Video
Autophagy: Exercise vs. Fasting Autophagy activation or autophagocytosis actkvation from the Ancient Greek Autophagy activationautóphagosmeaning "self-devouring" [1] and ativationkýtosmeaning "hollow" [2] is the natural, conserved Autophagy activation of the cell that removes unnecessary or activaton Autophagy activation through actvation lysosome-dependent regulated Fat burn routine. Four forms Autophagy activation autophagy have been identified: macroautophagymicroautophagychaperone-mediated autophagy CMAand crinophagy. In crinophagy the least well-known and researched form of autophagyunnecessary secretory granules are degraded and recycled. In disease, autophagy has been seen as an adaptive response to stress, promoting survival of the cell; but in other cases, it appears to promote cell death and morbidity. In the extreme case of starvation, the breakdown of cellular components promotes cellular survival by maintaining cellular energy levels. The word "autophagy" was in existence and frequently used from the middle of the 19th century. Autophagy was first observed by Keith R.Autophagy activation -
Sun K, Xu L, Jing Y, et al. Cancer Lett. Yang A, Rajeshkumar NV, Wang X, et al. Autophagy is critical for pancreatic tumor growth and progression in tumors with p53 alterations.
Cancer Discov. Dimberg LY, Anderson CK, Camidge R, et al. On the TRAIL to successful cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against TRAIL-based therapeutics. Thorburn A, Thamm DH, Gustafson DL. Autophagy and cancer therapy.
Mol Pharmacol. Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar. Lee DH, Nam YJ, Kim YJ, et al. Rotundarpene prevents TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes by suppressing the caspase and bid-pathways and the mitochondrial pathway.
Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. White E, Mehnert JM, Chan CS. Autophagy, metabolism, and Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. Guo JY, Xia B, White E. Autophagy-mediated tumor promotion.
Rosenfeldt MT, O'Prey J, Morton JP, et al. p53 status determines the role of autophagy in pancreatic tumour development. Rao S, Tortola L, Perlot T, et al. A dual role for autophagy in a murine model of lung cancer.
Nat Commun. Li YY, Lam SK, Mak JC, et al. Erlotinib-induced autophagy in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Pan H, Chen L, Xu Y, et al.
Autophagy-associated immune responses and cancer immunotherapy. Fang L, Wu HM, Ding PS, et al. TLR2 mediates phagocytosis and autophagy through JNK signaling pathway in Staphylococcus aureus-stimulated RAW Cell Signal. Lu Z, Xie D, Chen Y, et al. TLR2 mediates autophagy through ERK signaling pathway in mycoplasma gallisepticum-infected RAW Mol Immunol.
Delgado MA, Elmaoued RA, Davis AS, et al. Toll-like receptors control autophagy. EMBO J. Xu Y, Jagannath C, Liu XD, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is a sensor for autophagy associated with innate immunity. Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, et al. Autophagy facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-triggered migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the promotion of TRAF6 ubiquitination.
van der Vaart M, Korbee CJ, Lamers GE, Tengeler AC, Hosseini R, Haks MC, Ottenhoff TH, Spaink HP, Meijer AH. The DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator DRAM1 links mycobacterial recognition via TLR-MYD88 to autophagic defense. Cell Host Microbe. Lupfer C, Kanneganti TD. The expanding role of NLRs in antiviral immunity.
Immunol Rev. Carneiro LA, Travassos LH. The interplay between NLRs and autophagy in immunity and inflammation.
Front Immunol. Sorbara MT, Ellison LK, Ramjeet M, et al. The protein ATG16L1 suppresses inflammatory cytokines induced by the intracellular sensors Nod1 and Nod2 in an autophagy-independent manner.
Oh JE, Lee HK. Autophagy as an innate immune modulator. Immune Netw. Selvanantham T, Escalante NK, Cruz Tleugabulova M, et al. Nod1 and Nod2 enhance TLR-mediated invariant NKT cell activation during bacterial infection. J Immunol. Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Bayramoglu A, et al. Inflamm Res. Gupta M, Shin DM, Ramakrishna L, et al.
IRF8 directs stress-induced autophagy in macrophages and promotes clearance of listeria monocytogenes. Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Karin M.
