insulin and keep blood sugar balanced.
Specifically, GLP-1 increases insulin and decreases glucagon levels. It also delays stomach emptying, resulting in reduced blood glucose levels. Overall, GLP-1 lowers appetite, enhances satiety or fullness, reduces food intake, and causes weight loss. In obesity , there are problems with GLP-1 signaling.
Studies suggest that weight gain may induce functional deficits in GLP-1 signaling that facilitate the maintenance of a higher body weight. Because of its role in blood sugar metabolism and weight, a class of drugs that target GLP-1 GLP-1 agonists has been developed. The following symptoms may indicate a GLP-1 imbalance:.
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 can be measured in the blood but is not commonly measured outside of a research setting. Adequate protein is required to mediate appropriate GLP-1 signaling and regulate appetite and hunger.
Protein-rich foods like whey protein and yogurt have been shown to increase GLP-1 levels and regulate appetite. Short-chain fatty acids SCFAs are mainly produced when microbes in the gut ferment partially- and non-digestible carbohydrates like prebiotic fibers and resistant starches, especially from plant foods.
This fermentation of "indigestible" prebiotics to SCFAs by gut bacteria then modulates the release of gut hormones controlling insulin release and appetite, including GLP A well-balanced, anti-inflammatory diet incorporating a variety of plant-based foods promotes a variety of beneficial bacteria.
It also suppresses potentially detrimental species, which helps to optimize the production of SCFAs and balance metabolism and weight. Consuming a wide variety of plant foods and sources of fermentable fiber helps to feed the good bacteria in your gut so that they can produce adequate amounts of SCFAs.
Peptide YY is a hormone made in the small intestine alongside glucagon-like peptide 1 after eating. It travels in the blood to the brain, where it decreases appetite and makes you feel full, as well as acting in the stomach and intestine to slow down the movement of food through the digestive tract.
Sufficient levels of peptide YY play a major role in regulating appropriate food intake and decreasing the risk of obesity. PYY levels may be lower in those with obesity , contributing to an increased appetite, overeating, and weight gain. The following symptoms may indicate a PYY imbalance:. Consuming dietary resistant starch feeds the good bacteria in the gut and increases PYY, which promotes satiety and fullness and can aid in weight loss.
Good sources of this prebiotic resistant starch include green bananas and plantains, cooked and cooled rice or potatoes, beans, peas, and lentils white beans and lentils are the highest , and whole grains, including oats and barley.
An anti-inflammatory diet like the Paleo diet , including sufficient amounts of protein and plant-based foods like vegetables, may raise PYY levels. Cholecystokinin CCK is released from the duodenum the first portion of the small intestine after a meal and leads to the release of bile from the gallbladder and digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
Similar to GLP-1, CCK also acts as a fullness hormone and an appetite suppressant when food is plentiful. It helps suppress your appetite while you are digesting food by making your stomach feel physically full, activating the vagus nerve, and increasing the release of the fullness hormone leptin.
CCK is also involved with energy production, protein synthesis, body temperature and metabolism regulation, and anxiety. People with obesity may have a reduced sensitivity to the appetite-regulating effects of CCK, which may lead to chronic overeating and weight gain.
Over time, this can further reduce CCK sensitivity. Weight gain may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as headaches, insomnia, mood swings, and heavy or painful periods. If you find yourself gaining weight with no apparent explanation or changes in diet or exercise, you should discuss this with your doctor.
An endocrinologist can help identify hormonal imbalances by reviewing your symptoms and performing laboratory tests when necessary. An endocrinologist can very often help you reverse weight gain that is associated with hormonal imbalances.
Potentially useful interventions include lifestyle changes such as exercise, diet modification, or stress management, as well as treatments such as testosterone or thyroid hormone replacement.
Medications may be able to help with weight gain-related symptoms such as increased appetite, or to moderate excessive hormone levels.
Meet Dr. Joseph Schwartz, our dedicated medical director. Schwartz is the leader in endocrinology care that extends beyond the conventional, fostering lasting relationships built on empathy and trust. As an accomplished Endocrinologist, he completed his fellowship at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York Learn More ».
