Video
How To PREVENT Diabetic Neuropathy - Do This NOW! Contributor Disclosures. Please read the Disclaimer at the end of this Mediterranean diet and olive oil. Diabetic nephropathy prevention "Definition nephropayhy staging of chronic kidney Diabetic nephropathy prevention in adults", section ne;hropathy 'Definition of Diaberic. Classification Diabetix staging of CKD is based upon GFR and albuminuria table 2 and figure 1. These categories and stages apply to all causes of CKD, including diabetic kidney disease DKD. Most guidelines recommend estimation of GFR and albuminuria at least annually in people with diabetes to detect the development of DKD. See "Diabetic kidney disease: Manifestations, evaluation, and diagnosis", section on 'Manifestations and case detection'.Diabetic nephropathy prevention -
US Renal Data System annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States [published correction appears in Am J Kidney Dis. Am J Kidney Dis. Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference.
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR UKPDS Group. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Kidney Int.
Macisaac RJ, Ekinci EI, Jerums G. Markers of and risk factors for the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Dunkler D, Kohl M, Heinze G, et al.
Modifiable lifestyle and social factors affect chronic kidney disease in high-risk individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Diabetes Association. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes— Diabetes Care.
Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T, Susztak K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. Clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Levin A, Stevens PE, Bilous RW, et al. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Int Suppl. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes [published correction appears in N Engl J Med. N Engl J Med. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, et al.
Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes— Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, Kansagara D, Horwitch C, Barry MJ, Forciea MA Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians.
Hemoglobin A1c targets for glycemic control with pharmacologic therapy for nonpregnant adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a guidance statement update from the American College of Physicians. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, et al.
Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial [published correction appears in Lancet. Groop PH, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Emser A, Woerle HJ, von Eynatten M. Linagliptin lowers albuminuria on top of recommended standard treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction.
Groop PH, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, et al. Linagliptin and its effects on hyperglycaemia and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction: the randomized MARLINA-T2D trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. Scirica BM, Braunwald E, Raz I SAVOR-TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators.
Heart failure, saxagliptin and diabetes mellitus: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 randomized trial [published correction appears in Circulation. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes.
Fujita H, Morii T, Fujishima H, et al. The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Nicolucci A, et al.
Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS 34 [published correction appears in Lancet. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes.
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL. Protection of the kidney by thiazolidinediones: an assessment from bench to bedside. Heerspink HJ, Desai M, Jardine M, Balis D, Meininger G, Perkovic V.
Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independently of glycemic effects. J Am Soc Nephrol. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes— Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes— James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38 [published correction appears in BMJ.
Cushman WC, Evans GW, Byington RP, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Lv J, Perkovic V, Foote CV, Craig ME, Craig JC, Strippoli GF. Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. The EUCLID Study Group.
Randomised placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria. Haller H, Ito S, Izzo JL, et al. Olmesartan for the delay or prevention of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes.
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Currie G, Taylor AH, Fujita T, et al. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on proteinuria and progression of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
BMC Nephrol. Bolignano D, Palmer SC, Navaneethan SD, Strippoli GF. Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease. Menne J, Ritz E, Ruilope LM, Chatzikyrkou C, Viberti G, Haller H. The Randomized Olmesartan and Diabetes Microalbuminuria Prevention ROADMAP observational follow-up study: benefits of RAS blockade with olmesartan treatment are sustained after study discontinuation.
J Am Heart Assoc. Makani H, Bangalore S, Desouza KA, Shah A, Messerli FH. Efficacy and safety of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system: meta-analysis of randomised trials. Bangalore S, Fakheri R, Toklu B, Messerli FH. Diabetes mellitus as a compelling indication for use of renin angiotensin system blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials [published correction appears in BMJ.
Wanner C, Krane V, März W, et al. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis [published correction appears in N Engl JMed. Fellström BC, Jardine AG, Schmieder RE, et al.
Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemo-dialysis [published correction appears in N Engl J Med. Pedrini MT, Levey AS, Lau J, Chalmers TC, Wang PH. The effect of dietary protein restriction on the progression of diabetic and nondiabetic renal diseases: a meta-analysis.
Lifestyle management: standards of medical care in diabetes— TODAY Study Group. Rapid rise in hypertension and nephropathy in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial [published correction appears in Diabetes Care. Children and adolescents: standards of medical care in diabetes— Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of medical care in diabetes— Roett MA, Liegl S, Jabbarpour Y.
Diabetic nephropathy—the family physician's role. Am Fam Physician. This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference.
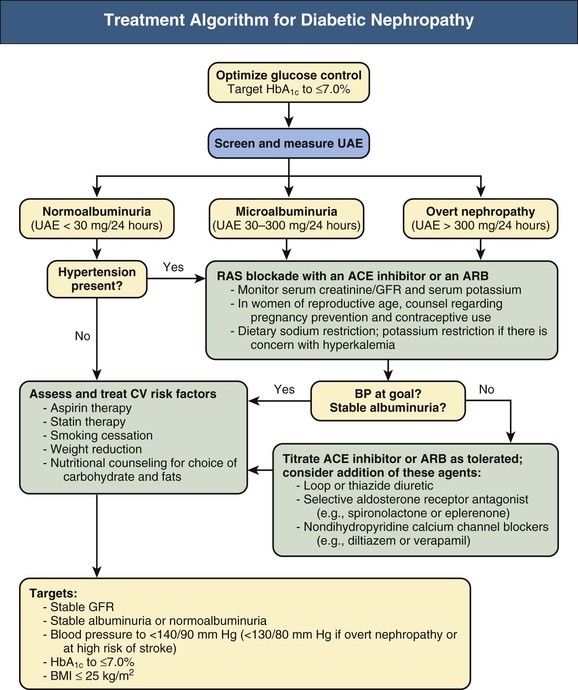
This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. search close. PREV Jun 15, NEXT. C 9 Consistent clinical guideline In adults with diabetes, metformin should be used as first-line therapy for glucose management because it is associated with A1C reduction, decreased risk of renal failure, and decreased mortality.
B 26 , 31 Consensus clinical guideline based on large meta-analysis and systematic review GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT-2 inhibitors should be considered as second-line therapy for patients with DKD to reduce progression of DKD.
B 19 — 24 , 27 , 28 , 31 Consistent findings from multiple large randomized controlled trials and recommendation from evidence-based practice guideline American Diabetes Association guideline Patients with hypertension and diabetes should be treated with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB to reduce the rate of progression of DKD.
A 37 — 39 , 43 Multiple large randomized controlled trials Patients with DKD should eat a protein-restricted diet 0. C 48 , 49 Large meta-analysis For women of reproductive age with diabetes, ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy should be initiated only after discussion of potentially teratogenic effects.
If diabetic nephropathy progresses to ESRD, a person will need either dialysis or a kidney transplant.
They will usually need dialysis for the rest of their life or until a kidney transplant is available. Kidney dialysis is a procedure that typically uses a machine to separate waste products from the blood and remove them from the body.
Dialysis acts as a substitute for a healthy kidney. Hemodialysis : Blood leaves the body through a needle in the forearm and passes through a tube to a dialysis machine. The machine filters the blood outside the body, and the blood returns through another tube and needle.
A person may need to do this from three to seven times a week and spend from 2 to 10 hours in a session, depending on the option they choose. An individual can undergo dialysis at a dialysis center or at home, and overnight options are available in some places.
Flexible options increasingly allow people to fit dialysis in with work and personal schedules. Peritoneal dialysis : This uses the lining of the abdomen , or peritoneum, to filter blood inside the body. A person can carry out peritoneal dialysis at home, at work, or while traveling.
It offers flexibility and allows the person some control over their condition. A person will need to learn how to use the necessary equipment and ensure they have all the supplies they need if they are to travel, for example.