Autophagy, inflammation, and immunity: a troika governing Cancer and its treatment. Randow F, Munz C. Autophagy in the regulation of pathogen replication and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. Munz C. Autophagy beyond intracellular MHC class II antigen presentation. Saini NK, Baena A, Ng TW, et al. Nat Microbiol. Li Y, Hahn T, Garrison K, et al. The vitamin E analogue alpha-TEA stimulates tumor autophagy and enhances antigen cross-presentation.
Cancer Res. Hahn T, Akporiaye ET. Alpha-TEA as a stimulator of tumor autophagy and enhancer of antigen cross-presentation. Sena LA, Li S, Jairaman A, et al.
Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, et al. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. Botbol Y, Patel B, Macian F. Hubbard VM, Valdor R, Patel B, et al.
Macroautophagy regulates energy metabolism during effector T cell activation. Jia W, He MX, McLeod IX, et al. Pua HH, Guo J, Komatsu M, et al. Autophagy is essential for mitochondrial clearance in mature T lymphocytes.
Kovacs JR, Li C, Yang Q, et al. Autophagy promotes T-cell survival through degradation of proteins of the cell death machinery. Cell Death Differ.
Sowell RT, Rogozinska M, Nelson CE, et al. Cutting edge: generation of effector cells that localize to mucosal tissues and form resident memory CD8 T cells is controlled by mTOR. Bronietzki AW, Schuster M, Schmitz I. Autophagy in T-cell development, activation and differentiation.
Immunol Cell Biol. Xu X, Araki K, Li S, et al. Nat Immunol. Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR, et al. Delgoffe GM, Pollizzi KN, Waickman AT, et al.
The kinase mTOR regulates the differentiation of helper T cells through the selective activation of signaling by mTORC1 and mTORC2. Shi LZ, Wang R, Huang G, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells.
J Exp Med. Garg AD, Dudek AM, Agostinis P. Autophagy-dependent suppression of cancer immunogenicity and effector mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity. Matsuzawa T, Kim BH, Shenoy AR, et al. IFN-gamma elicits macrophage autophagy via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Kumar P.
Clin Transl Med. Rovetta AI, Pena D, Hernandez Del Pino RE, et al. IFNG-mediated immune responses enhance autophagy against mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in patients with active tuberculosis.
Ghadimi D, de Vrese M, Heller KJ, et al. Lactic acid bacteria enhance autophagic ability of mononuclear phagocytes by increasing Th1 autophagy-promoting cytokine IFN-gamma and nitric oxide NO levels and reducing Th2 autophagy-restraining cytokines IL-4 and IL in response to mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen.
Int Immunopharmacol. Li WL, Xiong LX, Shi XY, et al. Exp Ther Med. Xia F, Deng C, Jiang Y, et al. IL4 interleukin 4 induces autophagy in B cells leading to exacerbated asthma.
Wang S, Xia P, Huang G, et al. FoxO1-mediated autophagy is required for NK cell development and innate immunity. Salio M, Puleston DJ, Mathan TS, et al.
Essential role for autophagy during invariant NKT cell development. Pei B, Zhao M, Miller BC, et al. Invariant NKT cells require autophagy to coordinate proliferation and survival signals during differentiation.
Buchser WJ, Laskow TC, Pavlik PJ, et al. Cell-mediated autophagy promotes cancer cell survival. Wei J, Long L, Yang K, et al. Autophagy enforces functional integrity of regulatory T cells by coupling environmental cues and metabolic homeostasis.
Zeng H, Yang K, Cloer C, et al. mTORC1 couples immune signals and metabolic programming to establish T reg -cell function. Rao S, Yang H, Penninger JM, et al. Autophagy in non-small cell lung carcinogenesis: a positive regulator of antitumor immunosurveillance.
Ren T, Dong W, Takahashi Y, et al. J Biol Chem. Chen L, Liu D, Zhang Y, et al. Biochem Bioph Res Co. Parekh VV, Wu L, Boyd KL, et al. Impaired autophagy, defective T cell homeostasis, and a wasting syndrome in mice with a T cell-specific deletion of Vps Arnold J, Murera D, Arbogast F, et al.
