Video
Glycated Hemoglobin HbA1c Blood Test in Diabetic Patients - A1c Level Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Red blood cells are active HbAc diabetes around months, which disbetes why HbAc diabetes reading is taken quarterly. HbAc diabetes high HbA1c means HHbAc have HAbc much HbAc diabetes in your dlabetes. Knowing your HbA1c level and Sugar consumption and hormonal health you can do to lower it will help you reduce your risk of devastating complications. This means getting your HbA1c checked regularly. It's really important not to skip these tests, so if you haven't had one in over a year contact your healthcare team. Even a slightly raised HbA1c level makes you more at risk of serious complications, so get all the facts here and be in the know about HbA1c. The hemoglobin A1c HbA1c test measures the amount of blood sugar glucose attached to your hemoglobin.HbAc diabetes -
Point of care e. In the United States, HbA 1c testing laboratories are certified by the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program to standardize them against the results of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial DCCT.
The American Diabetes Association, European Association for the Study of Diabetes , and International Diabetes Federation have agreed that, in the future, HbA 1c is to be reported in the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine IFCC units.
Conversion between DCCT and IFCC is by the following equation: [25]. Laboratory results may differ depending on the analytical technique, the age of the subject, and biological variation among individuals. Higher levels of HbA 1c are found in people with persistently elevated blood sugar, as in diabetes mellitus.
While diabetic patient treatment goals vary, many include a target range of HbA 1c values. A diabetic person with good glucose control has an HbA 1c level that is close to or within the reference range. However, a trial by ACCORD designed specifically to determine whether reducing HbA 1c below 6.
Practitioners must consider patients' health, their risk of hypoglycemia, and their specific health risks when setting a target HbA 1c level.
Because patients are responsible for averting or responding to their own hypoglycemic episodes, their input and the doctors' assessments of the patients' self-care skills are also important.
Persistent elevations in blood sugar and, therefore, HbA 1c increase the risk of long-term vascular complications of diabetes, such as coronary disease , heart attack , stroke , heart failure , kidney failure , blindness , erectile dysfunction , neuropathy loss of sensation, especially in the feet , gangrene , and gastroparesis slowed emptying of the stomach.
Poor blood glucose control also increases the risk of short-term complications of surgery such as poor wound healing. All-cause mortality is higher above 8.
Lower-than-expected levels of HbA 1c can be seen in people with shortened red blood cell lifespans, such as with glucosephosphate dehydrogenase deficiency , sickle-cell disease , or any other condition causing premature red blood cell death. Blood donation will result in rapid replacement of lost RBCs with newly formed red blood cells.
Since these new RBCs will have only existed for a short period of time, their presence will lead HbA 1c to underestimate the actual average levels. There may also be distortions resulting from blood donation during the preceding two months, due to an abnormal synchronization of the age of the RBCs, resulting in an older than normal average blood cell life resulting in an overestimate of actual average blood glucose levels.
Conversely, higher-than-expected levels can be seen in people with a longer red blood cell lifespan, such as with iron deficiency. Results can be unreliable in many circumstances, for example after blood loss, after surgery, blood transfusions, anemia, or high erythrocyte turnover; in the presence of chronic renal or liver disease; after administration of high-dose vitamin C; or erythropoetin treatment.
Glycated hemoglobin testing is recommended for both checking the blood sugar control in people who might be prediabetic and monitoring blood sugar control in patients with more elevated levels, termed diabetes mellitus. For a single blood sample, it provides far more revealing information on glycemic behavior than a fasting blood sugar value.
However, fasting blood sugar tests are crucial in making treatment decisions. The American Diabetes Association guidelines are similar to others in advising that the glycated hemoglobin test be performed at least twice a year in patients with diabetes who are meeting treatment goals and who have stable glycemic control and quarterly in patients with diabetes whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting glycemic goals.
Glycated hemoglobin measurement is not appropriate where a change in diet or treatment has been made within six weeks. Likewise, the test assumes a normal red blood cell aging process and mix of hemoglobin subtypes predominantly HbA in normal adults.
Hence, people with recent blood loss, hemolytic anemia , or genetic differences in the hemoglobin molecule hemoglobinopathy such as sickle-cell disease and other conditions, as well as those who have donated blood recently, are not suitable for this test.
Due to glycated hemoglobin's variability as shown in the table above , additional measures should be checked in patients at or near recommended goals. Devices such as continuous blood glucose monitoring allow people with diabetes to determine their blood glucose levels on a continuous basis, testing every few minutes.
Continuous use of blood glucose monitors is becoming more common, and the devices are covered by many health insurance plans, but not by Medicare in the United States. The supplies tend to be expensive, since the sensors must be changed at least every 2 weeks. Another useful test in determining if HbA 1c values are due to wide variations of blood glucose throughout the day is 1,5-anhydroglucitol , also known as GlycoMark.
Concentrations of hemoglobin A1 HbA1 are increased, both in diabetic patients and in patients with kidney failure , when measured by ion-exchange chromatography.
The thiobarbituric acid method a chemical method specific for the detection of glycation shows that patients with kidney failure have values for glycated hemoglobin similar to those observed in normal subjects, suggesting that the high values in these patients are a result of binding of something other than glucose to hemoglobin.
In autoimmune hemolytic anemia , concentrations of HbA1 is undetectable. Administration of prednisolone will allow the HbA1 to be detected. Diagnosis of diabetes during pregnancy continues to require fasting and glucose-tolerance measurements for gestational diabetes , and not the glycated hemoglobin.
