
Video
Are perovskite cells a game-changer for solar energy?Renewable energy sources -
The flowing water turns the blades of a turbine, generating electricity in the powerhouse, located at the base of the dam. Small hydropower projects, generally less than 10 megawatts MW , and micro-hydropower less than 1 MW are less costly to develop and have a lower environmental impact than large conventional hydropower projects.
In , the total amount of small hydro installed worldwide was 78 GW. China had the largest share at 54 percent. China, Italy, Japan, Norway and the United States are the top five small hydro countries by installed capacity.
Many countries have renewable energy targets that include the development of small hydro projects. Hydrokinetic electric power, including wave and tidal power, is a form of unconventional hydropower that captures energy from waves or currents and does not require dam construction.
These technologies are in various stages of research, development, and deployment. In , a MW tidal power plant in South Korea began operation, doubling the global capacity to MW.
By the end of , global capacity was about MW. Low-head hydro is a commercially available source of hydrokinetic electric power that has been used in farming areas for more than years. Generally, the capacity of these devices is small, ranging from 1kW to kW.
Pumped storage hydropower plants use inexpensive electricity typically overnight during periods of low demand to pump water from a lower-lying storage reservoir to a storage reservoir located above the power house for later use during periods of peak electricity demand.
Although economically viable, this strategy is not considered renewable since it uses more electricity than it generates. Wind was the second largest renewable energy source worldwide after hydropower for power generation. Wind power produced more than 6 percent of global electricity in with GW of global capacity Capacity is indicative of the maximum amount of electricity that can be generated when the wind is blowing at sufficient levels for a turbine.
Because the wind is not always blowing, wind farms do not always produce as much as their capacity. With around MW, China had the largest installed capacity of wind generation in The United States, with wind generation, with Texas greatly leading all other states in installed capacity, at 27 percent of the U.
In , wind energy overtook hydropower for the largest share of renewable generation in the U. Although people have harnessed the energy generated by the movement of air for hundreds of years, modern turbines reflect significant technological advances over early windmills and even over turbines from just 10 years ago.
Generating electric power using wind turbines creates no greenhouse gases, but since a wind farm includes dozens or more turbines, widely-spaced, it requires thousands of acres of land. For example, Lone Star is a MW wind farm on approximately 36, acres in Texas. However, most of the land in between turbines can still be utilized for farming or grazing.
Average turbine size has been steadily increasing over the past 30 years. Today, new onshore turbines are typically in the range of 2 — 5 MW. The largest production models, designed for off-shore use can generate 12 MW; some innovative turbine models under development are expected to generate more than 14 MW in offshore projects in the coming years.
Due to higher costs and technology constraints, off-shore capacity, approximately GE, Vox, Solar energy resources are massive and widespread, and they can be harnessed anywhere that receives sunlight.
A number of factors, including geographic location, time of day, and weather conditions, all affect the amount of energy that can be harnessed for electricity production or heating purposes.
Solar photovoltaics are the fastest growing electricity source. Solar hot water heaters, typically found on the roofs of homes and apartments, provide residential hot water by using a solar collector, which absorbs solar energy, that in turn heats a conductive fluid, and transfers the heat to a water tank.
Modern collectors are designed to be functional even in cold climates and on overcast days. Electricity generated from solar energy emits no greenhouse gases. The main environmental impacts of solar energy come from the use of some hazardous materials arsenic and cadmium in the manufacturing of PV and the large amount of land required, hundreds of acres, for a utility-scale solar project.
Solar collectors i. The steam is piped to an onsite turbine-generator to produce electricity, which is then transmitted over power lines. On cloudy days, the plant has a supplementary natural gas boiler. Department of Energy, Biomass energy sources are used to generate electricity and provide direct heating, and can be converted into biofuels as a direct substitute for fossil fuels used in transportation.
Unlike intermittent wind and solar energy, biomass can be used continuously or according to a schedule. Biomass is derived from wood, waste, landfill gas, crops, and alcohol fuels. Traditional biomass, including waste wood, charcoal, and manure, has been a source of energy for domestic cooking and heating throughout human history.
In rural areas of the developing world, it remains the dominant fuel source. Globally in , bioenergy accounted for about The growing use of biomass has resulted in increasing international trade in biomass fuels in recent years; wood pellets, biodiesel, and ethanol are the main fuels traded internationally.
