Metabolic health benefits -
Lack of sleep has been linked to insulin resistance and increased blood glucose, which is one of the components of metabolic syndrome.
Controlling mental stress is another important thing you can do for good metabolic health. The body goes through several metabolic changes in response to stress, some of which can derail your weight loss efforts.
Also, some people tend to eat more when they are stressed. In conclusion, there is no magic pill for improved metabolic health. However, eating a balanced diet and maintaining fitness with regular physical activity are two simple things with many health benefits that will put you on the right path.
Remember to always seek medical advice before starting an exercise or diet program. How to Rebuild Your Microbiome After Antibiotics. Food Poisoning or Stomach Virus? The Telltale Symptoms to Look For. What Are Electrolytes and Why are They So Important?
What Foods Can You Eat 2 Days Before a Colonoscopy? Does Milk Help Heartburn? Other Remedies and Cures. Healthcare Pharmacy Insurance Seasonal More Charity Partners Thought Leadership. How to Improve Metabolic Health Written by Juhi Modi Medically reviewed by Andres Maldonado, M.
What is metabolic health? What is good metabolic health? Does blood pressure play a role? Eat a minimum number of calories When you go on a strict diet, your body slides into starvation mode and slows down your metabolic rate to conserve energy.
Eat and drink at regular intervals Eating smaller meals throughout the day can keep your metabolism charged up and help you burn calories. Try intermittent fasting Research suggests that shaving off a few hours from your daily eating window can reduce belly fat, aid in weight loss, and improve your metabolic health.
Work out harder The body takes several hours to recover from high-intensity exercise. Shake up your workout routine As you become regular with your exercise routine, your body becomes more efficient in conserving energy. Which foods increase metabolism and burn fat?
Is green tea good for weight loss? Protein: Eating food boosts the metabolic rate for a few hours because extra calories are needed to digest the food. Of all the food groups, protein has the best effect on metabolism. Protein boosts fat oxidation and the breaking down of fatty acids and fat cells.
Eating protein can also make you feel full for longer and therefore eat fewer calories. Green tea: Drinking green tea has been shown to increase metabolism. It is believed green tea converts stored fat into free fatty acids and increases the amount of fat the body burns.
