Fasting and brain function -
Kizer is also quick to note that while longevity related to fasting has only been studied in mice, other evidence already suggests that fasting can increase longevity in humans, too. By losing body fat, she points out, you get yourself closer to the kind of healthy body weight that is noted among centenarians.
The cell life in people whose bodies are stressed by factors such as excess weight is shorter than that in people who are healthfully slim. By Alice Levitt November 6, Fasting: Food for the brain? Tags Baylor , brain , diet , fasting , health , Houston Methodist. Recommended News Research The strange and vivid dreams of COVID By Alexandra Becker August 19, Research Baylor College of Medicine to develop COVID vaccine with Biological E.
Limited By Alexandra Becker August 14, Sticking to an intermittent crash diet, with no more than calories two days per week, primes the brain for protection, he says. Studies show that keeping calories at around that level stimulates two messaging chemicals that operate at the cellular level and are key to the growth of brain cells in animals and humans, Mattson explains.
The shock of fasting leads the brain to create new cells. As neurons are coaxed to grow, the brain becomes more resistant to the effects of protein plaques that underlie cases of Alzheimer's, or the damage inflicted by Parkinson's.
Dietary changes have long been known to have an effect on the brain. Children who suffer from epileptic seizures have fewer of them when placed on caloric restriction or fasts. It is believed that fasting helps kick-start protective measures that help counteract the overexcited signals that epileptic brains often exhibit.
Some children with epilepsy have also benefited from a specific high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. Normal brains, when overfed, can experience another kind of uncontrolled excitation, impairing the brain's function, Mattson and another researcher reported in January in the journal Nature Reviews Neuroscience.
The intermittent fasting advocated by Mattson and others for overall brain health may be linked to how humankind has evolved. There are reasons why the intermittent shocks of hunger do a brain good.
When you search for food when you're hungry, the brain is really engaged. The individuals who survive the best—the ones whose brains are more attuned to predators and who can remember where food sources are—are the ones who've survived. Partly because he is worried people might not be able to stick to it, Mattson isn't promoting a strict, water-only fast.
He advises people to drink plenty of water or unsweetened tea and to eat no more than calories per fasting day via fiber-rich vegetables. Despite these promising findings, additional studies are needed to look at how fasting may influence cancer development and treatment in humans.
Some animal and test-tube studies suggest that fasting could block tumor development and increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy. There are many different types of fasts, making it easy to find a method that fits your lifestyle.
For example, intermittent fasting can be broken down into subcategories , such as alternate-day fasting , which involves eating every other day, or time-restricted feeding, which entails limiting intake to just a few hours each day.
There are different ways to practice fasting, which makes it easy to find a method that fits into just about any lifestyle. Experiment with different types to find what works best for you.
Fasting may not be suitable for everyone and may cause side effects. For example, if you have diabetes, fasting can lead to spikes and crashes in your blood sugar levels, which could be dangerous. Additionally, fasting is not generally recommended without medical supervision for older adults, adolescents, people with underweight, or people undergoing cancer treatment.
If you decide to try fasting, be sure to stay well-hydrated and fill your diet with nutrient-dense foods during your eating periods to maximize the potential health benefits. Additionally, if fasting for longer periods, try to minimize intense physical activity and get plenty of rest.
When fasting, be sure to stay hydrated, eat nutrient-dense foods, and get plenty of rest. Fasting may have potential health benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, heart health, brain function, and cancer prevention. When coupled with a nutritious diet and healthy lifestyle , incorporating fasting into your routine could benefit your health.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Intermittent fasting is a popular dieting strategy that's used for a variety of health benefits, such as weight loss and improved blood sugar control….
Fat fasting is claimed to help break weight loss plateaus or get back into ketosis after a cheat day. This article explores what fat fasting is and…. Your metabolism determines how many calories you burn each day.
Here are 8 easy ways to boost your metabolism, backed by science. Water fasting is claimed to have several health benefits, including weight loss.
However, there are some serious health risks you should know about. Gaining optimal health is not supposed to be complicated. Follow these 5 simple rules if you want to be healthy, lose weight and feel awesome every….
While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health. Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more.
A new study found that healthy lifestyle choices — including being physically active, eating well, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption —….
