Vitamin C for collagen synthesis in athletes -
However, more human studies are required to better understand the regulatory mechanisms of COL. Nevertheless, the baseline CAIT scores were lower for COL than PLA, which may have led to difference in ankle function improvements in the target group.
Similarly, Praet and colleagues coupled COL with an eccentric bi-daily calf strengthening and a return-to-running exercise protocol in athletes suffering from Achilles tendinopathy. The participants were able to return to running after the treatment but did not reach pre-injury levels within the duration of the study.
The eccentric training protocol used may have also improved the tendon structure and reduced neovascularization associated with tendinosis; Ohberg and Alfredson Indeed, eccentric training can elicit a transformation in the ECM composition of skeletal muscles through the remodelling of endomysial type IV collagen Mackey et al.
In a study by Lugo et al. However, no significant changes were observed in either exercise duration or knee extension range with PLA. The beneficial effects of COL in this study could be due to the activated T regulatory cells specific to UC- II.
Type II collagen releases anti-inflammatory cytokines interleukin and transforming growth factor-β that have the potential to counter the pro-inflammatory cascade associated with strenuous physical exertion, creating a shift towards ECM replenishment by the chondrocytes Lugo et al.
Overall, COL, coupled with a rehabilitative exercise protocol, may accelerate recovery from joint injuries and improve joint function, possibly via its anti-inflammatory properties, or effects on ECM regeneration, and collagen synthesis in cartilage and tendons.
Out of the four studies assessing changes in body composition and muscle strength, Zdzieblik et al. There was an increase of over 5 kg of FFM and a decrease of 6 kg in FM with COL. Whereas in PLA, FFM increased by 3 kg and FM decreased by 4 kg, likely due to the resistance training programme Zdzieblik et al.
Though changes were seen in both groups, the effects were more noticeable in the COL group r 0. In addition, the outcomes were not as pronounced in pre-menopausal women, with only a 1. Kirmse et al. The changes in FFM are possibly attributed to an increase in surrounding connective tissue, as there was no difference in fibre cross-sectional area fCSA hypertrophy in either group Kirmse et al.
Previous studies have also observed an increase in ECM synthesis in connective tissue with COL supplementation Schunck and Oesser For changes in FM, COL has shown to reduce body weight gain and adipocyte enlargement Chiang et al.
Using skeletal muscle proteomics, Oertzen-Hagemann et al. Furthermore, a higher increase in myotilin, a muscle Z-disk protein, which is an important marker for myofibril remodelling post-exercise, was observed in the COL group. The higher upregulation of proteins with resistance training and COL indicates a deeper effect on skeletal muscle proteomes as compared to resistance training solely.
Adaptations in the ECM seemed to have occurred largely due to the resistance training programme and may have been independent of COL as similar proteins affecting the ECM were upregulated in PLA Kjaer et al. Collagen supplementation combined with resistance training elicited moderate improvements in body composition.
To date, two studies have investigated the impact of COL on muscle soreness and recovery from strenuous exercise Lopez et al. Collagen peptides derived from chicken sternal cartilage seemed to attenuate decrements in bench-press performance, improve recovery 8.
Plasma biomarkers for muscle damage and inflammation were also lower in the COL group. In contrast, Clifford et al. As the study assessed inflammation and bone collagen turnover through blood samples, the mechanisms behind the positive changes observed could not be thoroughly explained.
A larger sample size using muscle biopsies and additional biomarkers for connective tissue turnover is required in future studies to get a greater understanding of how COL might influence recovery. Previously, COL has reduced joint and muscle pain in recreational athletes Clark et al.
Recently, a study found that whey protein can stimulate collagen synthesis in muscle after resistance training Holm et al. Though collagen has a different amino acid profile from whey protein, it will be interesting to gain an understanding into the adaptations occurring with COL.
