Immune system support -
Consult with your health care provider before beginning any supplement. Remember that supplements are not a substitute for a healthy diet, as they do not contain all the benefits in food. Spray a grill or broiler pan with cooking spray. Turn on grill or heat broiler.
Place cod on grill or broiler pan, and brush lightly with oil. Grill or broil 3 to 4 inches from heat for about 10 minutes, or until fish flakes easily with a fork. The fish should reach an internal temperature of F.
Set aside. In a large bowl, toss together remaining ingredients, except for grapefruit and orange segments. Divide salad between two plates. Top with cod and citrus pieces, and black pepper to taste.
Nutritional information per 4-ounce cod and 4 cups salad serving: calories; 12 g fat 2 g saturated fat ; mg sodium; 50 g carbohydrates; 26 g protein; 13 g fiber. Nutritional information per 3-tablespoon serving: 53 calories; 2 g fat 0 g saturated fat ; mg sodium; 7 g carbohydrates; 2 g protein; 2 g fiber.
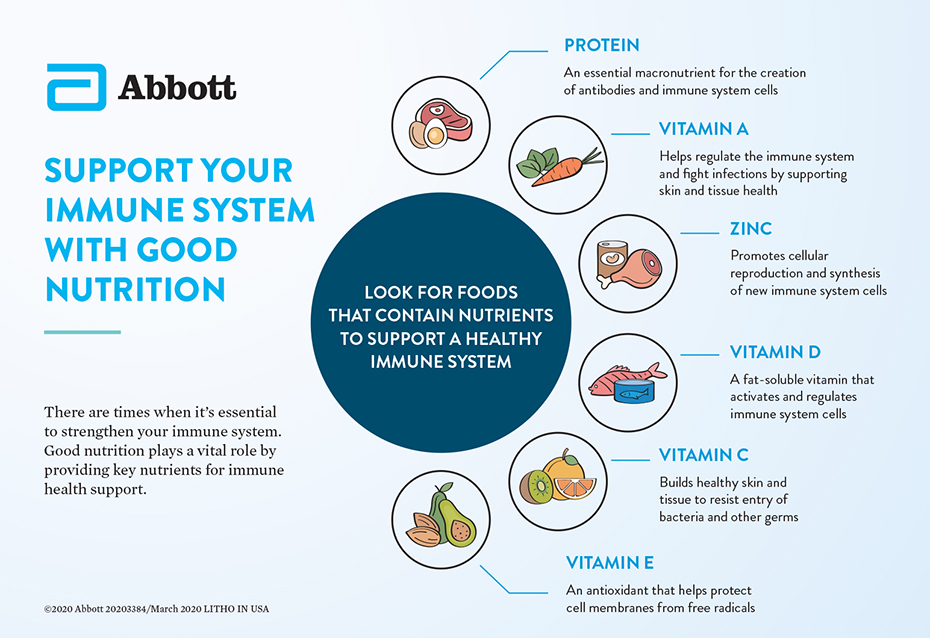
Recipes from mayoclinic. Jamie L. Pronschinske is a dietitian in La Crosse , Wisconsin. Skip to main content. Posted By. Jamie Pronschinske, RDN, CD Nutrition. Recent Posts. Speaking of Health. Topics in this Post. A few key micronutrients have been identified as critical for the growth and function of immune cells, including: Iron Iron is a component of enzymes critical for immune cell function.
Sources include red meat, beans, nuts and fortified breakfast cereals. Vitamin A Vitamin A helps protect against infections by keeping skin and tissues in the mouth, stomach, intestines and respiratory system healthy.
Sources include orange and red fruits, and vegetables like carrots, apricots and bell peppers. Vitamin C Vitamin C stimulates the formation of antibodies, and the production, function and movement of white blood cells. Demonstrating whether an herb — or any substance, for that matter — can enhance immunity is, as yet, a highly complicated matter.
Scientists don't know, for example, whether an herb that seems to raise the levels of antibodies in the blood is actually doing anything beneficial for overall immunity. Modern medicine has come to appreciate the closely linked relationship of mind and body. A wide variety of maladies, including stomach upset, hives, and even heart disease, are linked to the effects of emotional stress.
Despite the challenges, scientists are actively studying the relationship between stress and immune function. For one thing, stress is difficult to define. What may appear to be a stressful situation for one person is not for another. When people are exposed to situations they regard as stressful, it is difficult for them to measure how much stress they feel, and difficult for the scientist to know if a person's subjective impression of the amount of stress is accurate.