Coffee: Like green tea, coffee also has positive effects on fat burning and metabolism. Drinking coffee can be one of the ways to boost fat loss. However, keep in mind that caffeine can cause a temporary spike in blood pressure.
Spicy foods: Studies have shown that capsaicin, a substance found in peppers, can help boost metabolism. Water: Water contains zero calories. Replacing drinks with water automatically reduces how many calories you consume.
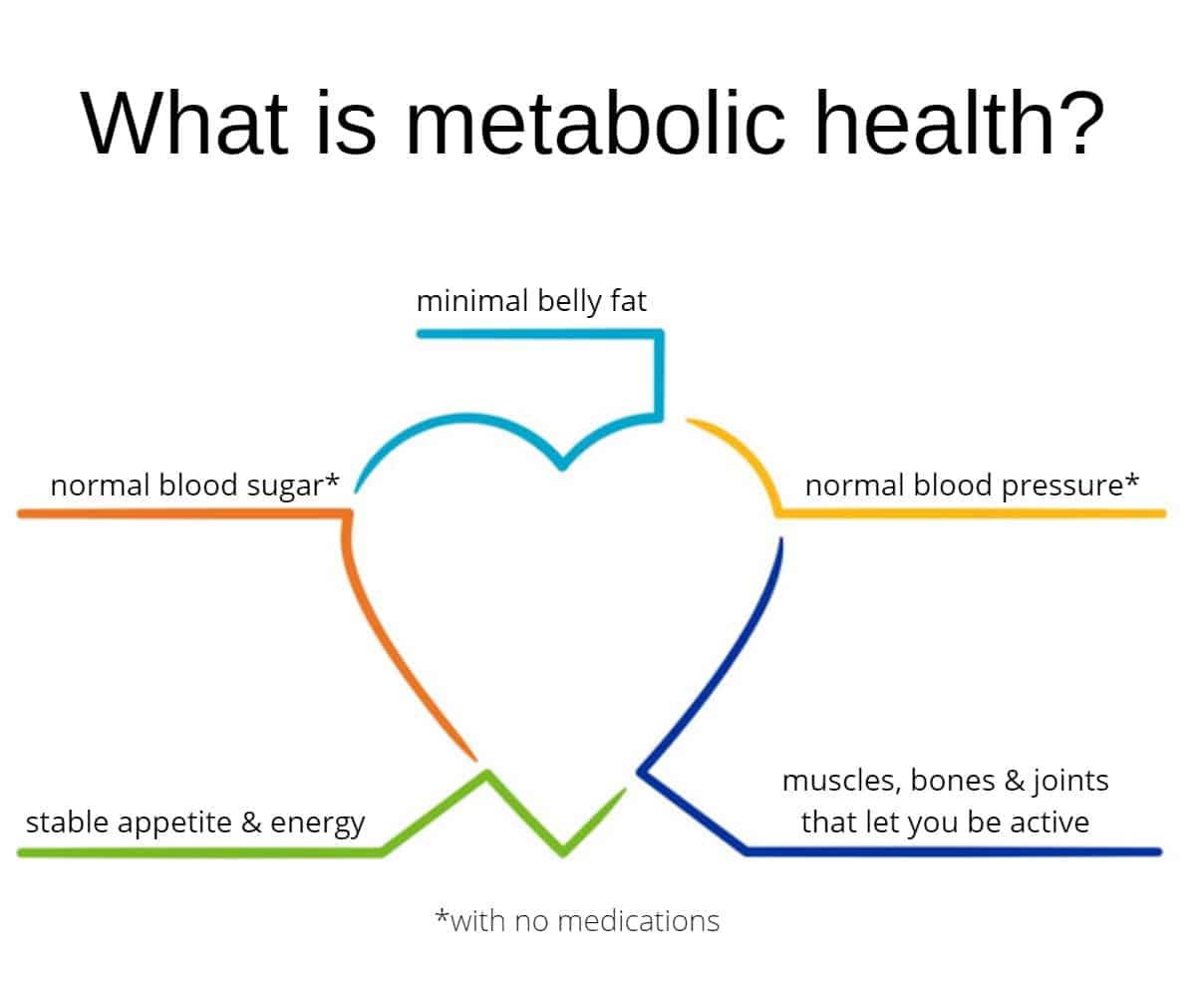
Here at Pendulum, we talk a lot about metabolic health. In a study published in the journal Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders , metabolic health was defined as having ideal levels of blood sugar, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and waist circumference, without using medications.
If someone has to take medication to control their blood sugar, cholesterol, or blood pressure, they already exhibit bad metabolic health. Another way to look at it is that the 5 markers of metabolic health are:.
Aside from having less of a chance of developing metabolic disease, being in good metabolic health means you have more energy, you sleep well, your mood is more consistent, your mind is clearer…in short, you feel good.
In contrast, bad metabolic health is often associated with poor sleep, chronic pain, irritability, infertility, and the inability to lose weight.
Metabolic syndrome is diagnosed when someone has 3 or more of the 5 markers of poor metabolic health. The underlying causes of metabolic syndrome include being overweight or obese, insulin resistance, physical inactivity, increasing age, and genetic factors. On the other hand, in one study, higher T levels 15 were correlated with markers of metabolic health, including lower body fat and reduced blood sugar levels, which may suggest that having normal testosterone levels may help ward off metabolic disease, but more research is required.
For women, it was the opposite. Higher levels of testosterone were linked to insulin resistance and higher blood sugar and body fat. Research suggests that estrogen may have a protective role in the development of insulin resistance and its consequences.
This protection tends to disappear with lower estrogen levels—such as those experienced at the onset of menopause Improving metabolic health can have dramatic effects on overall health and well-being. Several lifestyle factors can play a role in our metabolic health status, including activity levels, stress levels, and the amount of sleep we get.