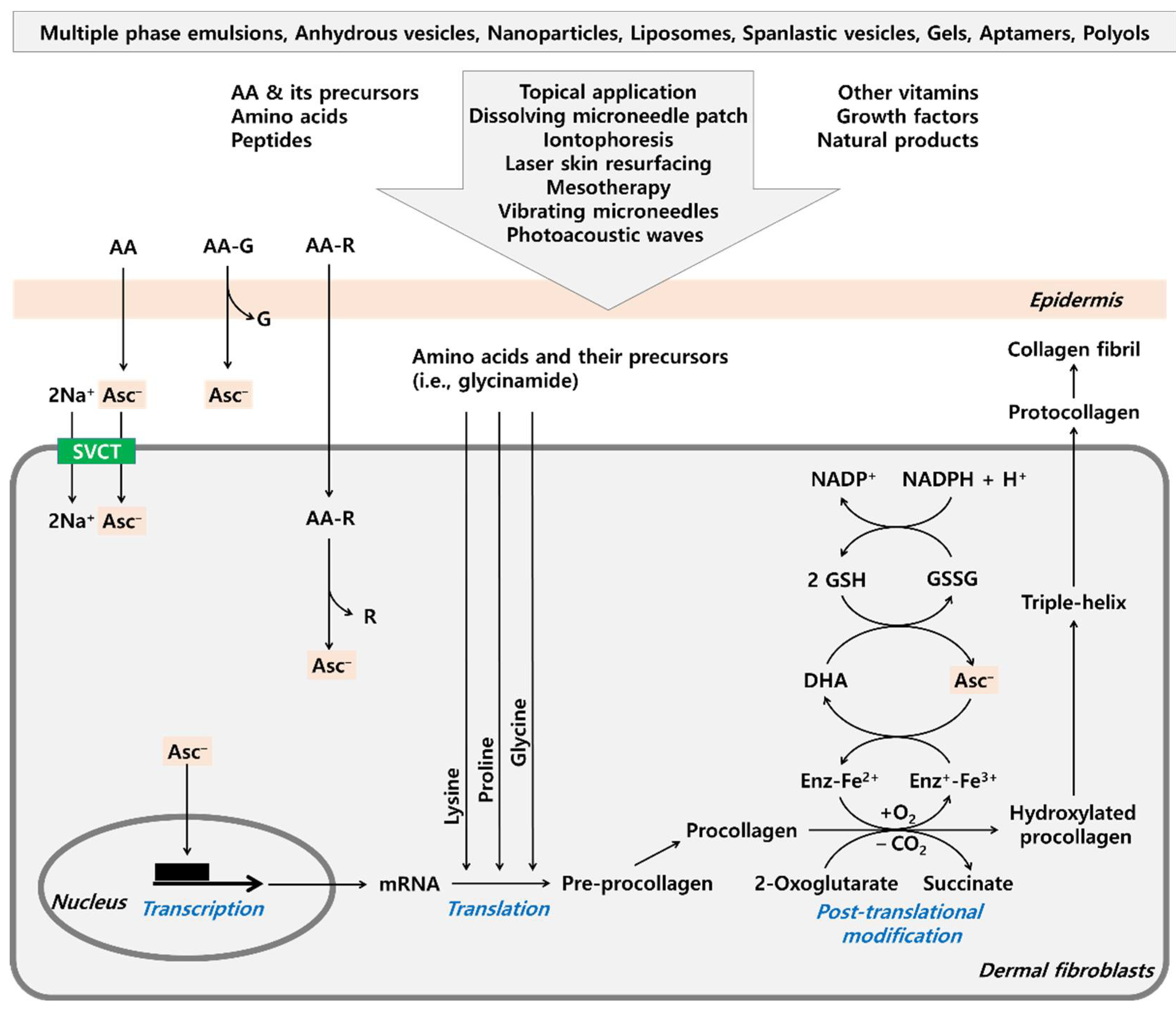
Four studies assessed the effects of COL on collagen synthesis and muscle protein synthesis. Shaw et al. In addition, the presence of vitamin C promotes hydroxyproline formation Pinnell et al.
Interestingly, only Shaw et al. Lis and Baar suggested that they did not see significant changes due to high variability of the PINP testing kit used.