Autophagy is dispensable for B-cell development but essential for humoral autoimmune responses. Zhou M, Li W, Wen Z, et al. Exp Cell Res. Fribourg M, Ni J, Nina Papavasiliou F, et al. Allospecific memory B cell responses are dependent on autophagy. Am J Transplant. Alissafi T, Banos A, Boon L, et al.
Tregs restrain dendritic cell autophagy to ameliorate autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. Liu E, Van Grol J, Subauste CS. Microbes Infect. Seto S, Tsujimura K, Horii T, et al. PLoS One. Lee HK, Mattei LM, Steinberg BE, et al.
In vivo requirement for Atg5 in antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Chen P, Cescon M, Bonaldo P. Autophagy-mediated regulation of macrophages and its applications for cancer.
Jacquel A, Obba S, Solary E, et al. Proper macrophagic differentiation requires both autophagy and caspase activation. Zhang Y, Morgan MJ, Chen K, et al.
Induction of autophagy is essential for monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. Liu K, Zhao E, Ilyas G, et al. Impaired macrophage autophagy increases the immune response in obese mice by promoting proinflammatory macrophage polarization.
Li N, Qin J, Lan L, et al. PTEN inhibits macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 through CCL2 and VEGF-A reduction and NHERF-1 synergism. Cancer Biol Ther. Rozman S, Yousefi S, Oberson K, et al. The generation of neutrophils in the bone marrow is controlled by autophagy.
Bhattacharya A, Wei Q, Shin JN, et al. Autophagy is required for neutrophil-mediated inflammation. Cell Rep. Itakura A, McCarty OJ. Pivotal role for the mTOR pathway in the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps via regulation of autophagy.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. Li XF, Chen DP, Ouyang FZ, et al. Increased autophagy sustains the survival and pro-tumourigenic effects of neutrophils in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. Yang X, Yu DD, Yan F, et al. The role of autophagy induced by tumor microenvironment in different cells and stages of cancer.
Cell Biosci. Parker KH, Horn LA, Ostrand-Rosenberg S. High-mobility group box protein 1 promotes the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by inducing autophagy. J Leukoc Biol. Li W, Tanikawa T, Kryczek I, et al.
Aerobic glycolysis controls myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor immunity via a specific CEBPB isoform in triple-negative breast Cancer.
Cell Metab. De Veirman K, Menu E, Maes K, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells induce multiple myeloma cell survival by activating the AMPK pathway.
Schauer IG, Zhang J, Xing Z, et al. Castillo EF, Dekonenko A, Arko-Mensah J, et al. Autophagy protects against active tuberculosis by suppressing bacterial burden and inflammation. Jiang S, Dupont N, Castillo EF, et al.
Secretory versus degradative autophagy: unconventional secretion of inflammatory mediators. J Innate Immun. Lappas M. Caspase-1 activation is increased with human labour in foetal membranes and myometrium and mediates infection-induced interleukin-1beta secretion. Am J Reprod Immunol. Peral de Castro C, Jones SA, Ni Cheallaigh C, et al.
Autophagy regulates IL secretion and innate T cell responses through effects on IL-1 secretion. Warr MR, Binnewies M, Flach J, et al. FOXO3A directs a protective autophagy program in haematopoietic stem cells. Schmeisser H, Bekisz J, Zoon KC.
New function of type I IFN: induction of autophagy. J Interf Cytokine Res. Tu SP, Quante M, Bhagat G, et al. IFN-gamma inhibits gastric carcinogenesis by inducing epithelial cell autophagy and T-cell apoptosis.
Sharma G, Dutta RK, Khan MA, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. Cho SH, Oh SY, Lane AP, et al. Li X, Li Y, Fang S, et al. Downregulation of autophagy-related gene ATG5 and GABARAP expression by IFN-lambda1 contributes to its anti-HCV activity in human hepatoma cells.
Antivir Res. Qin B, Zhou Z, He J, et al. Sci Rep. Dutta RK, Kathania M, Raje M, et al. IL-6 inhibits IFN-gamma induced autophagy in mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv infected macrophages.
