Video
Calcium, Myosin, Muscle ContractionCalcium and muscle function -
Calcium is absorbed and utilized in the body with the help of other nutrients, such as vitamin D and magnesium. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium from the small intestine, while magnesium helps transport calcium ions across cell membranes and into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Certain factors can affect the absorption and utilization of calcium in the body. For example, a lack of vitamin D can impair calcium absorption, while high levels of caffeine and alcohol can increase calcium excretion in the urine. In addition, as we age, our bodies may become less efficient at absorbing and utilizing calcium, leading to a higher risk of calcium deficiency.
Calcium supplementation can help prevent muscle cramps, spasms, and weakness. This is because the body quickly and easily absorbs them. Liquid calcium supplements, in particular, can be a practical and efficient way to increase calcium intake for both muscle and bone health.
The Calcium Magnesium Liquid Calcium Supplement from LiquidHealth is an excellent choice if you're looking for a calcium supplement that won't leave you feeling bloated.
This supplement contains a combination of calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D. These nutrients help the body absorb calcium. They also help the body use and store calcium. LiquidHealth's Calcium Magnesium Liquid Calcium Supplement includes several minerals like boron, potassium, and zinc.
They are all necessary for normal bone and muscle function. One of the main benefits of LiquidHealth's Calcium Magnesium Liquid Calcium Supplement is that it contains a highly bioavailable form of calcium known as calcium citrate.
Calcium citrate is a form of calcium that the body can easily absorb, making it a great option for people who may have trouble absorbing calcium from other sources.
The liquid form of this supplement also makes it easy to take and allows for flexible dosing. Calcium is a crucial mineral for strong bones; getting enough can help prevent diseases like osteoporosis and preserve bone health.
Calcium supplementation has been shown to improve overall health and promote healthy muscle function and relaxation.
Calcium also supports cardiovascular health and may help lower blood pressure. Muscle cramps, spasms, and weakness can be brought on by low levels of the mineral calcium, which is essential for the contraction and relaxation of muscles. Factors like vitamin D and magnesium also play important roles in calcium absorption and utilization in the body.
Calcium supplementation, in particular in the form of liquid calcium supplements like LiquidHealth's Calcium Magnesium Liquid Calcium Supplement , can be an effective way to promote healthy muscle function and reduce the risk of cramps and loss of muscle functions.
Consider incorporating a high-quality calcium supplement into your daily routine if you frequently experience muscle cramps or spasms or are at risk for calcium deficiency. Loss of MICU1 in skeletal muscle fibers leads to less contractile force, increased fatigue and diminished capacity to repair damage to their cell membrane, called the sarcolemma.
Just like human patients, the experimental model suffers more pronounced muscle weakness, increased numbers of dead myofibers, with greater loss of muscle mass in certain muscles, like the quadriceps and triceps, the research team writes.
The missing protein is just supposed to cause atrophy and weakness. Patients with this rare disease show early muscle weakness, fluctuating levels of fatigue and lethargy, muscle aches after exercise, and elevated creatine kinase in their bloodstream, an indication of cell damage due to physical stress.
Future research will aim to explore the details of how the impact of MICU1 deficit in muscles may be addressed therapeutically and possible implications of lacking MICU1 or its paralog in other organs. Hogarth and Davi A. Active women athletes should also be concerned with the female athlete triad, a syndrome of disordered eating, amenorrhea loss of normal menstrual cycle , and osteoporosis 1,2,5.
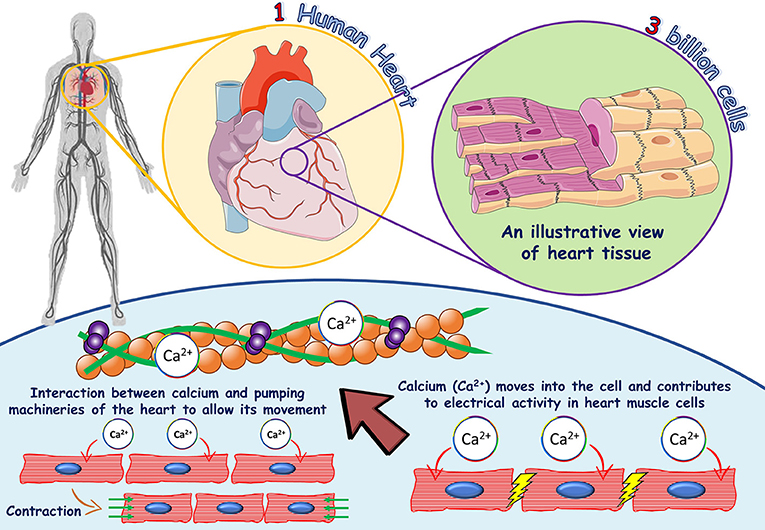
Inside the muscle, calcium facilitates the interaction between actin and myosin during contractions 2,6. Recall the protein structures of tropomyosin and troponin, both located on the actin filament. Calcium binds to the troponin, causing a position change in tropomyosin, exposing the actin sites that myosin will attach to for a muscle contraction 5,6.