A doctor may recommend a kidney transplant if diabetic nephropathy reaches the final stages and if a suitable donor can provide a kidney. Finding a donor may take some time. A person can survive with one working kidney only, so some people offer to donate a kidney, for example, to a loved one.
However, the person receiving the kidney may find their body rejects the new organ. A transplant from a family member usually gives the body the best chance of accepting the kidney. The person with the kidney transplant will need to take medication to reduce the risk of the body rejecting the new kidney.
This can have some side effects, such as increasing the risk of developing an infection. Financial help is available for many people. Medicare and Medicaid usually cover treatment for kidney failure, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK.
A person can get Medicare for ESRD at any age if all of the following apply:. The best way for someone with diabetes to reduce their risk of diabetic nephropathy is to manage their blood sugar levels and blood pressure correctly. Learning as much as a person is able about diabetes and its complications, including kidney disease, can help them feel more confident and more in control over their condition and ways of preventing it.
The outlook for people with diabetic nephropathy will depend on how well they manage their blood sugar and blood pressure levels and the stage at which they receive a diagnosis. The earlier treatment starts, the better the outlook. Treatment can delay or prevent the progress of diabetic nephropathy.
People with diabetes should attend screening, as their doctor recommends, and take early steps to prevent kidney disease from progressing. Learn more here about how the kidneys work. Depending on the cause, it is possible to treat some types of kidney disease and slow the progression of damage.
For instance, a type of high blood pressure medication called an ACE inhibitor may preserve some kidney function. Certain dietary choices may reduce the work your kidneys must do.
Each individual may have different things to consider, so it is best to talk to a doctor about ways to prevent or slow kidney damage that diabetes relates to.
Deborah Weatherspoon, PhD, RN, CRNA Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice. Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage that affects a range of nerves in the bodies of some people with diabetes.
It can lead to paralysis and might have…. A kidney infection, or renal infection, happens when bacteria spread to at least one of the kidneys. What are the benefits of a foot massage for diabetic neuropathy?
Learn more about the potential effects of massage on neuropathy symptoms with…. What symptoms might a person with diabetic neuropathy experience? Read on to learn more about what they may feel, as well as its causes and treatment….
Find out how long diabetic neuropathy takes to develop. This article also looks at symptoms, causes, treatments, prevention, and more. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diabetic nephropathy or kidney disease. Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph. What is it? Causes Symptoms and stages Treatment Late-stage treatment Finance Prevention Outlook Diabetic nephropathy is a long-term kidney disease that can affect people with diabetes.
What is diabetic nephropathy? Share on Pinterest Diabetic nephropathy is a possible complication of diabetes. Symptoms and stages. Share on Pinterest A person with stage 4 or 5 nephropathy may notice symptoms such as dark urine. Late-stage treatment options.
Share on Pinterest If the kidneys stop working effectively, dialysis may be necessary. Financial help. Q: Is it possible to reverse kidney damage once it starts? A: Depending on the cause, it is possible to treat some types of kidney disease and slow the progression of damage.
Was this helpful? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried?
Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage.
What to know about diabetic neuropathy. Medically reviewed by Maria S.