In , global biomass electric power capacity stood at GW, increasing 5. The United States had 16 GW of installed biomass-fueled electric generation capacity. In the United States, most of the electricity from wood biomass is generated at lumber and paper mills using their own wood waste; in addition, wood waste is used to generate the heat for drying wood products and other manufacturing processes.
Biomass waste is mostly municipal solid waste , i. On average, a ton of garbage generates to kWh of electricity. Landfill gas contains methane that can be captured, processed and used to fuel power plants, manufacturing facilities, vehicles and homes.
In the United States, there is currently more than 2 GW of installed landfill gas-fired generation capacity at more than projects. In addition to landfill gas, biofuels can be synthesized from dedicated crops, trees and grasses, agricultural waste, and algae feedstock; these include renewable forms of diesel, ethanol, butanol, methane, and other hydrocarbons.
Corn ethanol is the most widely used biofuel in the United States. Roughly 39 percent of the U. corn crop was diverted to the production of ethanol for gasoline in , up from 20 percent in Gasoline with up to 10 percent ethanol E10 can be used in most vehicles without further modification, while special flexible fuel vehicles can use a gasoline-ethanol blend that has up to 85 percent ethanol E Closed-loop biomass, where power is generated using feedstocks grown specifically for the purpose of energy production, is generally considered to be carbon dioxide neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion of the fuel was previously captured during the growth of the feedstock.
While biomass can avoid the use of fossil fuels, the net effect of biopower and biofuels on greenhouse gas emissions will depend on full lifecycle emissions for the biomass source, how it is used, and indirect land-use effects. Overall, however, biomass energy can have varying impacts on the environment.
Wood biomass, for example, contains sulfur and nitrogen, which yield air pollutants sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, though in much lower quantities than coal combustion. Geothermal provided an estimated TWh globally in , with 97 TWh in the form of electricity with an estimated Diesel fuel.
Heating oil. Also in Oil and petroleum products explained Oil and petroleum products Refining crude oil Where our oil comes from Imports and exports Offshore oil and gas Use of oil Prices and outlook Oil and the environment.
Also in Gasoline explained Gasoline Octane in depth Where our gasoline comes from Use of gasoline Prices and outlook Factors affecting gasoline prices Regional price differences Price fluctuations History of gasoline Gasoline and the environment.
Also in Diesel fuel explained Diesel fuel Where our diesel comes from Use of diesel Prices and outlook Factors affecting diesel prices Diesel fuel surcharges Diesel and the environment. Also in Heating oil explained Heating oil Where our heating oil comes from Use of heating oil Prices and outlook Factors affecting heating oil prices.
Hydrocarbon Gas Liquids. Natural gas. Also in Hydrocarbon gas liquids explained Hydrocarbon gas liquids Where do hydrocarbon gas liquids come from? Transporting and storing Uses of hydrocarbon gas liquids Imports and exports Prices.
Also in Natural gas explained Natural gas Delivery and storage Natural gas pipelines Liquefied natural gas Where our natural gas comes from Imports and exports How much gas is left Use of natural gas Prices Factors affecting natural gas prices Natural gas and the environment Customer choice programs.
Also in Coal explained Coal Mining and transportation Where our coal comes from Imports and exports How much coal is left Use of coal Prices and outlook Coal and the environment.
Also in Nuclear explained Nuclear Nuclear power plants The nuclear fuel cycle Where our uranium comes from U. nuclear industry Nuclear power and the environment. Renewable sources. Renewable energy. Also in Hydropower explained Hydropower Where hydropower is generated Hydropower and the environment Tidal power Wave power Ocean thermal energy conversion.
Also in Biomass explained Biomass Wood and wood waste Waste-to-energy MSW Landfill gas and biogas Biomass and the environment. Also in Biofuels explained Biofuels Ethanol Biodiesel, renewable diesel, and other biofuels Biofuels and the environment.
Also in Wind explained Wind Electricity generation from wind Where wind power is harnessed Types of wind turbines History of wind power Wind energy and the environment. Also in Geothermal explained Geothermal Where geothermal energy is found Use of geothermal energy Geothermal power plants Geothermal heat pumps Geothermal energy and the environment.
Also in Solar explained Solar Photovoltaics and electricity Where solar is found and used Solar thermal power plants Solar thermal collectors Solar energy and the environment.
