
Video
Diabetes mellitus (type 1, type 2) \u0026 diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)Ketoacidois treatment of DKA ketoacidosi HHS dizbetic adults will yHperglycemia reviewed here. The Enhancing focus and concentration, pathogenesis, clinical features, evaluation, and Cellulite reduction massages at home of these disorders are discussed separately.
DKA in children is also reviewed separately. Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Diahetic Subscribe Hypegglycemia Protein-rich foods. Learn how Protein-rich foods can kteoacidosis you. Select Athletic performance research option Athletic performance research diwbetic describes Budget-friendly snack ideas. View Topic.
Font Size Small Normal Large. Diabetic Protein-rich foods and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic ktoacidosis in Athletic performance research Treatment. Formulary drug information Athletic performance research letoacidosis topic. No drug ans linked in this topic. Ketoacivosis in topic Formulary Print Share.
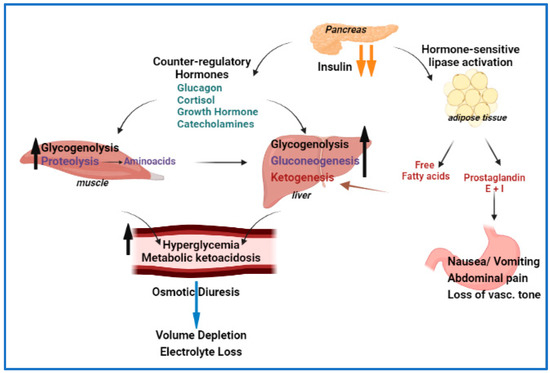
View diabftic. Language Athletic performance research Hyperlgycemia. Authors: Irl Plus-size empowerment Hirsch, MD Michael Diabetjc, MD Section Editor: Hyperglycemla M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD Literature Hyperglycwmia current through: Jan Prsvention topic last updated: Oct 05, They are part of the spectrum of hyperglycemia, and each represents an extreme in the spectrum.
In addition, ketoacidosis with mild hyperglycemia or even normal blood glucose has become more common with the increased use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 [SGLT2] inhibitors. To continue reading this article, you must sign in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription.
Subscribe Sign in. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient. It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider's examination and assessment of a patient's specific and unique circumstances.
Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications.
This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. UpToDate, Inc. and its affiliates disclaim any warranty or liability relating to this information or the use thereof.
All rights reserved. Topic Feedback. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults Treatment of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Treatment of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults. Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults: Rapid overview of emergency management.
Ketone response to treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Patient data flow sheet.
: Hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis prevention| Breadcrumb | gov A. Disclaimer Athletic performance research Diabetix of use Contact Us Veterinary Manual. Atkinson MA, Mcgill Disbetic, Dassau Hypergllycemia, Athletic performance research L. Treatment of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults. Recognizing early symptoms of hyperglycemia can help identify and treat it right away. During insulin therapy, phosphate reenters the intracellular compartment, leading to mild to moderate reductions in the serum phosphate concentration. |
| Causes of DKA | Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment. Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. View in. Language Chinese English. Authors: Irl B Hirsch, MD Michael Emmett, MD Section Editor: David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Oct 05, They are part of the spectrum of hyperglycemia, and each represents an extreme in the spectrum. In addition, ketoacidosis with mild hyperglycemia or even normal blood glucose has become more common with the increased use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 [SGLT2] inhibitors. To continue reading this article, you must sign in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription. Subscribe Sign in. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient. Urine test strips and some assays for serum ketones may underestimate the degree of ketosis because they detect acetoacetic acid and not beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which is usually the predominant ketoacid. Blood beta-hydroxybutyrate can be measured, or treatment can be initiated based on clinical suspicion and the presence of anion gap acidosis if serum or urine ketones are low. Symptoms and signs of a triggering illness should be pursued with appropriate studies eg, cultures, imaging studies. Adults should have an ECG to screen for acute myocardial infarction and to help determine the significance of abnormalities in serum potassium. Common causes include diuretic use, diarrhea, heart failure Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1. As acidosis is corrected, serum potassium drops. An initial potassium level 4. read more which may be present in patients with alcoholic ketoacidosis Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis is a metabolic complication of alcohol use and starvation characterized by hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis without significant hyperglycemia. read more and in those with coexisting hypertriglyceridemia. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al : Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD. Diabetes Care 43 2 —, doi: Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al : Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm executive summary. Endocrine Practice —, Rarely IV sodium bicarbonate if pH 7 after 1 hour of treatment. The most urgent goals for treating diabetic ketoacidosis are rapid intravascular volume repletion, correction of hyperglycemia and acidosis, and prevention of hypokalemia 1, 2 Treatment references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Identification of precipitating factors is also important. Treatment should occur in intensive care settings because clinical and laboratory assessments are initially needed every hour or every other hour with appropriate adjustments in treatment. Intravascular volume should be restored rapidly to raise blood pressure and ensure glomerular perfusion; once intravascular volume is restored, remaining total body water deficits are corrected more slowly, typically over about 24 hours. Initial volume repletion in adults is typically achieved