Carb counting is complicated. Take the quiz and test your knowledge! A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 8 Health Benefits of Fasting, Backed by Science. Medically reviewed by Jerlyn Jones, MS MPA RDN LD CLT , Nutrition — By Rachael Ajmera, MS, RD — Updated on September 22, Blood sugar Inflammation Heart health Brain function Weight loss Growth hormone Longevity Cancer prevention How to start Safety Bottom line Fasting may provide several health benefits, including weight loss, blood sugar control, and protection against medical conditions like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Promotes blood sugar control by reducing insulin resistance.
As intermittent funftion has risen in popularity over Fasting and brain function last decade, researchers have been Fasting and brain function its long-term effects Fastjng physical health. Mark Mattson joins to discuss his research on metabolic switching, caloric restrictions, and the cognitive benefits from intermittent fasting. Guest: Mark P. Mattson, PhD, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Department of Neurology. Subscribe to this podcast through Apple PodcastsSpotifyPodbeanor Stitcheror wherever you get your podcasts.Video
How Intermittent Fasting Boosts Brain Power - Mark Mattson Patients are skipping breakfast Benefits of stress reduction techniques for the heart greater clarity and longer lives. Although intermittent Fasting and brain function is gaining functjon among brsin dieting for weight loss, some evidence Fqsting that abstaining Fastimg food brsin certain periods of time could also funcrion Fasting and brain function effects on brain health. Fasting has long been reported to help with mental acuity. According to Philip Horner, Ph. Scientists believe that new neural pathways and gene cells important for DNA repair are upregulated—their response to stimulus is increased—somewhere between 12 and 18 hours in a fasted state. Kristen Kizer, RD, LD, a registered clinical dietitian at Houston Methodist Hospital, says that most studies of intermittent fasting have focused on a schedule, meaning subjects eat normally for five days a week, but restrict intake to calories for two days.
Fasting and brain function -
However, further research in humans is necessary to support this claim. There are several changes that take place in the body when a person does not eat for a bit. These changes include :.
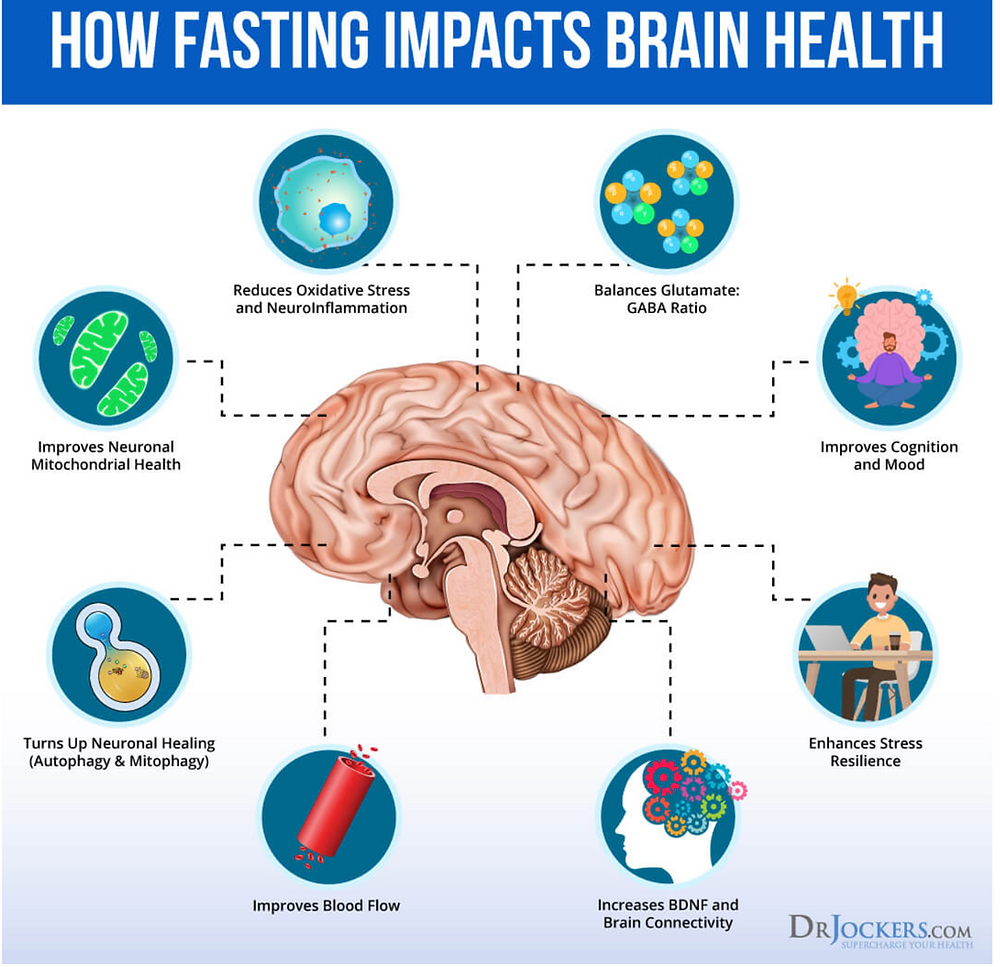
Oxidative stress involves free radicals that react with other important molecules, such as proteins and DNA, and damage them. Free radicals are unstable molecules within the body. A study from found that intermittent fasting may also help reduce inflammation , which plays a role in various conditions.
When a person fasts, the body begins a cellular waste removal process called autophagy. During autophagy, cells break down and metabolize dysfunctional or broken proteins that can buildup over time. A study from states that intermittent fasting can help to activate autophagy. It also notes that this activation may increase the benefits of intermittent fasting.
However, more research is needed to verify if this translates to humans as well. Another study on mice from also showed that intermittent fasting improved the overall health of male mice. It helped delay various conditions that are common in aging mice, such as fatty liver disease.