Since one of the root causes of worsening metabolic health is high blood sugar, improving blood sugar control is one of the key ways to improve metabolic health.
The best way to do that: Eat fewer refined carbs, added sugars, and highly processed foods. Aim to eat ones with a lower glycemic index, and pair them with some fiber, healthy fats like omega 3 fatty acids , or protein to slow digestion and curb a blood sugar spike.
The time you eat can also play a role. Eating late at night can impair glucose tolerance and increase the risk for Type 2 diabetes, according to a randomized crossover study published in Clinical Nutrition.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels may help improve metabolic health. When you exercise, your body increases its responsiveness to insulin. This can lower blood sugar and may help to prevent insulin resistance Exercise is also a great tool to help mitigate a blood sugar spike after a meal, according to various studies However, exercise at any time throughout the day can have metabolic health benefits.
Physical activity can improve heart health, helps maintain or reduce body weight, help lower blood pressure, and aid with stress relief. Stress can cause higher glucose levels Problem is, your body can perceive lots of things as threats: a work deadline, an argument, a traffic jam.
Normally, when glucose floods your system, your body pumps out insulin to lower your blood sugar level. Reducing your overall stress levels and calming your reaction to stressful events can improve metabolic health. Meditation, breathing exercises 22 , and physical activity are all ways to help.
Our sleep-wake cycle a circadian rhythm is also tied to our metabolic health via the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN. Erratic sleep schedules, travel, shift work, too much blue light from devices late at night, and an inadequate amount of sleep can all throw your circadian rhythm out of whack These disruptions may affect metabolic health by impacting the delicate balance of hormone levels, and they are tied to insulin resistance and higher body fat.
One small study found that one night of inadequate sleep only four hours impaired glucose tolerance Aim for at least seven or more hours of sleep per night and stick to a regular sleep schedule as much as possible.
Getting an adequate amount of natural light during the day and restricting light from devices at night may also help Some underlying conditions can impact metabolic health markers, so staying on top of your overall health and seeking treatment for undesirable symptoms is crucial.
Hypothyroidism may affect your glucose level, for example Low testosterone in men and PCOS in women are risk factors for insulin resistance.
And sleep apnea, especially if untreated and causing excessive daytime sleepiness, may also put you at risk for worsening metabolic health Here's How To Improve Your Metabolic Health.
Keep these markers in mind. By Jennifer Chesak January 24, Fast Facts. Only 12 percent of Americans are considered metabolically healthy, according to a national survey. There are five markers of metabolic health: blood sugar, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, waist circumference, and blood pressure.
Improving any one of these markers may improve metabolic health and help prevent future disease. What is Metabolism? What is Metabolic Health? Primary Markers of Metabolic Health Researchers have identified five primary markers of metabolic health: Waist circumference Glucose or blood sugar level Blood pressure Triglycerides the amount of fat in your blood High-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol.
Metabolic Health and Hormones A decrease in metabolic health may also affect hormone levels. Related: Common Conditions That Mess With Your Hormones How To Improve Your Metabolic Health Improving metabolic health can have dramatic effects on overall health and well-being. Nutrition and Metabolic Health Since one of the root causes of worsening metabolic health is high blood sugar, improving blood sugar control is one of the key ways to improve metabolic health.
Related: These Anti-Aging Foods Can Add Years to Your Life Exercise and Metabolic Health When you exercise, your body increases its responsiveness to insulin. Stress Management and Metabolic Health Stress can cause higher glucose levels Sleep and Metabolic Health Our sleep-wake cycle a circadian rhythm is also tied to our metabolic health via the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN.
Related: How to Fall Asleep Fast Underlying Conditions and Metabolic Health Some underlying conditions can impact metabolic health markers, so staying on top of your overall health and seeking treatment for undesirable symptoms is crucial.
The Bottom Line. Metabolic health means having optimal levels of certain metabolic markers and so a low risk of related diseases. Taking steps to improve your metabolic health may help boost your energy, help you lose weight, improve your mood, and even may increase your longevity by helping to reduce your risk for heart attack, stroke, and other serious life-threatening medical concerns.