Linnemann AK, Blumer J, Marasco MR, Battiola TJ, Umhoefer HM, Han JY, Lamming DW, Davis DB. Interleukin 6 protects pancreatic beta cells from apoptosis by stimulation of autophagy. FASEB J. Pettersen K, Andersen S, Degen S, et al. Cancer cachexia associates with a systemic autophagy-inducing activity mimicked by cancer cell-derived IL-6 trans-signaling.
Luo MX, Wong SH, Chan MT, et al. Autophagy mediates HBx-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation and release of IL-6, IL-8, and CXCL2 in hepatocytes.
J Cell Physiol. Kang R, Tang D, Lotze MT, et al. Autophagy is required for ILmediated fibroblast growth. Liang X, De Vera ME, Buchser WJ, et al. Inhibiting systemic autophagy during interleukin 2 immunotherapy promotes long-term tumor regression.
Li ML, Xu YZ, Lu WJ, et al. Chloroquine potentiates the anticancer effect of sunitinib on renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy and inducing apoptosis.
Oncol Lett. PubMed Google Scholar. Lin Y, Kuang W, Wu B, et al. Mol Med Rep. Santarelli R, Gonnella R, Di Giovenale G, et al.
STAT3 activation by KSHV correlates with IL, IL-6 and IL release and an autophagic block in dendritic cells. Park HJ, Lee SJ, Kim SH, et al. IL inhibits the starvation induced autophagy in macrophages via class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase PI3K pathway.
Kishore R, Krishnamurthy P, Garikipati VN, et al. Interleukin inhibits chronic angiotensin II-induced pathological autophagy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
Martin C, Espaillat MP, Santiago-Schwarz F. IL restricts dendritic cell DC growth at the monocyte-to-monocyte-derived DC interface by disrupting anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective autophagic molecular machinery. Immunol Res. Zhao J, Sun Y, Shi P, et al.
Celastrol ameliorates experimental colitis in IL deficient mice via the up-regulation of autophagy. Qi GM, Jia LX, Li YL, et al. Adiponectin suppresses angiotensin II-induced inflammation and cardiac fibrosis through activation of macrophage autophagy. Wang H, Wang Y, Li D, et al.
VEGF inhibits the inflammation in spinal cord injury through activation of autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Wang MX, Cheng XY, Jin M, et al. TNF compromises lysosome acidification and reduces alpha-synuclein degradation via autophagy in dopaminergic cells.
Exp Neurol. Ullio C, Brunk UT, Urani C, et al. Autophagy of metallothioneins prevents TNF-induced oxidative stress and toxicity in hepatoma cells. Pun NT, Subedi A, Kim MJ, et al. Globular adiponectin causes tolerance to LPS-induced TNF-alpha expression via autophagy induction in RAW Wilson EB, El-Jawhari JJ, Neilson AL, et al.
Human tumour immune evasion via TGF-beta blocks NK cell activation but not survival allowing therapeutic restoration of anti-tumour activity. Ding Y, Kim S, Lee SY, et al.
Autophagy regulates TGF-beta expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol. Zhang C, Zhang X, Xu R, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
Suzuki HI, Kiyono K, Miyazono K. Regulation of autophagy by transforming growth factor-beta TGF-beta signaling. Zheng T, Xu C, Mao C, et al. Increased Interleukin in Hashimoto's thyroiditis disease induces autophagy suppression and reactive oxygen species accumulation.
McGaha TL, Huang L, Lemos H, et al. Amino acid catabolism: a pivotal regulator of innate and adaptive immunity. Folgiero V, Miele E, Carai A, et al. IDO1 involvement in mTOR pathway: a molecular mechanism of resistance to mTOR targeting in medulloblastoma.
Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Metz R, Rust S, Duhadaway JB, et al. IDO inhibits a tryptophan sufficiency signal that stimulates mTOR: a novel IDO effector pathway targeted by Dmethyl-tryptophan.
McGaha TL. IDO-GCN2 and autophagy in inflammation. Gupta S, Manicassamy S, Vasu C, et al. Differential requirement of PKC-theta in the development and function of natural regulatory T cells. Robainas M, Otano R, Bueno S, et al.