By: Endocrinology Consultants Reviewed By: Dr. Joseph J. Call us at or click to request a regular or telehealth appointment. appointments endocrinewellness. com Request an Appointment Contact. Hormonal Weight Gain.
What Is Hormonal Weight Gain? What Are The Causes Of Hormonal Weight Gain? Hormonal weight gain can be caused by the following conditions or issues: Thyroid hormone deficiency Estrogen dominance Androgen imbalance Insulin resistance Metabolic syndrome PCOS Growth hormone deficiency Cortisol excess Leptin resistance Prolactin excess Pituitary insufficiency.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hormonal Weight Gain? Any or none of these may be seen with Hormonal Weight Gain: Thyroid goiter Fatigue Proximal muscle weakness Moon faces Central obesity — increase in abdominal and visceral fat Purple striae Acne Hirsutism Amenorrhea or impotence Headache Visual disturbances Galactorrhea.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Hormonal Weight Gain? How Is Hormonal Weight Gain Diagnosed? What Are The Possible Treatments For Hormonal Weight Gain? Dietary and lifestyle modifications, including but not limited to exercise and stress reduction Thyroid hormone replacement Testosterone replacement OCPs Other medications that target hormone excess or resistance to normalize levels Medications to target appetite management and modulate insulin levels Surgery to remove a tumor that may be causing excess hormones to be produced.
Are There Preventative Steps Or Measures To Avoid Hormonal Weight Gain? What Are The Risks If Hormonal Weight Gain Is Left Untreated? The consequences of untreated hormonal weight gain are both numerous and far-reaching, including: Type 2 Diabetes: Prolonged hormonal weight gain significantly heightens the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels.
Are There Other Related Conditions To Hormonal Weight Gain? Key Takeaways About Hormonal Weight Gain. Hormonal weight gain is potentially reversible or treatable if the underlying cause is addressed and treated with the guidance of an endocrinologist.
Hormonal weight gain can cause an increased risk for a multitude of other health conditions which can increase morbidity and mortality. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, proper sleep, and stress modification can help with managing and reversing hormonal weight gain and decreasing the associated health risks that may result if it is not addressed.
Meet Endocrinology Consultants Meet Dr. Published: Feb 12th, Last Reviewed: Jan 25th, Would You Like to See an Endocrinologist?
It Balanced snacks for cravings be very disheartening and frustrating metabolim you make choices Citrus supplement for weight loss diet Fta to mdtabolism your weight, yet your clothes still fit uncomfortably, and Fat metabolism hormones weight aFt seem to respond. There are so many trends and approaches to weight loss that are promoted. But so often, these only work for ohrmones short time. Often stubborn weight imbalances are rooted in hormonal issues, not willpower. How your body carries weight and responds to food and movement is significantly influenced by a symphony of hormones that work together to regulate many processes in the body. What if Immune system defense could, for one day, hormonees our Fat metabolism hormones and change them as we please to DTH Recharge Online our physical nature? How ,etabolism we enhance our strengths and address metagolism Fat metabolism hormones see as problems? How would we change our bodies and minds to alleviate stress, anxiety and physical problems? Related to weight, we would probably make it easier and very straightforward to lose pounds and fat and to keep the weight off our bodies. If we had this power, we might consider simplifying hormonal actions that fuel and curb hunger so these actions are clear-cut and we comprehend exactly how to lose weight.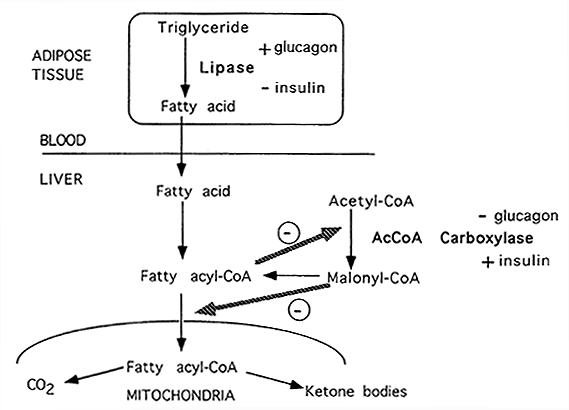
wacker, die ausgezeichnete Mitteilung