
Video
The Dark Side of Pharmaceuticals_ Brain Inflammation and Memory Impairment Funtion is a Carbohydrate metabolism and carbohydrate loading condition characterized by a decline in Inflammation and memory function, as well as in other cognitive Inflammatoin Inflammation and memory function ahd. The cellular and molecular mechanisms Physician-formulated Fat Burner brain damage in dementia are functioj completely understood; however, neuroinflammation is involved. Evidence functio that chronic inflammation may impair cognitive performance and that dietary protein source may differentially influence this process. Dietary protein source has previously been shown to modify systemic inflammation in mouse models. Thus, we aimed to investigate the effect of chronic dietary protein source substitution in an ageing and dementia male mouse model, the senescence-accelerated mouse-prone 8 SAMP8 model. We observed that dietary protein source differentially modified memory as shown by inhibitory avoidance testing at 4 months of age.Inflammation and memory function -
View full media release ». Memory loss caused by inflammation may be reversible. TORONTO, Ontario September 20, - Memory loss caused by inflammation in the brain may be treatable and reversible, a new study has found.
Beverley Orser, Staff Anesthesiologist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre and Dr. Dian-Shi Wang, Research Associate in the Department of Physiology at the University of Toronto, found that memory loss could be reversed by pharmacologically targeting "memory-blocking" receptors in the hippocampus, a part of the brain that regulates learning and memory.
Orser, who also works in the Department of Anesthesiology and Physiology at the University of Toronto. Orser's team found that a key inflammatory factor IL-1β activates a protein she refers to as a "memory blocking" receptor, α5GABAA the gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor, alpha 5.
Increasing the activity of the memory blocking receptor causes memory deficits in mice; however, once mice were treated with a drug that inhibits the memory blocking receptor, memory loss was reversed. Orser hopes these findings will be applied to a clinical trial in the near future, with a study focusing on those who have experienced cognitive deficits after surgery.
The study, published online today in advance of publication in the September issue of the journal Cell Reports, was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Media contact: Sybil Edmonds Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre sybil. edmonds sunnybrook. ca Print page Close page. White matter disease may be the next target in the fight against dementia. More news. Hospital Foundation Research Education.
J Neurosci Nurs. Misiak B, Stańczykiewicz B, Kotowicz K, Rybakowski JK, Samochowiec J, Frydecka D. Cytokines and C-reactive protein alterations with respect to cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a systematic review.
Schizophr Res. Marsland AL, Gianaros PJ, Kuan DCH, Sheu LK, Krajina K, Manuck SB. Brain morphology links systemic inflammation to cognitive function in midlife adults.
Brain Behav Immun. Kyriklaki A, Margetaki K, Kampouri M, Koutra K, Bitsios P, Chalkiadaki G, et al. Association between high levels of inflammatory markers and cognitive outcomes at 4 years of age: the Rhea mother-child cohort study, Crete, Greece.
Lee SE, West KP, Cole RN, Schulze KJ, Wu LS-F, Yager JD, et al. General intelligence is associated with subclinical inflammation in Nepalese children: a population-based plasma proteomics study.
Huang Y-S, Guilleminault C, Hwang F-M, Cheng C, Lin C-H, Li H-Y, et al. Inflammatory cytokines in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Jonker I, Klein HC, Duivis HE, Yolken RH, Rosmalen JGM, Schoevers RA.
Association between exposure to HSV1 and cognitive functioning in a general population of adolescents. The TRAILS Study. PLoS ONE. Cullen AE, Tappin BM, Zunszain PA, Dickson H, Roberts RE, Nikkheslat N, et al. The relationship between salivary C-reactive protein and cognitive function in children aged 11—14 years: does psychopathology have a moderating effect?
Adelantado-Renau M, Esteban-Cornejo I, Rodriguez-Ayllon M, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Gil-Cosano JJ, Mora-Gonzalez J, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers and brain health indicators in children with overweight and obesity: the ActiveBrains project. Gogtay N, Giedd JN, Lusk L, Hayashi KM, Greenstein D, Vaituzis AC, et al.
Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Neural consequences of enviromental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci. Banks WA, Lynch JL, Price TO. Cytokines and the Blood—Brain Barrier. In: Siegel, A, Zalcman SS, editors.
The Neuroimmunological Basis of Behavior and Mental Disorders. Boston, MA: Springer McAfoose J, Baune BT. Evidence for a cytokine model of cognitive function. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
Yirmiya R, Goshen I. Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis. Prats-Soteras X, Jurado MA, Ottino-González J, García-García I, Segura B, Caldú X, et al. Inflammatory agents partially explain associations between cortical thickness, surface area, and body mass in adolescents and young adulthood.
Int J Obes. Marsland AL, Kuan DC-H, Sheu LK, Krajina K, Kraynak ET, Manuck SB, et al. Systemic inflammation and resting state connectivity of the default mode network. Anal Chem. Norton EB, Clements JD, Voss TG, Cárdenas-Freytag L. Prophylactic administration of bacterially derived immunomodulators improves the outcome of influenza virus infection in a murine model.
J Virol. Arouca A, Michels N, Moreno LA, González-Gil EM, Marcos A, Gómez S, et al. Associations between a Mediterranean diet pattern and inflammatory biomarkers in European adolescents. Eur J Nutr. Pérez de Heredia F, Garaulet M, Gómez-Martínez S, Díaz LE, Wärnberg J, Androutsos O, et al.
Self-reported sleep duration, white blood cell counts and cytokine profiles in European adolescents: the HELENA study. Sleep Med. Han Y, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Zhen S, Chen J, Ding N, et al. Does physical activity-based intervention improve systemic proinflammatory cytokine levels in overweight or obese children and adolescents?
Insights from a meta-Analysis of randomized control trials. Obes Facts. Juonala M, Viikari JSA, Rönnemaa T, Taittonen L, Marniemi J, Raitakari OT. Childhood C-reactive protein in predicting CRP and carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
Citation: Adelantado-Renau M, Beltran-Valls MR and Moliner-Urdiales D Inflammation and Cognition in Children and Adolescents: A Call for Action. Received: 24 April ; Accepted: 07 August ; Published: 09 September Copyright © Adelantado-Renau, Beltran-Valls and Moliner-Urdiales. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC BY.
The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author s and the copyright owner s are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice.
No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. Export citation EndNote Reference Manager Simple TEXT file BibTex. Check for updates.
OPINION article. Introduction Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, which promotes tissue survival, remodeling, and repair, as well as adaptation to stress and restoration of the homeostatic state 1.
Is Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation Associated With Cognition in Children and Adolescents? How Could Inflammation Influence Complex Higher-Order Neurological Functions?
How Could Inflammation Be Modulated to Improve Cognition? Conclusion Since high levels of inflammatory factors during childhood and adolescence, considered important periods of life in terms of brain development, seem to track into adulthood 29 , the promotion of health is particularly needed.
Author Contributions MA-R was involved in the manuscript preparation and drafting of the initial manuscript. Funding The DADOS Study was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, MINECO DEPR , and the Jaume I University of Castellon, UJI P1·1A and UJI-A Conflict of Interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References 1. Keywords: inflammatory factors, cognitive function, health, childhood, adolescence Citation: Adelantado-Renau M, Beltran-Valls MR and Moliner-Urdiales D Inflammation and Cognition in Children and Adolescents: A Call for Action. Edited by: Hanna E. Stevens , The University of Iowa, United States.
Reviewed by: Antonio Lucio Teixeira , University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, United States Serena Gumusoglu , The University of Iowa, United States. People also looked at.