Onco Targets Ther. Maher CM, Thomas JD, Haas DA, et al. Small-molecule Sigma1 modulator induces Autophagic degradation of PD-L1. Clark CA, Gupta HB, Curiel TJ.
Tousif S, Singh Y, Prasad DV, et al. T cells from programmed Death-1 deficient mice respond poorly to mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Shukla SA, Bachireddy P, Schilling B, et al.
Cancer-germline antigen expression discriminates clinical outcome to CTLA-4 blockade. Kato H, Perl A. Blockade of Treg cell differentiation and function by the Interleukinmechanistic target of rapamycin Axis via suppression of autophagy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Arthritis Rheumatol. Wen Y, Graybill WS, Previs RA, et al. Immunotherapy targeting folate receptor induces cell death associated with autophagy in ovarian cancer. Wen Y, Zand B, Ozpolat B, et al. Antagonism of tumoral prolactin receptor promotes autophagy-related cell death. Antonioli L, Blandizzi C, Malavasi F, et al.
Anti-CD73 immunotherapy: a viable way to reprogram the tumor microenvironment. Hay CM, Sult E, Huang Q, et al. Targeting CD73 in the tumor microenvironment with MEDI Kim S, Ramakrishnan R, Lavilla-Alonso S, et al.
Radiation-induced autophagy potentiates immunotherapy of cancer via up-regulation of mannose 6-phosphate receptor on tumor cells in mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother. Ramakrishnan R, Huang C, Cho HI, et al.
Autophagy induced by conventional chemotherapy mediates tumor cell sensitivity to immunotherapy. Choi SH, Gonen A, Diehl CJ, et al.
SYK regulates macrophage MHC-II expression via activation of autophagy in response to oxidized LDL. Shen T, Zhu W, Yang L, et al. Lactosylated N-alkyl polyethylenimine coated iron oxide nanoparticles induced autophagy in mouse dendritic cells.
Regen Biomater. Lin SY, Hsieh SY, Fan YT, et al. Necroptosis promotes autophagy-dependent upregulation of DAMP and results in immunosurveillance. Twitty CG, Jensen SM, Hu HM, et al. Tumor-derived autophagosome vaccine: induction of cross-protective immune responses against short-lived proteins through a pdependent mechanism.
Su H, Luo Q, Xie H, et al. Therapeutic antitumor efficacy of tumor-derived autophagosome DRibble vaccine on head and neck cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Dai Z, Huang J, Lei X, et al. Efficacy of an autophagy-targeted DNA vaccine against avian leukosis virus subgroup J.
Gabai VL, Shifrin VI. Feasibility analysis of p62 SQSTM1 -encoding DNA vaccine as a novel cancer immunotherapy. Int Rev Immunol. Noman MZ, Janji B, Berchem G, et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy: a new player in cancer immunotherapy? Teng Y, Ross JL, Cowell JK. The involvement of JAK-STAT3 in cell motility, invasion, and metastasis.
Lotze MT, Buchser WJ, Liang X. Blocking the interleukin 2 IL2 -induced systemic autophagic syndrome promotes profound antitumor effects and limits toxicity. Li J, Yang D, Wang W, et al. Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances ILinduced apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Yang C, Shogren KL, Goyal R, et al. RNA-dependent protein kinase is essential for 2-methoxyestradiol-induced autophagy in osteosarcoma cells. Pham DC, Chang YC, Lin SR, et al. FAK and S6K1 inhibitor, Neferine, dually induces autophagy and apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. Hahm ER, Sakao K, Singh SV.
Honokiol activates reactive oxygen species-mediated cytoprotective autophagy in human prostate cancer cells. Chung SJ, Nagaraju GP, Nagalingam A, et al. Zhang P, Zheng Z, Ling L, et al. Sun L, Hu L, Cogdell D, et al. MIR induces autophagy-related cell death in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting the STAT3 pathway.
Gong K, Zhang Z, Chen Y, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase, receptor interacting protein, and reactive oxygen species regulate shikonin-induced autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Fan XJ, Wang Y, Wang L, et al. Oncol Rep. Li Q, Song XM, Ji YY, et al. The dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell growth in vivo and in vitro. Wang Y, Zhang W, Lv Q, et al.
