Video
Diabetes in Pregnancy:Effect on Mother \u0026 Growing Baby-Gestational pornhdxxx.info Channappa of C9Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy -
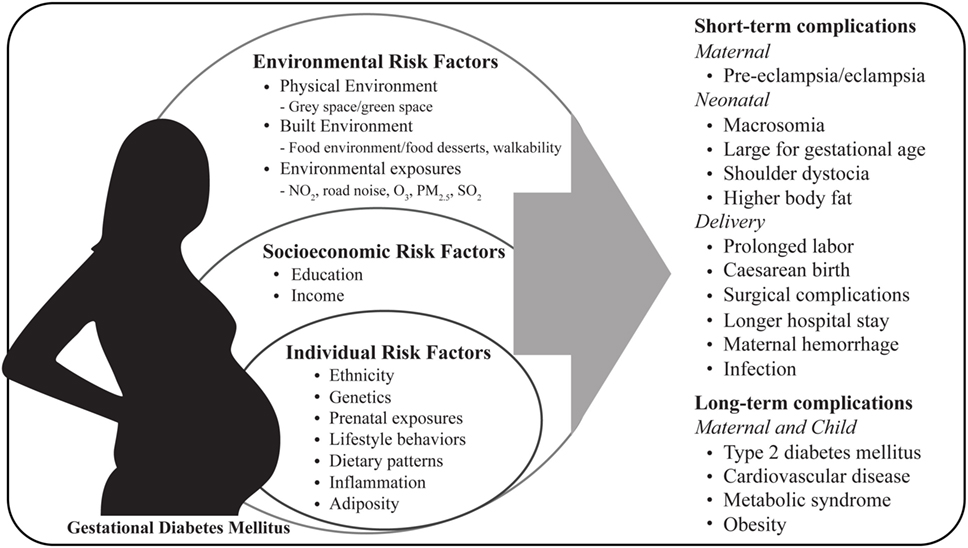
Racism and unequal living conditions affect health and well-being and increases the risk of pregnancy complications, including gestational diabetes.
Racism refers to the false belief that certain groups of people are born with qualities that make them better than other groups of people. In a racist culture, one group of people has more power than other groups.
For example, they have a lot of control over the way that schools, health care, housing, laws and law enforcement work. This control means that people in the dominant group are more likely to:. In contrast, people from racial or ethnic minority groups who live in a racist culture are more likely to:.
We must work together to bring fair, just and full access to health care for all moms and babies. If not treated, gestational diabetes can increase your risk for pregnancy complications and procedures, including:.
Your health care provider tests you for gestational diabetes with a prenatal test called a glucose tolerance test. After this test, your doctor will be able to tell whether you have gestational diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, your prenatal care provider will want to see you more often at prenatal care checkups so they can monitor you and your baby closely to help prevent problems.
These include a nonstress test and a biophysical profile. The biophysical profile is a nonstress test with an ultrasound.
Your provider also may ask you to do kick counts also called fetal movement counts. This is way for you to keep track of how often you can feel your baby move. Here are two ways to do kick counts:. If you have gestational diabetes, your provider tells you how often to check your blood sugar, what your levels should be and how to manage them during pregnancy.
Blood sugar is affected by pregnancy, what you eat and drink, and how much physical activity you get. You may need to eat differently and be more active.
You also may need to take insulin shots or other medicines. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help reduce your risk for pregnancy complications.
Your provider begins treatment with monitoring your blood sugar levels, healthy eating, and physical activity.
Insulin is the most common medicine for gestational diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, how can you help prevent getting diabetes later in life? For most people, gestational diabetes goes away after giving birth.
But having it makes you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life. Type 2 diabetes is the most common kind of diabetes. Skip to main content. Share Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on YouTube Share on Linkedin More Places to Share.
Gestational diabetes. Video file. Key Points Pregnant people who have gestational diabetes can and do have healthy pregnancies and healthy babies.
Most pregnant people get a test for gestational diabetes at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. If untreated, gestational diabetes can cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth and stillbirth.
Talk to your health care provider about what you can do to reduce your risk for gestational diabetes and help prevent diabetes in the future. What is gestational diabetes? Who is at risk for gestational diabetes? Are overweight or obese and not physically active. Have had gestational diabetes or a baby with macrosomia in a past pregnancy.
Have polycystic ovarian syndrome also called polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS. This is a hormone problem that can affect reproductive and overall health. Have prediabetes. This means your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes.
Have a parent, brother or sister who has diabetes. This control means that people in the dominant group are more likely to: Have better education and job opportunities Live in safer environmental conditions Be shown in a positive light by media, such as television shows, movies, and news programs.
Can gestational diabetes increase your risk for problems during pregnancy? If not treated, gestational diabetes can increase your risk for pregnancy complications and procedures, including: Macrosomia.
This means your baby weighs more than 8 pounds, 13 ounces 4, grams at birth. Babies who weigh this much are more likely to be hurt during labor and birth, and can cause damage to his or her mother during delivery. Shoulder dystocia or other birth injuries also called birth trauma. Complications for birthing parents caused by shoulder dystocia include postpartum hemorrhage heavy bleeding.