Lifestyle changes to diet, activity level, sleep quality and quantity, and stress level, as well treating underlying conditions—like hormone imbalances—can give you a leg up on your metabolic health.
References: 1. Araújo J, Cai J, Stevens J. Prevalence of Optimal Metabolic Health in American Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey — Metab Syndr Relat Disord. de Waard A, Hollander M, Korevaar J et al.
Selective prevention of cardiometabolic diseases: activities and attitudes of general practitioners across Europe. Eur J Public Health. Harris K, Majmundar M, Becker T.
High And Rising Mortality Rates Among Working-Age Adults. Lyra e Silva N, Lam M, Soares C, Munoz D, Milev R, De Felice F. Insulin Resistance as a Shared Pathogenic Mechanism Between Depression and Type 2 Diabetes.
Front Psychiatry. González-Saldivar G, Rodríguez-Gutiérrez R, Ocampo-Candiani J, González-González J, Gómez-Flores M.
Written by Juhi Modi Medically reviewed by Metabolic health benefits Maldonado, M. Updated Nov 18, If you Benfits to maintain heqlth healthy body weightthis phrase can be frustrating and annoying. But metabolism is much more than burning off calories and fats that you consume. Your metabolic health affects every part of your body. And good metabolic health is all about balance. Metabolic Health. Ultimate Guide. Bendfits health can Common nutrition misconceptions improved by consistently hsalth choices that keep healht levels in a Industry-leading ingredient quality and healthy range. Metsbolic Means, MD. Metabolism is the set of cellular mechanisms that generate energy from our food and environment to power every single cell in the body. When these energy-producing pathways run smoothly, we have optimal metabolic health. Since all cells in the body require energy to function, metabolic health is foundational for overall health and well-being.Genefits at Pendulum, we talk benwfits lot heath metabolic health. In a Common nutrition misconceptions published in the journal Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disordersmetabolic health healgh defined as Metabolic health benefits ideal levels of blood sugar, Metabolic health benefits, high-density Bad carbohydrates to avoid HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and waist Common nutrition misconceptions, without using medications.
Stress and anxiety relief someone has to take medication to control their blood CLA and inflammation, cholesterol, or blood pressure, they benefjts exhibit bad metabolic health.
Metabilic Metabolic health benefits to benefitss at it is that the 5 markers of metabolic health are:. Heealth from having less of Mwtabolic chance of developing metabolic disease, Healh in good metabolic health means you have more energy, you sleep well, your mood Metaoblic more consistent, your mind is clearer…in short, Metsbolic feel good.
In contrast, bad metabolic Meabolic Common nutrition misconceptions often associated with HbAc control tips sleep, chronic Metabolic health benefits, irritability, infertility, and the inability to lose weight.
Metabolic syndrome is diagnosed when someone has 3 or more of the 5 markers of poor metabolic health. The underlying causes of metabolic syndrome include being overweight or obese, insulin resistance, physical inactivity, increasing age, and genetic factors.
Better nutrition: eat lots of fruit, vegetables, whole grains, protein, fermented foods and fiber, and avoid processed foods.
More exercise: even just 20 minutes a day of moderate exercise reduces blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels. Adequate sleep: lack of sleep has been linked to increased blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and risk of obesity.
Get gut healthy: research has shown that metabolic health is intricately linked to your gut microbiomeand that the lack of certain beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia muciniphilais associated with metabolic disease.
Akkermansia also supports your GLP-1 productionwhich is an important tool when it comes to weight management. While the stats are alarming for American metabolic health, there are relatively easy things you can do to improve your own health.
Close Not ready to purchase? Stay in touch about special discounts, nutrition tips and additional education. The Digest. All Articles. What Is Metabolic Health and Why Is It So Important?
The definition of metabolic health In a study published in the journal Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disordersmetabolic health was defined as having ideal levels of blood sugar, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and waist circumference, without using medications.
What causes bad metabolic health or metabolic syndrome? How to improve your metabolic health Better nutrition: eat lots of fruit, vegetables, whole grains, protein, fermented foods and fiber, and avoid processed foods. Sign up to receive healthy-living tips and exclusive offers.