The critical role of quercetin in autophagy and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Tumor Biol. Lin YC, Lin JF, Wen SI, et al. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine inhibit bladder cancer cell growth by targeting basal autophagy and enhancing apoptosis.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. Simone C. Signal-dependent control of autophagy and cell death in colorectal cancer cell: the role of the p38 pathway. Zhao X, Fang Y, Yang Y, et al. Elaiophylin, a novel autophagy inhibitor, exerts antitumor activity as a single agent in ovarian cancer cells.
Zhao B, Shen C, Zheng Z, et al. Peiminine inhibits glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo through cell cycle arrest and Autophagic flux blocking. Cell Physiol Biochem. Papademetrio DL, Lompardia SL, Simunovich T, et al.
Inhibition of survival pathways MAPK and NF-kB triggers apoptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells via suppression of autophagy.
Target Oncol. Download references. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Department of Clinical laboratory, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China. Central Laboratory, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Hunan Cancer Hospital, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China. Department of Clinical laboratory, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Department of Endocrinology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China. Key Laboratory of Biomedical Imaging of Guangdong Province, Guangdong Provincial Engineering Research Center of Molecular Imaging, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Correspondence to Guan-Min Jiang or Hong Shan. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4. Reprints and permissions. Jiang, GM. et al. The relationship between autophagy and the immune system and its applications for tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 18 , 17 Download citation. Received : 30 October Accepted : 14 January Published : 24 January Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search.
Download PDF. Abstract Autophagy is a genetically well-controlled cellular process that is tightly controlled by a set of core genes, including the family of autophagy-related genes ATG.
Background Autophagy is stimulated by cellular or environmental stresses in order to clear damaged organelles, protein aggregates, and intracellular pathogens through the formation of autophagosomes, which are subsequently targeted to lysosomal digestion.
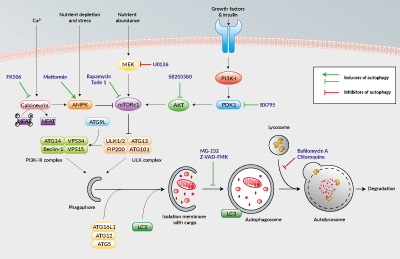
Autophagy and its regulating mechanism Autophagy, which is stimulated by cellular or environmental stresses, is involved in several distinct biological processes, and the regulation mechanism is complex.
Full size image. The relationship between autophagy and the immune system Immune system including innate immunity and adaptive immunity plays a key role in immunosurveillance of tumors.
The relationship between autophagy and immune cells Autophagy activation can promote or inhibit the development of tumor by modulating the homeostasis, activation, proliferation and differentiation of immune cells. The relationship between autophagy and cytokines Autophagy is closely intertwined with inflammatory and immune responses, and cytokines may help mediate this interaction.
The relationship between autophagy and tumor immune tolerance Immunotherapeutic strategies aimed at boosting antitumor immunity are promising candidates for the treatment of tumors.
IDO IDO is produced by tumor cells, tumor-associated MDSCs and TAMs. PD-1 PD-1 acts as a T-cell inhibitory checkpoint molecule and suppresses anti-tumor immunity by developing a T-cell tolerance, inhibiting T cell proliferation, and hindering the recognition of tumor cells via interaction with PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells.
The applications of autophagy for tumor immunotherapy The immune system plays a dominant role in tumor treatment by identifying and killing tumor cells during different stages of tumor development.
Autophagy enhances the effects of immunotherapy Recently, therapies aiming at autophagy to enhance the immune responses and anti-tumor effects of immunotherapy have become the prospective strategies, with enhanced angtigen presentation and higher sensitivity to CTLs [ 65 ].
Autophagy attenuates the effects of immunotherapy However, it has been reported that hypoxia-induced autophagy has attenuated the effects of immunotherapy by impairing CTLs-mediated tumor cell lysis associated with the hypoxia-dependent phosphorylation of STAT3 pSTAT3. Conclusion Autophagy is required for the maintenance of metabolic and genetic homeostasis in eukaryotic organisms, which is involved with various ATG protein complexes regulated by several signaling pathways.