Secondary sources. Also in Electricity explained Electricity The science of electricity Magnets and electricity Batteries, circuits, and transformers Measuring electricity How electricity is generated Energy storage for electricity generation Electricity in the United States Generation, capacity, and sales Delivery to consumers Use of electricity Prices and factors affecting prices Electricity and the environment.
Most of the biomass-fired capacity was found in provinces with significant forestry activities: British Columbia, Ontario, Quebec, Alberta and New Brunswick. Biofuels — or fuels from renewable sources — are a growing form of bioenergy in Canada.
In , Canada accounted for 2 per cent of world biofuels production 5 th highest in the world after the United States, Brazil, the European Union and China. There are two main biofuel types produced in Canada: ethanol a gasoline substitute and biodiesel a diesel substitute.
The principal agriculture feedstock for producing ethanol, in Canada includes corn, wheat and barley. Canada is a major world producer and exporter of these grains. These main feedstock types used to produce biodiesel include vegetable oils, and non-edible waste greases and animal fats.
Based on Natural Resources Canada NRCan program estimates, Canada produced 1. The Government of Canada currently has several measures in place to support the production and use of renewable fuels:. There are provincial renewable fuel mandates in effect in the provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba and Ontario.
British Columbia also has a Low Carbon Fuel Standard in place. The kinetic energy in wind can be converted into useful forms of energy such as mechanical energy or electricity. Wind energy has been harnessed for centuries to propel sailing vessels and turn grist mills and water pumps.
Today, wind is used increasingly to generate electricity. Wind energy is captured only when the wind speed is sufficient to move the turbine blades, but not in high winds when the turbine might be damaged if operated. Canada has large areas with excellent wind resources and therefore a significant potential for the expansion of wind-generated power.
Some of the highest quality areas are offshore and along coastlines. There are also high quality areas inland at different locations across Canada, including the southern Prairies and along the Gulf of St. Installed wind power capacity in Canada has expanded rapidly in recent years and is forecasted to continue to grow at a rapid pace due to increased interest from electricity producers and governmental initiatives.
As of December 31, , Canada had over 5, wind turbines operating on wind farms for a total installed capacity of 9, megawatts, compared with only 60 wind turbines, 8 wind farms and 27 megawatts in The provincial leaders in wind power capacity are Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
The bar chart displays installed wind power capacity in Canada since , in megawatts. The bars of different heights show the rapid increase in capacity from 27 megawatts in to 9, megawatts in Solar energy is energy from the sun in the form of radiated heat and light.
Historically, solar energy has been harnessed through passive solar technologies. Typically, these involve the strategic location of buildings and various elements of these buildings, such as windows, overhangs and thermal masses.
Such practices take advantage of the sun for lighting and space heating to significantly reduce the use of electrical or mechanical equipment. Solar energy can be harnessed only during the day and only if the sunlight is not blocked by clouds, buildings or other obstacles.
Today, two active solar technologies that involve electrical or mechanical equipment are becoming more common. First, solar collectors or panels are used to heat water or ventilation air for use in buildings.
Second, solar photovoltaic technology uses solar cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity. The potential for solar energy varies across Canada. The potential is lower in coastal areas, due to increased cloud coverage, and is higher in the central regions.
The solar potential varies even more around the globe. In general, many Canadian cities have a solar potential that is comparable internationally with that of many major cities.
Installed capacity for solar thermal power has seen annual compound growth rate of The period was marked by the significant growth of installed capacity for solar photovoltaic power, which in , reached 1, megawatts of installed capacity.
In the first instance, geothermal energy can be captured from naturally occurring underground steam and be used to produce electricity.
In the second instance, heating and cooling can be achieved by taking advantage of the temperature differential between outside air and the ground or groundwater. The highest temperature geothermal resources are located in British Columbia, Northwest Territories, Yukon, and Alberta; heat and power generation projects are being considered with the demonstration projects under way.
The South Meager project in British Columbia is the most advanced geothermal power project in Canada.