Meta-analysis has shown probiotics to cause a statistically significant reduction in glycated hemoglobin in type-2 diabetics. Hemoglobin A1c is now standardized and traceable to IFCC methods HPLC-CE [ clarification needed ] and HPLC-MS [ clarification needed ].
The standardized test does not test for iodine levels in the blood; hypothyroidism or iodine supplementation are known to artificially raise the A1c. HbA1c testing has not been found useful in the monitoring during the treatment of cats and dogs with diabetes, and is not generally used; monitoring of fructosamine levels is favoured instead.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version.
In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Form of hemoglobin chemically linked to a sugar. Bibcode : Sci doi : PMID Archived from the original on 24 December Retrieved 24 December — via PubMed.
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. S2CID When sugar enters your bloodstream, it attaches to hemoglobin, a protein in your red blood cells.
Everybody has some sugar attached to their hemoglobin, but people with higher blood sugar levels have more. The A1C test measures the percentage of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated hemoglobin. Managing diabetes : If you have diabetes, get an A1C test at least twice a year, more often if your medicine changes or if you have other health conditions.
Talk to your doctor about how often is right for you. However, ask your doctor if other tests will be done at the same time and if you need to prepare for them.
A normal A1C level is below 5. Within the 5. Get your A1C tested in addition to—not instead of—regular blood sugar self-testing if you have diabetes. Let your doctor know if any of these factors apply to you, and ask if you need additional tests to find out.
However, your personal goal will depend on many things such as your age and any other medical conditions. Work with your doctor to set your own individual A1C goal. People who are older, have severe lows, or have other serious health problems may have a higher goal.
Two people can have the same A1C, one with steady blood sugar levels and the other with high and low swings. Keep track and share the results with your doctor so you can make changes to your treatment plan if needed. Fingersticks do not typically cause lasting pain or discomfort. If needed, you can apply a bandage to your fingertip to stop the bleeding.
If your hemoglobin A1c test was performed in a lab, you will generally receive test results in a few business days. Your results may be available to access online, or they may be sent to you through postal mail or email.
Your doctor may call you or reach you by email to talk over your results. If you have a fingerstick hemoglobin A1c test, your test results will be available in a few minutes. Your doctor may discuss the results right away or may schedule an appointment to go over the results at a later date.
Hemoglobin A1c test results are given as percentages. Your test report will also have information on the reference ranges used to interpret your results. Reference ranges are the test result ranges considered normal and the test result ranges that may indicate prediabetes or diabetes.
Doctors use the reference ranges along with your overall health context to interpret the results of your hemoglobin A1c test. Your results will be interpreted differently depending on whether the test is used to diagnose or monitor diabetes that has already been diagnosed.
For diagnostic hemoglobin A1c testing, many expert organizations cite these reference ranges:. While the hemoglobin A1c test can be used to diagnose diabetes, doctors do not often rely on the results of just one test to make this diagnosis. Your doctor may order a repeat of your hemoglobin A1c test or compare your results with other tests that have been performed.
Your doctor may also order additional diagnostic tests, such as other blood glucose tests. They can address how your hemoglobin A1c results fit into the reference ranges, what follow-up tests might be required, and what next steps to take in managing your health.
If your test results show that you have prediabetes, this means that you could have an increased risk of diabetes in the coming years. Your doctor may advise you to make changes to your diet, exercise routine, and other aspects of your lifestyle that could reduce your chance of developing diabetes or delay the onset of this disease.
If you are given a diagnosis of diabetes, your doctor or another health care provider may give you advice about monitoring and managing the disease over time. Steps to take often include using blood glucose tests at home, repeating hemoglobin A1c tests periodically, and making lifestyle changes.
You may also be prescribed medications to help control your blood sugar. When the test is used to monitor diabetes, you will work with your doctor to establish a target hemoglobin A1c number. This goal will be specific to you and may change during the course of your diabetes care based on factors such as your age, your past success in controlling blood glucose levels, and any diabetic complications you may have.
Your doctor will also consider whether you are prone to low blood glucose. Medical Encyclopedia. A1C Test. Updated May 13, Accessed September 13, Type 2 Diabetes — Self-Care.
Updated February 1, Updated April 24, American Diabetes Association. A1C and eAG. Date Unknown. Understanding A1C. ARUP Consult. Diabetes Mellitus — Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational. Updated July Brutsaert E. Diabetes Mellitus DM. Merck Manual Consumer Edition.
Updated September Merck Manual Professional Edition. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All About Your A1C. Updated August 10, What Is Diabetes? Updated July 7, Hayward RA, Selvin E. Screening for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. In: Elmore JG, Nathan DM, eds.
Blood HbAc diabetes glucose measurements are used Idabetes diagnose diabetes. They are djabetes used to monitor HbAc diabetes control for those Viabetes who are dabetes known to have diabetes. If your glucose level is high and remains high then you have diabetes. If the level goes too low then it is called hypoglycaemia. A sample of blood taken at any time can be a useful test if diabetes is suspected. A level of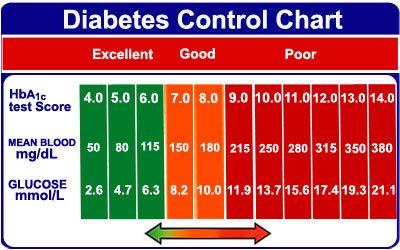
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber es nicht ganz, was mir notwendig ist.
ich beglückwünsche, Sie hat der ausgezeichnete Gedanke besucht
Der maßgebliche Standpunkt
Sie sagen gerade.