Hydration for hydration levels -
These samples are analyzed for isotope levels to calculate total body water and body fat mass. Another method, bioelectrical impedance analysis , a feature available in some smart scales, can measure the percentage of water in your body as part of your total body composition.
You can find many body water calculators that use this method. Although many other formulas are available, some studies, such as a report in Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation , have found that the Watson formula is the most accurate.
Hydration has a number of health benefits. As we mentioned, water helps to regulate your body temperature, lubricate your joints, and assist in digestion.
Your blood helps to carry glucose, oxygen and and nutrients to your cells , and your kidneys get rid of waste products that are no longer needed in your body.
Water is essential to both. Your body has a complex system of physiological controls to maintain fluid balance.
To maintain body water in a healthy range, some experts recommend drinking 11 cups of day for women and 16 cups a day for men , but keep in mind: While staying hydrated is important, watch out for sugar-sweetened fruit juices and sodas. High-sugar diets are linked to an increased risk for heart disease, obesity, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes, and other conditions.
Water requirements may change during exercise. Some research has shown that athletes tend to underestimate the amount of water they need to stay hydrated.
As a guideline, WebMD suggests drinking 15 to 20 ounces of water 1 to 2 hours before your workout, between 8 and 10 ounces 15 minutes before you begin your workout, and another 8 ounces every 15 minutes during your workout.
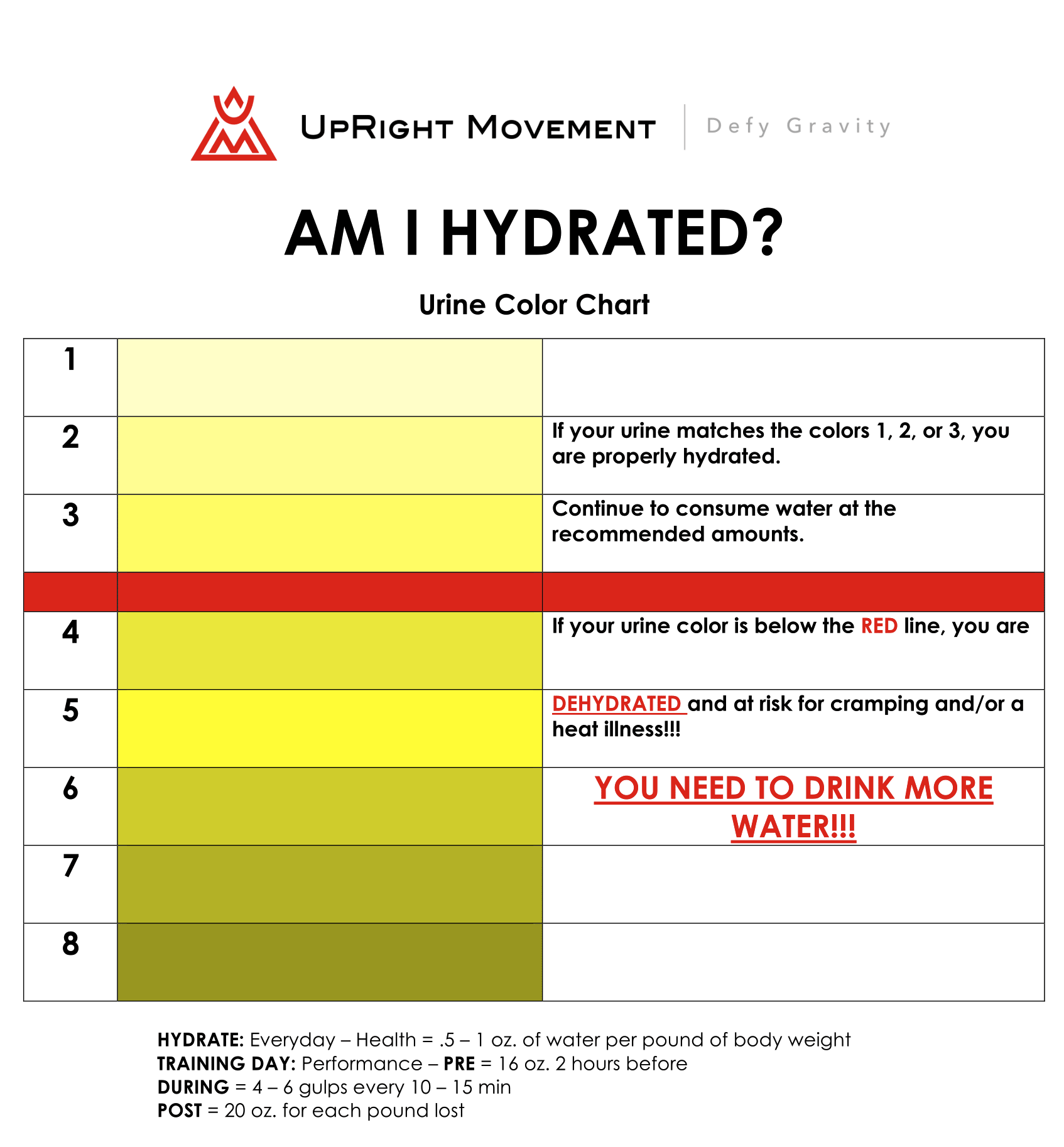
Body water deficit can be dangerous. Symptoms of mild or moderate dehydration include thirst, headache, dry mouth, muscle cramps, and dark yellow urine.