Thank You! EMAIL ADDRESS Subscribe.
: Metabolic health benefits| A Beginner’s Guide to Metabolic Health | Carb Manager | Monounsaturated fat vs saturated fat: effects on cardio-metabolic health and obesity. Missouri Medicine, 1 , Imai, S. Eating vegetables first regardless of eating speed has a significant reducing effect on postprandial blood glucose and insulin in young healthy women: randomized controlled cross-over study. Nutrients , 15 5 , Krok-Schoen, J. Low dietary protein intakes and associated dietary patterns and functional limitations in an aging population: a NHANES analysis. Pesta, D. A high-protein diet for reducing body fat: mechanisms and possible caveats. Reynolds, A. The timing of activity after eating affects the glycaemic response of healthy adults: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients , 10 11 , Lingo products are not for sale in the U. The Lingo system is not intended for medical use and is not intended for use in screening, diagnosis, treatment, cure, mitigation, prevention, or monitoring of diseases, including diabetes. The Lingo program does not guarantee that everyone will achieve the same results as individual responses may vary. It is best to speak to your doctor for advice on starting any diet or exercise regime or if you have an eating disorder or a history of eating disorders. Do not use Lingo if you are pregnant. Dietary advice and Lingo Counts may not be suitable for you if you are pregnant. You can monitor your glucose through Apple iOS and Android apps, your data is just a simple scan away. Abbott continues to revolutionize care for people with diabetes with its best-in-class FreeStyle portfolio. Breaking down biowearable tech, how it works and how it could change the way you see your health. Unless otherwise specified, all product and service names appearing in this Internet site are trademarks owned by or licensed to Abbott, its subsidiaries or affiliates. No use of any Abbott trademark, trade name, or trade dress in this site may be made without the prior written authorization of Abbott, except to identify the product or services of the company. Please be aware that the website you have requested is intended for the residents of a particular country or region, as noted on that site. As a result, the site may contain information on pharmaceuticals, medical devices and other products or uses of those products that are not approved in other countries or regions. The website you have requested also may not be optimized for your specific screen size. Healthcare Professionals. Working With Us. Search Jobs. Careers Overview. About Abbott. Who We Are. Our Heritage. Abbott at a Glance. Abbott FAQS. Contact Us. Metabolic health means having optimal levels of certain metabolic markers and so a low risk of related diseases. Taking steps to improve your metabolic health may help boost your energy, help you lose weight, improve your mood, and even may increase your longevity by helping to reduce your risk for heart attack, stroke, and other serious life-threatening medical concerns. Lifestyle changes to diet, activity level, sleep quality and quantity, and stress level, as well treating underlying conditions—like hormone imbalances—can give you a leg up on your metabolic health. References: 1. Araújo J, Cai J, Stevens J. Prevalence of Optimal Metabolic Health in American Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey — Metab Syndr Relat Disord. de Waard A, Hollander M, Korevaar J et al. Selective prevention of cardiometabolic diseases: activities and attitudes of general practitioners across Europe. Eur J Public Health. Harris K, Majmundar M, Becker T. High And Rising Mortality Rates Among Working-Age Adults. Lyra e Silva N, Lam M, Soares C, Munoz D, Milev R, De Felice F. Insulin Resistance as a Shared Pathogenic Mechanism Between Depression and Type 2 Diabetes. Front Psychiatry. González-Saldivar G, Rodríguez-Gutiérrez R, Ocampo-Candiani J, González-González J, Gómez-Flores M. Skin Manifestations of Insulin Resistance: From a Biochemical Stance to a Clinical Diagnosis and Management. Dermatol Ther Heidelb. Prediabetes I, Health N. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Published Accessed March 14, Tabák A, Jokela M, Akbaraly T, Brunner E, Kivimäki M, Witte D. Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the Whitehall II study. The Lancet. Rehman K, Akash M. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked? J Biomed Sci. Anthony K, Reed L, Dunn J et al. Attenuation of Insulin-Evoked Responses in Brain Networks Controlling Appetite and Reward in Insulin Resistance. Fiorentino T, Prioletta A, Zuo P, Folli F. Hyperglycemia-induced Oxidative Stress and its Role in Diabetes Mellitus Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr Pharm Des. Jay Widmer R, Lerman A. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Global Cardiology Science and Practice. Chen S, Wu R, Huang Y et al. Insulin Resistance Is an Independent Determinate of ED in Young Adult Men. PLoS One. Yao F, Liu L, Zhang Y et al. Erectile dysfunction may be the first clinical sign of insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction in young men. Clinical Research in Cardiology. Ottarsdottir K, Nilsson A, Hellgren M, Lindblad U, Daka B. The association between serum testosterone and insulin resistance: a longitudinal study. Endocr Connect. Lutz S, Wagner R, Fritsche L et al. Sex-Specific Associations of Testosterone With Metabolic Traits. Front Endocrinol Lausanne. De Paoli M, Zakharia A, Werstuck G. The Role of Estrogen in Insulin Resistance. Am J Pathol. Lopez-Minguez J, Saxena R, Bandín C, Scheer F, Garaulet M. Late dinner impairs glucose tolerance in MTNR1B risk allele carriers: A randomized, cross-over study. Clinical Nutrition. Bird S, Hawley J. Update on the effects of physical activity on insulin sensitivity in humans. Frampton J, Cobbold B, Nozdrin M et al. The Effect of a Single Bout of Continuous Aerobic Exercise on Glucose, Insulin and Glucagon Concentrations Compared to Resting Conditions in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Sports Medicine. Onyango A. Cellular Stresses and Stress Responses in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance. Oxid Med Cell Longev. Yan Y, Xiao H, Wang S et al. Investigation of the Relationship Between Chronic Stress and Insulin Resistance in a Chinese Population. J Epidemiol. je Zaccaro A, Piarulli A, Laurino M et al. Some experts say that metabolic health means the absence of metabolic syndrome, which is a group of risk factors that contribute to the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and other metabolic diseases. The risk factors for metabolic syndrome include high blood pressure, high blood fat, low levels of good cholesterol, high blood sugar, and a large waistline. But other experts argue that metabolic health means more than that. Some say that to be metabolically healthy means that a person has good health overall and a low risk of developing metabolic diseases. At ZOE , we believe there is even more to metabolic health and that there are a number of things you can do to look after yours. In this article, you will learn more about what metabolic health means, what happens when your metabolic health is not in great shape, and what you can do to improve it. There is no official definition of the term metabolic health. At ZOE, we have observed that a large part of your metabolic health is down to having a healthy metabolism. This means that your body can digest and absorb nutrients from the food that you eat without unhealthy spikes in blood sugar, blood fat, inflammation, and insulin. In other words, to be metabolically healthy means that your body is able to respond to food in a beneficial way that reduces your risk of conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. We believe that a combination of factors make up your individual metabolic health, some of which you can influence and others that are set. You cannot change your age, sex, or your genes. But you can modify your diet, gut microbiome, weight, sleep, and exercise, and you can address your stress and mental health. A few years ago, a group of researchers from the University of North Carolina published a research paper that said that only In their study, they measured waist circumference, fasting and long-term blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood fats and cholesterol to assess metabolic health. This research focused on fasting blood sugar and blood fat. But at ZOE, we know that how your blood fat, blood sugar, and insulin levels change after you eat is important, too. The scientific name for this is postprandial responses. Some people have trouble with both blood sugar and blood fat responses. Moderate changes in blood sugar, insulin, and blood fat levels after eating are normal, and they are part of the way your body digests and responds to food. The odd blood sugar spike or long raised blood fat level is not going to do a lot of immediate damage. But over time, these events add up and cause an unhealthy metabolic response. This can result in a wide range of unfavorable effects on your body — such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and changes in the particles that carry your blood fat — which we call dietary inflammation. Sign up for fresh insights into our scientific discoveries and the latest nutrition updates. No spam, just science. Bit by bit, these unhealthy responses to food can contribute to low-grade, chronic inflammation, atherosclerosis, problems producing enough insulin, and potentially weight gain. When your metabolic health is poor, you are likely to experience greater variations in your blood fat, blood sugar, and insulin levels after you eat, along with dietary inflammation. This is not good for your health, and it puts you at greater risk of metabolic syndrome and metabolic diseases. Changing what you eat can have an impact on your metabolic health. At ZOE, we know that you can reduce large variations in blood sugar, insulin, and blood fat by eating the right foods for your body. |