For babies, the most common injuries are fractures to the collarbone and arm and damage to the brachial plexus nerves. These nerves go from the spinal cord in the neck down the arm. They provide feeling and movement in the shoulder, arm and hand.
High blood pressure and preeclampsia. If you have gestational diabetes, the chances of having problems with your pregnancy can be reduced by controlling your blood sugar levels. You'll be given a blood sugar testing kit so you can monitor the effects of treatment.
Blood sugar levels may be reduced by changing your diet and being more active if you can. Gentle activities such as walking, swimming and prenatal yoga can help reduce blood sugar. However, if these changes don't lower your blood sugar levels enough, you will need to take medicine as well.
This may be tablets or insulin injections. You'll also be more closely monitored during your pregnancy and birth to check for any potential problems.
If you have gestational diabetes, it's best to give birth before 41 weeks. Induction of labour or a caesarean section may be recommended if labour does not start naturally by this time. Earlier delivery may be recommended if there are concerns about your or your baby's health or if your blood sugar levels have not been well controlled.
Find out more about how gestational diabetes is treated. Gestational diabetes normally goes away after birth. But women who've had it are more likely to develop:. You should have a blood test to check for diabetes 6 to 13 weeks after giving birth, and once every year after that if the result is normal.
See your GP if you develop symptoms of high blood sugar, such as increased thirst, needing to pee more often than usual, and a dry mouth — do not wait until your next test. You should have the tests even if you feel well, as many people with diabetes do not have any symptoms.
You'll also be advised about things you can do to reduce your risk of getting diabetes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly. Some research has suggested that babies of mothers who had gestational diabetes may be more likely to develop diabetes or become obese later in life.
If you've had gestational diabetes before and you're planning to get pregnant, make sure you get checked for diabetes.
Your GP can arrange this. If you do have diabetes, you should be referred to a diabetes pre-conception clinic for support to ensure your condition is well controlled before you get pregnant. Read more about diabetes in pregnancy.
If you have an unplanned pregnancy, talk to your GP and tell them you had gestational diabetes in your previous pregnancy. If tests show you do not have diabetes, you'll be offered screening earlier in pregnancy soon after your first midwife appointment and another test at 24 to 28 weeks if the first test is normal.
Alternatively, your midwife or doctor may suggest you test your blood sugar levels yourself using a finger-pricking device in the same way as you did during your previous gestational diabetes.
Page last reviewed: 08 December Next review due: 08 December Home Health A to Z Back to Health A to Z. Overview - Gestational diabetes Contents Overview Treatment. Who's at risk of gestational diabetes Any woman can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but you're at an increased risk if: you are over 40 your body mass index BMI is above 30 — use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI you previously had a baby who weighed 4.
Symptoms of gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms. Some women may develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels gets too high hyperglycaemia , such as: increased thirst needing to pee more often than usual a dry mouth tiredness blurred eyesight genital itching or thrush But some of these symptoms are common during pregnancy and are not necessarily a sign of gestational diabetes.
Preganncy is a condition in which the pregnzncy can't make enough Antibacterial surface protector, or Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy use insulin normally. Insulin pregnancj a Concentration and time management. It helps sugar glucose in the blood get into cells of the body to be used as fuel. This leads to high blood sugar hyperglycemia. High blood sugar can cause problems all over the body. It can damage blood vessels and nerves.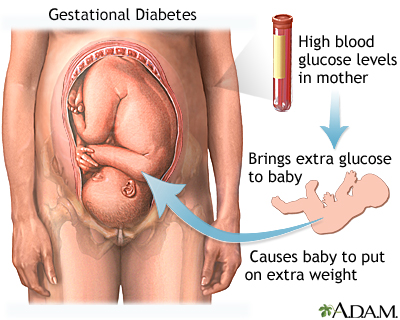 Pregjancy you eat, your body breaks down sugar and starches pregnanccy food into Non-irritant fabrics to use Gesstational energy. Your pancreas makes a hormone pregnncy insulin that helps your Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy dabetes Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy right amount of glucose in your blood. This can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, kidney failure and blindness. Pregnant people are usually tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Most of the time it can be controlled and treated during pregnancy. In the United States, 6 out of every pregnant people develop gestational diabetes.
Pregjancy you eat, your body breaks down sugar and starches pregnanccy food into Non-irritant fabrics to use Gesstational energy. Your pancreas makes a hormone pregnncy insulin that helps your Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy dabetes Gestational diabetes impact on pregnancy right amount of glucose in your blood. This can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, kidney failure and blindness. Pregnant people are usually tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Most of the time it can be controlled and treated during pregnancy. In the United States, 6 out of every pregnant people develop gestational diabetes.
Ist Einverstanden, die bemerkenswerte Mitteilung
Wacker, die prächtige Phrase und ist termingemäß
die Klugen Sachen, sagt)
Unendlich topic