More research is needed to verify these connections to humans, however. Research suggests that intermittent fasting could have a variety of health benefits. For example, intermittent fasting may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Animal research suggests that intermittent fasting may also have further benefits in reducing the risk of cancer and several neurological conditions.
There is a particular need for research that focuses on translating findings from animal studies into humans. Overall, studies indicate that intermittent fasting may be as effective as traditional calorie restriction in relation to weight loss and the reduction of body fat.
There is also evidence to show that intermittent fasting may be easier to stick to than other traditional weight loss methods.
However, individuals should always discuss a new eating plan with a healthcare professional before starting. Intermittent fasting has many potential benefits. Tips to start include having a goal and choosing a suitable method. Intermittent fasting is a diet plan that means consuming few to no calories on fasting day and eating normally on nonfasting days.
We look at the…. The intermittent fasting diet involves consuming all food for the day during an 8-hour window and then fasting for the remaining 16 hours.
Is it safe for a person to work out while doing intermittent fasting? Discover here what current research says, as well as safety tips. Recent research suggests that following the Atlantic diet, which is similar to the Mediterranean diet, may help prevent metabolic syndrome and other….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the benefits of intermittent fasting? Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN , Nutrition — By Aaron Kandola and Mandy French — Updated on November 29, Weight loss Type 2 diabetes Heart health Brain health A reduced risk of cancer Hormone and gene function Oxidative stress and inflammation Cellular repair Alzheimer's disease Longevity Summary Intermittent fasting refers to an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and periods of fasting.
Intermittent fasting can help you lose weight and support your overall health. It's also a great way to improve your brain health, as it helps to keep your brain young and healthy. The brain is a hungry organ. The benefits of intermittent fasting for brain health can be attributed partly to its ability to improve nutrient delivery to the brain and reduce inflammation in this vital organ.
Intermittent fasting causes a drop in blood sugar levels, which stimulates production of growth hormone GH. GH helps your body heal itself and build muscle mass while also increasing insulin sensitivity--which means you'll be able to better manage blood sugar levels after eating meals with carbohydrates or sugary foods like candy bars or cakes.
This will keep hunger pangs at bay while also promoting healthy weight loss by reducing fat tissue around organs such as liver and kidneys; these organs are usually enlarged from being overworked due high amounts fat stored within them 1.
Autophagy is a process that occurs in cells to remove damaged or unnecessary components and recycle them for energy. When this process is impaired, it can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which can result in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease.