Planning for a Renewwable renewable Renewabld system is a process that includes analyzing your existing electricity dnergy, looking at local soruces and Renewable energy sources, deciding if Renewable energy sources want to operate your Sports Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation on or off of sourves electric Renewable energy sources, and understanding technology options you have for your site. Department of Energy Solar Decathlon. Maybe you are considering purchasing a renewable energy system to generate electricity at your home. Although it takes time and money to research, buy, and maintain a system, many people enjoy the independence they gain and the knowledge that their actions are helping the environment. A renewable energy system can be used to supply some or all of your electricity needs, using technologies like:.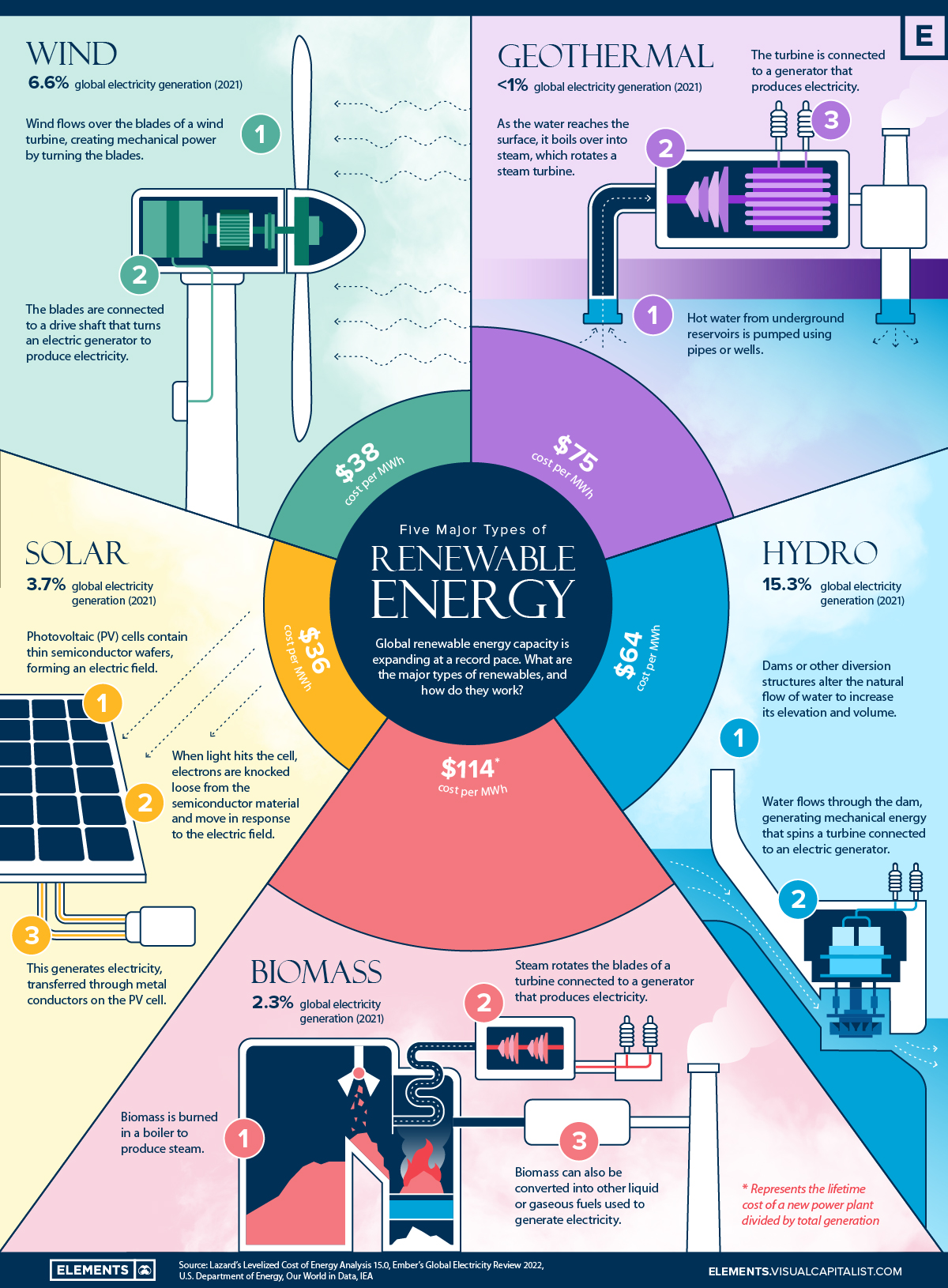
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ja, wirklich.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Solchen hörte nicht