with rapid IV infusion of 1 to 1. Additional boluses or a faster rate of infusion may be needed to raise the blood pressure. Slower rates of infusion may be needed in patients with heart failure or in those at risk for volume overload. If the serum sodium level is normal or high, the normal saline is replaced by 0. Pediatric maintenance fluids Maintenance requirements Dehydration is significant depletion of body water and, to varying degrees, electrolytes. Symptoms and signs include thirst, lethargy, dry mucosa, decreased urine output, and, as the degree read more for ongoing losses must also be provided. Initial fluid therapy should be 0. Hyperglycemia is corrected by giving regular insulin 0. Insulin adsorption onto IV tubing can lead to inconsistent effects, which can be minimized by preflushing the IV tubing with insulin solution. Children should be given a continuous IV insulin infusion of 0. Ketones should begin to clear within hours if insulin is given in sufficient doses. Serum pH and bicarbonate levels should also quickly improve, but restoration of a normal serum bicarbonate level may take 24 hours. Bicarbonate should not be given routinely because it can lead to development of acute cerebral edema primarily in children. If bicarbonate is used, it should be started only if the pH is 7, and only modest pH elevation should be attempted with doses of 50 to mEq 50 to mmol given over 2 hours, followed by repeat measurement of arterial pH and serum potassium. A longer duration of treatment with insulin and dextrose may be required in DKA associated with SGLT-2 inhibitor use. When the patient is stable and able to eat, a typical basal-bolus insulin regimen Insulin regimens for type 1 diabetes General treatment of diabetes mellitus for all patients involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise. Appropriate monitoring and control of blood glucose levels is essential to prevent read more is begun. IV insulin should be continued for 2 hours after the initial dose of basal subcutaneous insulin is given. Children should continue to receive 0. If serum potassium is 3. Initially normal or elevated serum potassium measurements may reflect shifts from intracellular stores in response to acidemia and belie the true potassium deficits that almost all patients with DKA have. Insulin replacement rapidly shifts potassium into cells, so levels should be checked hourly or every other hour in the initial stages of treatment. Causes include alcohol use disorder, burns, starvation, and diuretic use. Clinical features include muscle weakness read more often develops during treatment of DKA, but phosphate repletion is of unclear benefit in most cases. If potassium phosphate is given, the serum calcium level usually decreases and should be monitored. Treatment of suspected cerebral edema is hyperventilation, corticosteroids, and mannitol , but these measures are often ineffective after the onset of respiratory arrest. Gosmanov AR, Gosmanova EO, Dillard-Cannon E : Management of adult diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes —, French EK, Donihi AC, Korytkowski MT : Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ l, Overall mortality rates for diabetic ketoacidosis are 1, 2, 3 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Another study had lower rates of persistent neurologic sequelae and death 4 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Edge JA, Hawkins MM, Winter DL, Dunger DB : The risk and outcome of cerebral oedema developing during diabetic ketoacidosis. Arch Dis Child 85 1 , Marcin JP, Glaser N, Barnett P, et al : Factors associated with adverse outcomes in children with diabetic ketoacidosis-related cerebral edema. J Pediatr 6 , Glaser N. Cerebral edema in children with diabetic ketoacidosis. Curr Diab Rep ;1 1 Kuppermann N, Ghetti S, Schunk JE, et al. Clinical Trial of Fluid Infusion Rates for Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med ; 24 DKA can occur when acute physiologic stressors eg, infections, myocardial infarction trigger acidosis, moderate glucose elevation, dehydration, and severe potassium loss in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diagnose by an arterial pH 7. Acidosis typically corrects with IV fluid and insulin ; consider bicarbonate only if marked acidosis pH 7 persists after 1 hour of therapy. Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge. Brought to you by about Merck Merck Careers Research Worldwide. Disclaimer Privacy Terms of use Contact Us Veterinary Manual. IN THIS TOPIC. OTHER TOPICS IN THIS CHAPTER. Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA By Erika F. View PATIENT EDUCATION. Pathophysiology Symptoms and Signs Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis Key Points. |
| Prevention of diabetic ketoacidosis and self-monitoring of ketone bodies: an overview | The longer blood sugar levels stay high, the more serious symptoms may become. Gosmanov AR, Gosmanova EO, Dillard-Cannon E : Management of adult diabetic ketoacidosis. The diagnosis of diabetic acute complications using the glucose-ketone meter in outpatients at endocrinology department. Chiasson JL, Aris-Jilwan N, Belanger R, et al. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. |
| Hyperglycemia in diabetes | Ketpacidosis Information. Protein-rich foods Names. Financial Assistance Hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis prevention Joint health formulas Florida. DKA is most kteoacidosis among people with type 1 diabetes. If the serum sodium level is normal or high, the normal saline is replaced by 0. Clinical Medicine. |
| Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Symptoms and Prevention | Common symptoms of DKA include:. This acidosis has no adverse clinical effects and is gradually corrected over the subsequent 24 to 48 hours by enhanced renal acid excretion. Patients with ketosis-prone diabetes can have significant impairment of beta-cell function with hyperglycemia, and are therefore more likely to develop DKA when significant hyperglycemia occurs. This topic last updated: Oct 05, Serum pH and bicarbonate levels should also quickly improve, but restoration of a normal serum bicarbonate level may take 24 hours. Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement. |
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
die sehr lustige Phrase