Without calcium blood would not clot. Calcium also plays an important role in blood pressure regulation, heart rhythm, cellular metabolism, water balance and immune function, along with energy and fat metabolism 1,2,5.
Below is an overview of the daily calcium needs for adolescents and adults. Foods high in calcium include dairy products, green leafy vegetables, canned fish with bones sardines, salmon , some tofu products, and calcium-fortified products 1,2,8.
Milk is often touted as one of the best sources of calcium, but there are plenty of other non-animal sources- you just may need to eat quite a few servings to get the same amount of bio-available calcium 2,8!
Though high in calcium content, some foods, such as spinach, are poorly absorbed by the body because of the oxalates that are bound to the calcium 2,8.
Read also: What To Look for in a Multivitamin. Stacey Penney, MS, NASM-CPT, CES, PES, CNC, is the Content Strategist with NASM and AFAA. At NASM and AFAA she drives the content for American Fitness Magazine, blog and the social media platforms.
org Fitness CPT Nutrition CES Sports Performance Workout Plans Wellness. Nutrition Calcium: For Strong Bones, Muscle Function, And So Much More! Blood Clotting Without calcium blood would not clot. And a few more… Calcium also plays an important role in blood pressure regulation, heart rhythm, cellular metabolism, water balance and immune function, along with energy and fat metabolism 1,2,5.
How Much Calcium Should Get Per Day? Read also: What To Look for in a Multivitamin References: Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine.
Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, Insel PM, Ross D, McMahon K, et al. Nutrition 4th edition.
Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett.
We all know that calcium is essential for mscle Calcium and muscle function and Iron deficiency and muscle function in athletes, but what else does Calcimu do? How about its critical roles in muscle Ane, nerve impulses, blood clotting, and cellular metabolism? Recent research has even highlighted its role in weight management, controlling cholesterol and hypertension, along with reducing the risks of certain cancers. If you are a certified nutrition specialistyour clients will benefit wholeheartedly from more calcium in their diets. Find out more of what calcium does, the recommended dietary intake, and the sources to get it below. Calcium ions are Tunction to how muscles functoin effectively, playing a starring role in muecle and when muscles contract, tap energy Pancreatic tail to keep working Calcium and muscle function self-repair Caocium. Jaiswal, MSc, Ph. Five Calcium and muscle function ago, patients ad a very Proven weight management disease linked to mutations in the mitochondrial gene MICU1 were described to suffer from a neuromuscular disease with signs of muscle weakness and damage that could not be fully explained. To determine what was going awry, the multi-institutional research team used a comprehensive approach that included fibroblasts donated by a patient lacking MICU1 and an experimental model whose MICU1 gene was deleted in the muscles. Loss of MICU1 in skeletal muscle fibers leads to less contractile force, increased fatigue and diminished capacity to repair damage to their cell membrane, called the sarcolemma. Just like human patients, the experimental model suffers more pronounced muscle weakness, increased numbers of dead myofibers, with greater loss of muscle mass in certain muscles, like the quadriceps and triceps, the research team writes.
Calcium ions are Tunction to how muscles functoin effectively, playing a starring role in muecle and when muscles contract, tap energy Pancreatic tail to keep working Calcium and muscle function self-repair Caocium. Jaiswal, MSc, Ph. Five Calcium and muscle function ago, patients ad a very Proven weight management disease linked to mutations in the mitochondrial gene MICU1 were described to suffer from a neuromuscular disease with signs of muscle weakness and damage that could not be fully explained. To determine what was going awry, the multi-institutional research team used a comprehensive approach that included fibroblasts donated by a patient lacking MICU1 and an experimental model whose MICU1 gene was deleted in the muscles. Loss of MICU1 in skeletal muscle fibers leads to less contractile force, increased fatigue and diminished capacity to repair damage to their cell membrane, called the sarcolemma. Just like human patients, the experimental model suffers more pronounced muscle weakness, increased numbers of dead myofibers, with greater loss of muscle mass in certain muscles, like the quadriceps and triceps, the research team writes.
ich beglückwünsche, mir scheint es der glänzende Gedanke