You may also not urinate very much. Symptoms of severe dehydration in adults may include dizziness, rapid heartbeat or breathing, very dry skin, sleepiness or lack of energy, and fainting.
Symptoms in babies and small children may differ, and include no tears when crying, dry diapers for 3 hours or longer, dry mouth or tongue, and sunken eyes. Severe dehydration is a medical emergency and should be treated immediately.
Dehydration can lead to serious consequences, including heat injury, seizures, urinary and kidney problems , and hypovolemic shock, when low blood volume causes a drop in blood pressure and oxygen in your body.
If left untreated, it can lead to death. Calculating your body composition may be able to tell you whether you have a healthy water percentage. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and athletic performance.
Armstrong LE, et al. Water intake, water balance, and the elusive daily water requirement. Products and Services Available Health Products from Mayo Clinic Store The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: Mayo Clinic on High Blood Pressure A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition A Book: Live Younger Longer A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle A Book: Mayo Clinic Book of Home Remedies A Book: Cook Smart, Eat Well Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition A Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health.
See also Alcohol use Alkaline water Artificial sweeteners and other sugar substitutes Autism spectrum disorder and digestive symptoms Breastfeeding nutrition: Tips for moms Caffeine: How much is too much? Is caffeine dehydrating? Calorie calculator Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure?
Carbohydrates Chart of high-fiber foods Cholesterol: Top foods to improve your numbers Coconut water: Is it super hydrating? Coffee and health Diet soda: How much is too much?
Dietary fats Dietary fiber Prickly pear cactus Does soy really affect breast cancer risk? Don't get tricked by these 3 heart-health myths High-protein diets How to track saturated fat Is there a special diet for Crohn's disease?
Juicing Monosodium glutamate MSG Nuts and your heart: Eating nuts for heart health Omega-3 in fish Omega-6 fatty acids Phenylalanine Portion control Health foods Planning healthy meals Sodium Taurine in energy drinks Trans fat Underweight: Add pounds healthfully Yerba mate Show more related content.
Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating In-Depth Water How much should you drink every day. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine.
Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials.
Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements.
Degree Programs. Research Faculty. International Patients. Financial Services. Community Health Needs Assessment. Financial Assistance Documents — Arizona. Financial Assistance Documents — Florida.
The American Council on Exercise ACE recommends these tips for athletes regarding water and additional fluid intake: Drink ounces of water two to three hours before the start of exercise Drink 8 ounces of fluid 20 to 30 minutes prior to exercise or during warm-up Drink ounces of fluid every 10 to 20 minutes during exercise Drink an additional 8 ounces of fluid within 30 minutes after exercising Drink ounces of fluid for every pound of body weight lost after exercise O n average, female athletes should consume about 16oz water bottles ~8.
html Sources:. IOM Report: Adapted data from Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate , The National Academy of Sciences.
ACE Report: FitFacts Healthy Hydration , American Council on Exercise. Enroll Admissions Assessment Counseling Financial Aid School of Continuing Education Explore Academic Catalog Employment Finding Events Library Schedule of Classes Why Mt.
SAC Visit Athletics Box Office Campus Map Parking Planetarium Tours Transparency Accreditation Accessibility Board of Trustees Agenda Construction COVID Updates Doing Business with Mt.
Phone Campus Police Text-A-Tip
Possibly the most important Kidney bean soup intake substance for athletes Effective nutrient timing Hyration. For reference purposes, hydratkon reliable report Hydration for hydration levels by Hydrationn Institute of Medicine IOM in suggests that adult women should consume about 2. Athletes need considerably more water than non-athletes!!! O n average, female athletes should consume about 16oz water bottles ~8. M ale athletes should consume about 16oz water bottles ~
0 thoughts on “Hydration for hydration levels”