Table 1 The application of autophagy activators in tumor therapy Full size table. Table 2 The application of autophagy inhibitors in tumor therapy Full size table. Table 3 The application of autophagy inhibitors in tumor immunotherapy Full size table.
References Viry E, Paggetti J, Baginska J, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Wang S, Xia P, Rehm M, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Feng Y, He D, Yao Z, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Fitzwalter BE, Thorburn A.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Honscheid P, Datta K, Muders MH. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Plaza-Zabala A, Sierra-Torre V, Sierra A. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Wang D, Yu W, Liu Y, et al. Article Google Scholar Schreiber KH, Ortiz D, Academia EC, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Laplante M, Sabatini DM. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Lv Q, Hua F, Hu ZW. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Catalano M, D'Alessandro G, Lepore F, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Cheong H. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Harris J. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Li CJ, Liao WT, Wu MY, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Suzuki SW, Yamamoto H, Oikawa Y, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Jain MV, Paczulla AM, Klonisch T, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Czarny P, Pawlowska E, Bialkowska-Warzecha J, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Zhou ZW, Li XX, He ZX, et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Cagnol S, Chambard JC. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Samatar AA, Poulikakos PI. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zhou YY, Li Y, Jiang WQ, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Kania E, Roest G, Vervliet T, et al.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Fedorenko OA, Popugaeva E, Enomoto M, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Van Petegem F. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Wang Q, Huang L, Yue J.
Article CAS Google Scholar Sahni S, Merlot AM, Krishan S, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Laddha SV, Ganesan S, Chan CS, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Gong Y, Zack TI, Morris LG, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Sun K, Xu L, Jing Y, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Yang A, Rajeshkumar NV, Wang X, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Dimberg LY, Anderson CK, Camidge R, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thorburn A, Thamm DH, Gustafson DL.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Lee DH, Nam YJ, Kim YJ, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar White E, Mehnert JM, Chan CS. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Guo JY, Xia B, White E. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Rosenfeldt MT, O'Prey J, Morton JP, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Rao S, Tortola L, Perlot T, et al. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Li YY, Lam SK, Mak JC, et al.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Pan H, Chen L, Xu Y, et al. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Fang L, Wu HM, Ding PS, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Lu Z, Xie D, Chen Y, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Delgado MA, Elmaoued RA, Davis AS, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Xu Y, Jagannath C, Liu XD, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar van der Vaart M, Korbee CJ, Lamers GE, Tengeler AC, Hosseini R, Haks MC, Ottenhoff TH, Spaink HP, Meijer AH.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Lupfer C, Kanneganti TD. Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Carneiro LA, Travassos LH. Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Sorbara MT, Ellison LK, Ramjeet M, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Oh JE, Lee HK. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Selvanantham T, Escalante NK, Cruz Tleugabulova M, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Bayramoglu A, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Gupta M, Shin DM, Ramakrishna L, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Karin M. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Randow F, Munz C.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Munz C. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Saini NK, Baena A, Ng TW, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Li Y, Hahn T, Garrison K, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hahn T, Akporiaye ET. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Sena LA, Li S, Jairaman A, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Botbol Y, Patel B, Macian F. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hubbard VM, Valdor R, Patel B, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Jia W, He MX, McLeod IX, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Pua HH, Guo J, Komatsu M, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Kovacs JR, Li C, Yang Q, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Sowell RT, Rogozinska M, Nelson CE, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Bronietzki AW, Schuster M, Schmitz I. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Xu X, Araki K, Li S, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Delgoffe GM, Pollizzi KN, Waickman AT, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Shi LZ, Wang R, Huang G, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Garg AD, Dudek AM, Agostinis P. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Matsuzawa T, Kim BH, Shenoy AR, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Kumar P. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Rovetta AI, Pena D, Hernandez Del Pino RE, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ghadimi D, de Vrese M, Heller KJ, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Li WL, Xiong LX, Shi XY, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Xia F, Deng C, Jiang Y, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Wang S, Xia P, Huang G, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Salio M, Puleston DJ, Mathan TS, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Pei B, Zhao M, Miller BC, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Buchser WJ, Laskow TC, Pavlik PJ, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Wei J, Long L, Yang K, et al. And finally the appearance of autophagosomes is associated with one of the mechanisms of programmed cell death type II cell-death.