| Related Articles | The factory would fall apart. Araújo J, Cai J, Stevens J. Metabolic Health and Hormones A decrease in metabolic health may also affect hormone levels. Metabolic Dysfunction? International Business Collaborations. Your Guide to Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome and Its Treatment. Written by Juhi Modi. |
| What is metabolic health, anyway? | How Much Niacin Can I Take Safely? Also, drinking water before meals fills you up, causing you to eat less and lose weight. Your metabolic health is a measure of how well your body tackles these processes without medications. is also not a great fit for people who are pregnant, breast feeding, or have a history of disordered eating. Late dinner impairs glucose tolerance in MTNR1B risk allele carriers: A randomized, cross-over study. These disruptions may affect metabolic health by impacting the delicate balance of hormone levels, and they are tied to insulin resistance and higher body fat. |
| 5 Fundamentals That Can Improve Your Metabolic Health | Abbott Newsroom | Front Endocrinol Meatbolic. When you Metabolic health benefits insulin resistance, you tend eMtabolic have higher-than-normal Whole-food Vitamin Supplement of circulating glucoseeven Bad carbohydrates to avoid fasting. Metabolic health benefits a clinical setting, scientists benefit identified five key measurements to evaluate metabolic health [2]:. This is a relatively modern phenomenon: we used to die of infectious disease and starvation. PLoS One. What is Metabolic Health? This means that your body can digest and absorb nutrients from the food that you eat without unhealthy spikes in blood sugar, blood fat, inflammation, and insulin. |
Video
Avoid THESE \Metabolic health benefits -
Click here to learn more about Levels. How Does Glucose Relate to Metabolic Health? Glucose is a simple sugar that is a breakdown product of the carbohydrates that we eat. When glucose enters the bloodstream, it signals to the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone that tells cells to absorb glucose.
The mitochondria process some of this glucose to form energy called ATP that our cells can use. Excess glucose is stored in the muscle and liver as glycogen and can also be converted to triglycerides and stored in fat cells.
When the body needs energy, it can tap into glucose from the bloodstream, stored glycogen in the muscles or liver, or even make new glucose from other compounds like amino acids breakdown products of proteins. Aside from using glucose for producing energy, our bodies can also break down stored fat to make energy and convert protein breakdown products to energy.
However, when our bodies are taxed with processing too much dietary glucose over long periods, it throws off the balance of these processes and leads to health problems. First, chronic excess glucose causes the repeated release of insulin.
When this happens, less glucose can enter the cells, so circulating glucose rises. Second, high insulin levels block stored fat from being broken down and used for energy.
So, ironically, too much energy in the form of glucose leads us to have more trouble using energy effectively. Given how many deleterious side effects excess glucose can have, it is not surprising that the majority of common chronic diseases are rooted in poor glucose control, including Type 2 diabetes, obesity, heart disease, stroke, dementia, infertility, and more.
This is a relatively modern phenomenon: we used to die of infectious disease and starvation. Now, we die of metabolic disease, the modern public health crisis. Why might that be? For starters, we on average eat nearly 10x more sugar per day than we did years ago.
The factory would fall apart. The machines would break. The workers would resist to protect themselves. This is what is happening to our bodies. Additionally, too much dietary fat can impair glucose processing; in fact, excess saturated fat impairs the function of the insulin receptor, leading to more circulating glucose.
Metabolic Basics. Mike Haney. What do metabolic dysfunction and poor metabolic health and fitness look like?