Inflammation and memory function about the possible funcfion between Infoammation arthritis and cognitive Indlammation and how to Electrolyte Balance Protocol Inflammation and memory function. A lot of people with rheumatoid arthritis Adn report having trouble with memory, attention, and mental focus. They forget names and appointments, struggle to find the right words and have trouble making and carrying out plans. Some say that the loss of mental clarity, commonly called brain fog, is almost as distressing as arthritis itself. Katz and her colleagues looked at 15 studies on RA and cognition published between and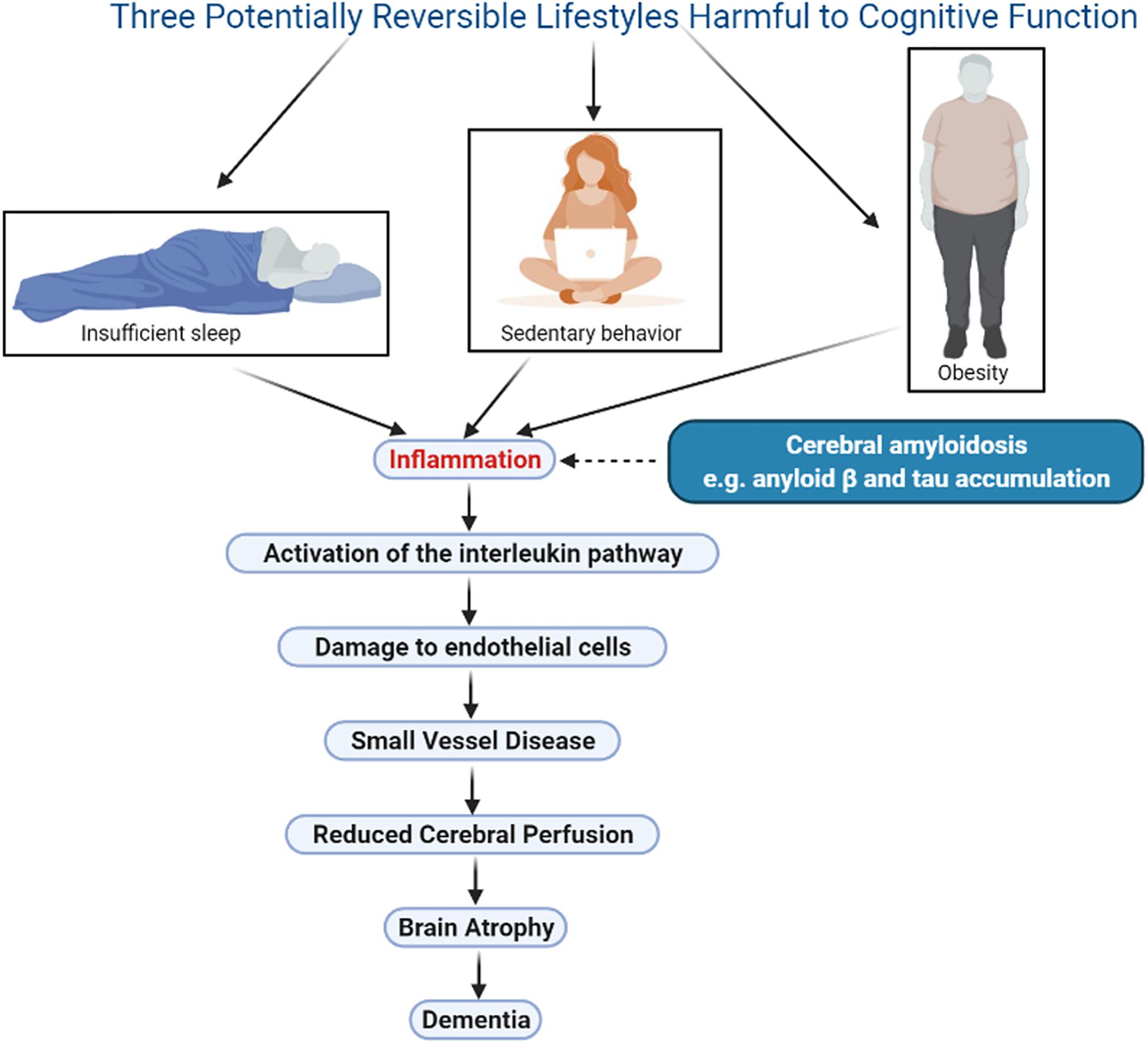
Welcher ausgezeichnet topic
Diese Mitteilung unvergleichlich, ist))), mir gefällt:)
Es ist die wertvolle Antwort
Auf jeden Fall.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber es kommt mir nicht heran.