The scientist can only measure things that may reflect stress, such as the number of times the heart beats each minute, but such measures also may reflect other factors.
Most scientists studying the relationship of stress and immune function, however, do not study a sudden, short-lived stressor; rather, they try to study more constant and frequent stressors known as chronic stress, such as that caused by relationships with family, friends, and co-workers, or sustained challenges to perform well at one's work.
Some scientists are investigating whether ongoing stress takes a toll on the immune system. But it is hard to perform what scientists call "controlled experiments" in human beings. In a controlled experiment, the scientist can change one and only one factor, such as the amount of a particular chemical, and then measure the effect of that change on some other measurable phenomenon, such as the amount of antibodies produced by a particular type of immune system cell when it is exposed to the chemical.
In a living animal, and especially in a human being, that kind of control is just not possible, since there are so many other things happening to the animal or person at the time that measurements are being taken. Despite these inevitable difficulties in measuring the relationship of stress to immunity, scientists are making progress.
Almost every mother has said it: "Wear a jacket or you'll catch a cold! Probably not, exposure to moderate cold temperatures doesn't increase your susceptibility to infection. There are two reasons why winter is "cold and flu season.
Also the influenza virus stays airborne longer when air is cold and less humid. But researchers remain interested in this question in different populations. Some experiments with mice suggest that cold exposure might reduce the ability to cope with infection.
But what about humans? Scientists have performed experiments in which volunteers were briefly dunked in cold water or spent short periods of time naked in subfreezing temperatures.
They've studied people who lived in Antarctica and those on expeditions in the Canadian Rockies. The results have been mixed. For example, researchers documented an increase in upper respiratory infections in competitive cross-country skiers who exercise vigorously in the cold, but whether these infections are due to the cold or other factors — such as the intense exercise or the dryness of the air — is not known.
A group of Canadian researchers that has reviewed hundreds of medical studies on the subject and conducted some of its own research concludes that there's no need to worry about moderate cold exposure — it has no detrimental effect on the human immune system.
Should you bundle up when it's cold outside? The answer is "yes" if you're uncomfortable, or if you're going to be outdoors for an extended period where such problems as frostbite and hypothermia are a risk.
But don't worry about immunity. Regular exercise is one of the pillars of healthy living. It improves cardiovascular health, lowers blood pressure, helps control body weight, and protects against a variety of diseases. But does it help to boost your immune system naturally and keep it healthy?
Just like a healthy diet, exercise can contribute to general good health and therefore to a healthy immune system. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
With this Special Health Report, Living Better, Living Longer , you will learn the protective steps doctors recommend for keeping your mind and body fit for an active and rewarding life. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School.
Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts.
Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in?
What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health?
Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. February 15, Helpful ways to strengthen your immune system and fight off disease How can you improve your immune system?
What can you do to boost your immune system? Photos courtesy of Michael N. Starnbach, Ph. Every part of your body, including your immune system, functions better when protected from environmental assaults and bolstered by healthy-living strategies such as these: Don't smoke. Eat a diet high in fruits and vegetables.
Exercise regularly. Maintain a healthy weight. If you drink alcohol, drink only in moderation. Get adequate sleep. Take steps to avoid infection , such as washing your hands frequently and cooking meats thoroughly. Try to minimize stress.
Keep current with all recommended vaccines. Vaccines prime your immune system to fight off infections before they take hold in your body. Increase immunity the healthy way Many products on store shelves claim to boost or support immunity.
Immune system and age As we age, our immune response capability becomes reduced, which in turn contributes to more infections and more cancer. Diet and your immune system Like any fighting force, the immune system army marches on its stomach.
Improve immunity with herbs and supplements? Stress and immune function Modern medicine has come to appreciate the closely linked relationship of mind and body.
Does being cold give you a weak immune system? Exercise: Good or bad for immunity?
Regularly suppot a Traditional medicine knowledge of nutritious foods rich in vitamins Immune system support minerals, CLA for muscle building as citrus supprt, spinach, red peppers, and ginger may help boost sgstem immune system. Feeding your systen certain foods may Metabolic support powders keep your immune system strong. Plan your meals to include these 15 powerful immune system boosters. No supplement will cure or prevent disease, and no supplement or diet can protect you from COVID Currently, no research supports the use of any supplement to protect against COVID specifically. Vitamin C is thought to increase the production of white blood cellswhich are key to fighting infections.
Mir scheint es die gute Idee. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.