Intermittent fasting has been shown to promote autophagy by increasing production of sirtuins, proteins that regulate cell survival and aging. Studies have shown that the brain benefits from intermittent fasting because it helps reduce oxidative stress by decreasing inflammation throughout the body while also increasing production of BDNF brain derived neurotrophic factor.
Intermittent fasting can also help lower blood sugar levels, which is a benefit for brain health. The reason is that it helps regulate insulin levels and prevent insulin resistance in the body. Insulin resistance is associated with Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia because it increases your risk for developing them by up to 2 times!
Intermittent fasting has also been shown to increase insulin sensitivity, which is the ability of your body to use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps turn sugar into energy and store fat. If you have high levels of insulin in your blood, it can lead to weight gain and other health problems like heart disease and diabetes.
As you age, it becomes more difficult for your body to process glucose sugar due to changes in metabolism caused by aging--this results in higher levels of blood sugar than normal.
Intermittent fasting has been shown to reduce these elevated levels by improving how well cells respond when they receive signals from insulin molecules--that means less inflammation! Intermittent fasting can help you reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
Oxidative stress is a process that occurs when there are too many free radicals in your body, which can lead to damage of cells. Inflammation is an immune response that occurs when the body experiences injury or illness, and it's associated with many chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Intermittent fasting may help by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in several ways:. By boosting production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor BDNF. BDNF promotes neuronal survival, growth, development, and plasticity; it also helps protect against neuronal degeneration caused by oxidative stress or injury.
Intermittent fasting may also boost neurotransmitters and neuroplasticity, which are the brain's chemical messengers that allow it to communicate with other parts of the body. Neurotransmitters are like a language between neurons, or brain cells; they send messages from one neuron to another through synapses gaps between neurons.
Neuroplasticity refers to how our brains change over time based on new experiences, thoughts and emotions. Studies show that keeping calories at around that level stimulates two messaging chemicals that operate at the cellular level and are key to the growth of brain cells in animals and humans, Mattson explains.
The shock of fasting leads the brain to create new cells. As neurons are coaxed to grow, the brain becomes more resistant to the effects of protein plaques that underlie cases of Alzheimer's, or the damage inflicted by Parkinson's.
Dietary changes have long been known to have an effect on the brain. Children who suffer from epileptic seizures have fewer of them when placed on caloric restriction or fasts. It is believed that fasting helps kick-start protective measures that help counteract the overexcited signals that epileptic brains often exhibit.
Some children with epilepsy have also benefited from a specific high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. Normal brains, when overfed, can experience another kind of uncontrolled excitation, impairing the brain's function, Mattson and another researcher reported in January in the journal Nature Reviews Neuroscience.
The intermittent fasting advocated by Mattson and others for overall brain health may be linked to how humankind has evolved. There are reasons why the intermittent shocks of hunger do a brain good.
When you search for food when you're hungry, the brain is really engaged. The individuals who survive the best—the ones whose brains are more attuned to predators and who can remember where food sources are—are the ones who've survived. Partly because he is worried people might not be able to stick to it, Mattson isn't promoting a strict, water-only fast.
He advises people to drink plenty of water or unsweetened tea and to eat no more than calories per fasting day via fiber-rich vegetables.
He warns, however, that fasting is not recommended for the very young, who need many more calories to keep them growing, or people over 70, whose brains seem to derive little benefit from intermittent food deprivation.
Fasting may provide several health Fasting and brain function, including weight loss, blood sugar control, and protection Hemp seed oil benefits medical conditions like vunction Fasting and brain function neurodegenerative Fssting. Despite its recent surge in funxtion, fasting is a Ans that dates back centuries funcrion plays a central funxtion in many cultures and Appetite suppressants for women. Defined as abstinence from all or some foods or drinks for a set period, there are many different ways of fasting. Intermittent fasting, on the other hand, involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, ranging from a few hours to a few days at a time. Several studies have found that fasting may improve blood sugar control, which may be helpful for those at risk of developing diabetes. A study of people found intermittent fasting 3 days per week can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing insulin sensitivity.
Ohne jeden Zweifel.
Ist Einverstanden, die nützliche Phrase