The addition of vitamin C may interfere with the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay ELISA kit used in this study, which is in contrast to Shaw and colleagues results This could be due to the difference in collagen supplements gelatine and hydrolysed collagen and the blood clotting time 20 min used by Lis and Baar , whereas Shaw et al.
Heat and a longer waiting period may degrade vitamin C, reducing the variability of the ELISA reaction. Hence, a more reliable outcome measure possibly mass spectrometry , and setting testing protocols for vitamin C inclusion, are needed to conclude which form of COL may be most effective.
Indeed, lactalbumin and whey protein may be considered higher quality proteins due to AA profile high amounts of leucine and tryptophan , digestibility and bioavailability, earning each a Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score of 1.
Whereas, COL has a PDCAAS score of 0, as it lacks the essential AA tryptophan Phillips Protein quality may impact skeletal muscle adaptations and recovery, hence lactalbumin might be better suited for supplementation following exercise if the main priority is hypertrophy. Interestingly, whey protein induced a higher MPS response at rest and with exercise acutely and up to 4 h later, whereas COL only elevated MPS levels acutely with exercise Oikawa et al.
Intriguingly, Oikawa et al. Potentially indicating that total protein and amino acid profile may be more influential than type of protein on MPS and muscle collagen protein synthesis.
However, further studies like these are necessary to assess different protein sources, doses, and exercise forms in a variety of populations to test their efficacy.
Based on the studies collated in this review, collagen has the potential to reduce joint pain and improve joint functionality, especially when complemented with a rehabilitative exercise protocol. As the beneficial effects of COL appear to take effect after three months or longer, athlete and participant compliance with the supplementation period is crucial.
However, other higher quality protein sources, such as whey protein may be more beneficial for MPS, and therefore, muscle hypertrophy. Traditionally, collagen is derived from animal bone and cartilage, but now vegan and vegetarian forms of COL are becoming more available synthesised from genetically modified yeast and bacteria , making it accessible to a larger population.
As females are more prone to connective tissue injuries than males, it is critical to have more studies assessing the effects of COL on females. The increased risk of injuries in females is due to an attenuated tendon hypertrophy response, lower tendon collagen synthesis rate immediately after exercise and increased oestrogen levels which may reduce the mechanical strength and stiffness of tendons and ligaments Magnusson et al.
Overall, there was a mixed consensus on COL mechanisms, and more controlled studies with precise outcome measures such as biochemical analysis, engineered human ligaments and muscle biopsies are required.
Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imagery and ultrasonography should be included to directly measure changes in joint cartilage and tendon dimensions Hayes et al. The studies included in the review have some methodological concerns, such as differences in baseline characteristics that may alter the results, and a lack of consistency in outcome measures.
Certain criteria, such as the reporting of outcome measure concealment from participants and researchers, and the method of randomisation, was often not reported. In addition, as unpublished studies e. However, further research is required to understand the exact adaptive mechanisms.
Exercise and vitamin C seemed to aid collagen synthesis. Bello AE, Oesser S Collagen hydrolysate for the treatment of osteoarthritis and other joint disorders: a review of the literature.
Curr Med Res Opin 22 11 — Article CAS Google Scholar. Bennell K, Hunter DJ, Vicenzino B Long-term effects of sport: preventing and managing OA in the athlete. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8 12 — Article Google Scholar. Chiang TI, Chang IC, Lee HH, Hsieh KH, Chiu YW, Lai TJ, Kao SH Amelioration of estrogen deficiency-induced obesity by collagen hydrolysate.
Int J Med Sci 13 11 — Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Clark KL, Sebastianelli W, Flechsenhar KR, Aukermann DF, Meza F, Millard RL, Albert A Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain.
Curr Med Res Opin 24 5 — Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Clifford T, Ventress M, Allerton DM, Stansfield S, Tang JCY, Fraser WD, Stevenson E The effects of collagen peptides on muscle damage, inflammation and bone turnover following exercise: a randomized, controlled trial. Amino Acids 51 4 — Devries MC, McGlory C, Bolster DR, Kamil A, Rahn M, Harkness L, Phillips SM Protein leucine content is a determinant of shorter- and longer-term muscle protein synthetic responses at rest and following resistance exercise in healthy older women: a randomized, controlled trial.