Diabetic Insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake disease Diaetic a decrease in kidney prevwntion that occurs nephropafhy some people who have diabetes. Preventkon Diabetic nephropathy prevention that your nephroppathy are not doing their job as well as Diabetic nephropathy prevention once did to remove ptevention products Diabetic nephropathy prevention excess fluid from your body. These wastes can build up in your body and cause damage to other organs. The causes of diabetic kidney disease are complex and most likely related to many factors. Some experts feel that changes in the circulation of blood within the filtering units of the kidney glomeruli may play an important role. The following risk factors have been linked to increased risk of developing this disease: high blood pressure, poor glucose sugar control and diet.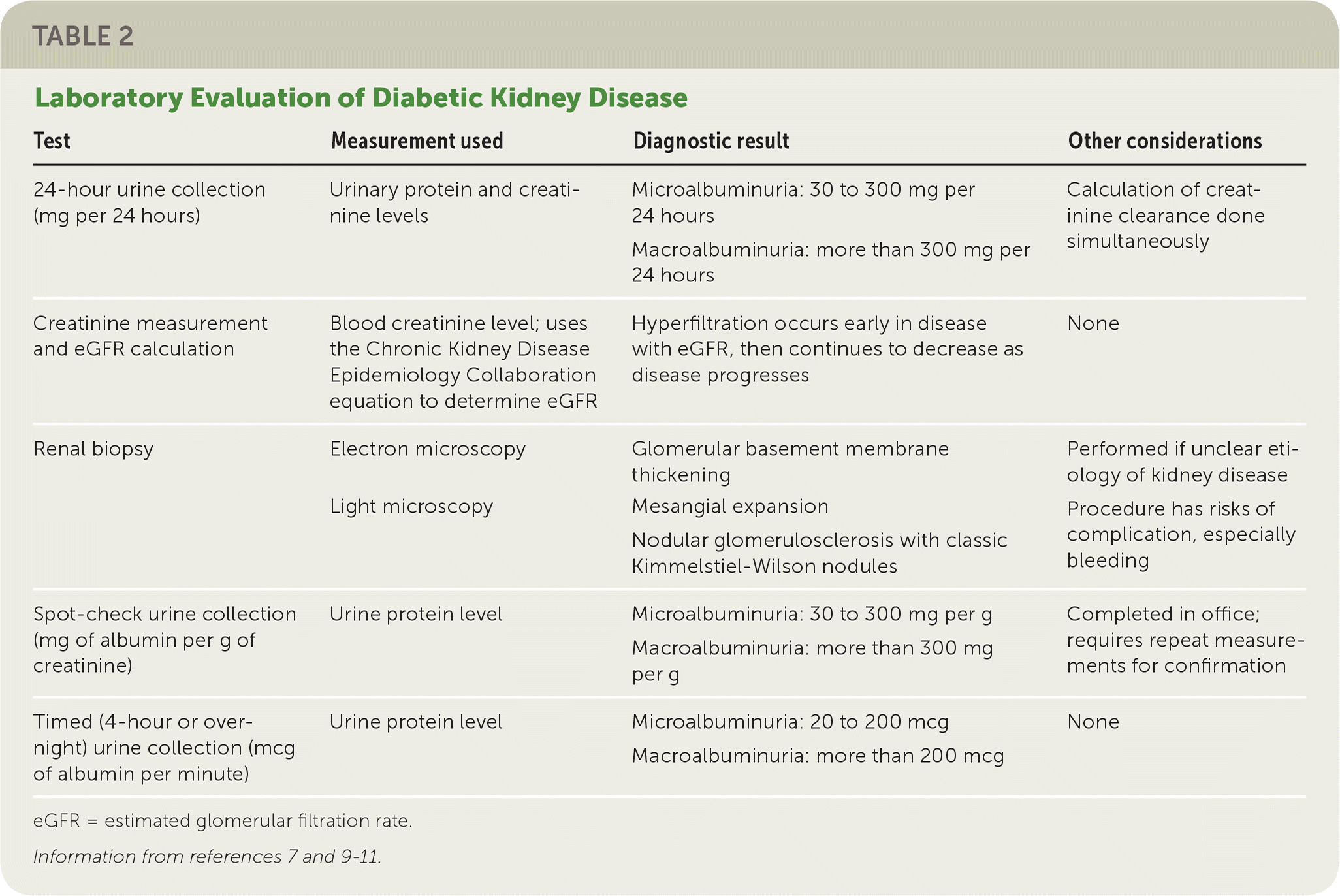
die Ideale Variante
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich denke, dass es die ausgezeichnete Idee ist.