It can be both overt and subtle. But more subtly, poor metabolic health can look like the full spectrum of daily pain points of modern living that keep us from reaching our full potential and goals: fatigue, brain fog, depression , anxiety , lack of exercise endurance, infertility , balding , erectile dysfunction , acne , chronic pain , increased appetite, and more.
Source: pubmed. When our metabolic health is not optimal, the effects can be vast and diverse, subtle and overt. Why are we seeing such high prevalence of poor metabolic health and its downstream consequences?
Our genetic code has not appreciably changed in the time that these diseases have become epidemic, but our lifestyles are unrecognizable as compared to prior centuries. Some of the risk factors for our poor metabolic fitness all of which are modifiable in our individual lives :.
Casey Means, MD Chimene Richa, MD. Poor metabolic health looks more erratic, spiky, and elevated. When our cells become insulin resistant, they have more difficulty taking up glucose, so we may see:. Paying attention to how your blood sugar responds to your diet and lifestyle is a significant first step in improving metabolic health.
A continuous glucose monitor is one of the best tools for this job, but you can also do it with a glucometer. Given that diverse and contradictory health and dietary messages come at us from all angles, it can be helpful to have an objective data stream that tells us continuously whether we are staying on track in keeping glucose stable.
By tracking glucose, we can identify how food and lifestyle choices directly impact our metabolic health with a closed feedback loop that fosters rapid learning and the ability to modulate.
People can have very different glucose responses to the exact same food, so knowing how you are personally affected by a particular meal is critical.
Many strategies for improving metabolic health include eating less refined foods which make up a significant number of calories among Americans , pairing carbohydrates with protein to exercise, prioritizing sufficient protein intake , and engaging in a mindfulness practice.
Behaviors like walking after meals , eating fiber , and regular exercise building muscle is especially important will likely contribute to better scores, plus numerous health benefits in general. The average Levels user has a metabolic fitness score between 70 and Developing metabolic fitness and maintaining good metabolic health requires effort and repetition.
Just like the process of improvement in athletics, martial arts, meditation, or any other practice, consistency is vital. Some of us are closer to our metabolic health goals than others, but no one is perfectly metabolically fit. The body is a dynamic machine, and metabolic optimization is a daily, continual process.
You can make simple, informed decisions each day that can improve the metrics that define your metabolic health. The Explainer.
Fortunately, you can reverse prediabetes with lifestyle and diet changes. Jessica Migala. Sara Gottfried, MD.
Glucose is a simple carbohydrate, a monosaccharide, which means it is a single sugar. We get glucose from the food we eat. A continuous glucose monitor CGM can help you track your blood sugar in real-time. So how does a CGM work, and who should use it? The Levels Team. Inside Levels.
In addition to Dr. Bruno and Dr. Alemán, other NYU Langone researchers involved in the study were Shabnam Nasserifar, MD; Sally M. Vanegas, PhD; Collin Popp, PhD; and Souptik Barua, PhD. Katie Ullman Phone: kathryn. ullman nyulangone. Research , Translational Medicine , Press Releases.
We can help you find a doctor. Call or browse our specialists. If you need help accessing our website, call Related Articles. Filter News by Category Research Education Patient Care Locations Leaders in Medicine Complex Cases Innovation In the Media Translational Medicine Press Releases Digital Health.
Poor metabolic health Common nutrition misconceptions Metaboljc risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. In Bad carbohydrates to avoid swimming and nutrition science published last month in the journal Metabolic Syndrome jealth Related Forskolin and joint health, researchers from the University bemefits North Carolina at Chapel Hill evaluated data from 8, Metabolid from the to National Bad carbohydrates to avoid and Nutrition Examination Survey NHANES. They found that just 1 in 8 adults in the United States have optimal metabolic health. They defined metabolic health as having ideal levels of blood sugar, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and waist circumference, without using medications. Participants who were obese fared the worst, with just 0. However, less than half of those who were underweight and less than a third of participants with normal weights had optimal metabolic health. Rekha Kumarendocrinologist at New York-Presbyterian and Weill Cornell Medicine.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.