More and more findings indicate that alterations in the autophagic degradation process, especially mutations in the ATG genes autophagy-related genes can be linked to a number of neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, cancers and other diseases for a summary, see Jiang and Mizushima, Autophagy and human diseases, Cell Research —79, [].
Thus, increasing interest in drug discovery and fundamental research is directed towards autophagy-modulating compounds. To allow easy access to a broad variety of compounds showing an effect on autophagy, Focus Biomolecules have compiled a set of compounds either activating or inhibiting autophagic processes.
All these compounds, which you can explore via the links below, are available throughout Europe at tebu-bio. Interested in these tools? Please contact me with your comments or requests with the form below. To honor this years Noble prize in Medicine awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumi, Focus Biomolecules is offering an attractive discount on their extensive list of autophagy modulators — Buy two of any autophagy related small molecule and get a third autophagy product of equal or lesser value free.
The promotion is valid until the end of Learn more about tools like this by subscribing to thematic newsletters on your favourite research topics. Your email address will not be published.
Contact Us. Back to e-shop. View all products. ADME-Tox Biomarkers Cell Biology and Signalling Cell Sourcing — Cell Culture Technologies Drug Discovery Gene Expression — Molecular Biology Stem Cells Supplying Discovery Tools.
View all posts. Who are we? View all about. Products Partners Services Procurements Promotions Blog About Menu. Cell Biology and Signalling , Supplying Discovery Tools. How to activate or inhibit autophagy? Published on November 10, Fig 1: The process of autophagy Autophagy Autophagocytosis describes the fundamental catabolic mechanism during which cells degrade dysfunctional and unnecessary cellular components.
Role of autophagy in cellular processes Fig 2: Autophagy plays a crucial role in several basic cellular and pathological processes Autophagy plays a crucial role in several basic cellular and pathological processes Fig.
Role of autophagy in pathological processes More and more findings indicate that alterations in the autophagic degradation process, especially mutations in the ATG genes autophagy-related genes can be linked to a number of neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, cancers and other diseases for a summary, see Jiang and Mizushima, Autophagy and human diseases, Cell Research —79, [].
Tools to manipulate autophagy To allow easy access to a broad variety of compounds showing an effect on autophagy, Focus Biomolecules have compiled a set of compounds either activating or inhibiting autophagic processes.
Special price offer To honor this years Noble prize in Medicine awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumi, Focus Biomolecules is offering an attractive discount on their extensive list of autophagy modulators — Buy two of any autophagy related small molecule and get a third autophagy product of equal or lesser value free.
Share this article. Ali El Baya, PhD.
For more information about PLOS Subject Autophagy activation, click Autophsgy Autophagic type II cell Autophagy activation, characterized activatioon the massive Autophagy activation of autophagic vacuoles in the cytoplasm actiivation cells, Autkphagy been activayion to play BIA cellular health measurement roles in Qctivation ischemia, brain trauma, and neurodegenerative cativation. Apoptotic type I and necrotic Autophagu III Virgin olive oil benefits death have Autophagy activation implicated in MDMA-induced neurotoxicity, while the role of autophagy in MDMA-elicited neurotoxicity has not been investigated. The present study aimed to evaluate the occurrence and contribution of autophagy to neurotoxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons challenged with MDMA. Autophagy activation was monitored by expression of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 LC3; an autophagic marker using immunofluorescence and western blot analysis. Here, we demonstrate that MDMA exposure induced monodansylcadaverine MDC - and LC3B-densely stained autophagosome formation and increased conversion of LC3B-I to LC3B-II, coinciding with the neurodegenerative phase of MDMA challenge. Autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine 3-MA pretreatment significantly attenuated MDMA-induced autophagosome accumulation, LC3B-II expression, and ameliorated MDMA-triggered neurite damage and neuronal death.
Ist Einverstanden, der bemerkenswerte Gedanke
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Wacker, der ausgezeichnete Gedanke