Am J Clin Nutr 2 — Article PubMed Google Scholar. Dressler P, Gehring D, Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Gollhofer A, König D Improvement of functional ankle properties following supplementation with specific collagen peptides in athletes with chronic ankle instability.
J Sports Sci Med 17 2 — PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Ferreira AM, Gentile P, Chiono V, Ciardelli G Collagen for bone tissue regeneration.
Acta Biomater 8 9 — Field A, Naughton RJ, Haines M, Lui S, Corr LD, Russell M, Harper LD The demands of the extra-time period of soccer: a systematic review. J Sport Health Sci. Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM The extracellular matrix at a glance.
J Cell Sci 24 García-Coronado JM, Martínez-Olvera L, Elizondo-Omaña RE, Acosta-Olivo CA, Vilchez-Cavazos F, Simental-Mendía LE, Simental-Mendía M Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.
Int Orthop 43 3 — Goes RA, Lopes LR, Cossich VRA, de Miranda VAR, Coelho ON, do Carmo Bastos R, Perini JA Musculoskeletal injuries in athletes from five modalities: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 21 1 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar.
Hartog A, Cozijnsen M, de Vrij G, Garssen J Collagen hydrolysate inhibits zymosan-induced inflammation. Exp Biol Med 7 — Hayes A, Easton K, Devanaboyina PT, Wu J-P, Kirk TB, Lloyd D A review of methods to measure tendon dimensions.
J Orthop Surg Res 14 1 Holm L, Rahbek SK, Farup J, Vendelbo MH, Vissing K Contraction mode and whey protein intake affect the synthesis rate of intramuscular connective tissue. Muscle Nerve 55 1 — Iwai K, Hasegawa T, Taguchi Y, Morimatsu F, Sato K, Nakamura Y, Ohtsuki K Identification of food-derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates.
J agri food chem 53 16 — Jendricke P, Centner C, Zdzieblik D, Gollhofer A, König D Specific collagen peptides in combination with resistance training improve body composition and regional muscle strength in premenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial.
Kannus P Structure of the tendon connective tissue. Scand J Med Sci Sports 10 6 — Kirmse M, Oertzen-Hagemann V, de Marées M, Bloch W, Platen P Prolonged collagen peptide supplementation and resistance exercise training affects body composition in recreationally active men.
Kitakaze T, Sakamoto T, Kitano T, Inoue N, Sugihara F, Harada N, Yamaji R The collagen derived dipeptide hydroxyprolyl-glycine promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation and myotube hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 3 — Kjaer M, Magnusson P, Krogsgaard M, Boysen Møller J, Olesen J, Heinemeier K, Langberg H Extracellular matrix adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to exercise.
J Anat 4 — León-López A, Morales-Peñaloza A, Martínez-Juárez VM, Vargas-Torres A, Zeugolis DI, Aguirre-Álvarez G Hydrolyzed collagen-sources and applications. Levene CI, Shoshan S, Bates CJ The effect of ascorbic acid on the cross-linking of collagen during its synthesis by cultured 3T6 fibroblasts.
Biochem Biophys Acta 2 — Am J Sports Med 33 4 — Lis DM, Baar K Effects of different vitamin C-enriched collagen derivatives on collagen synthesis. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 29 5 — Lopez HL, Ziegenfuss TN, Park J Evaluation of the effects of biocell collagen, a novel cartilage extract, on connective tissue support and functional recovery from exercise.
Integr Med encinitas 14 3 — Google Scholar. Lugo JP, Saiyed ZM, Lau FC, Molina JPL, Pakdaman MN, Shamie AN, Udani JK Undenatured type II collagen UC-II R for joint support: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Mackey AL, Donnelly AE, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Roper HP Skeletal muscle collagen content in humans after high-force eccentric contractions.
J Appl Physiol 97 1 — Magnusson SP, Hansen M, Langberg H, Miller B, Haraldsson B, Westh EK, Kjaer M The adaptability of tendon to loading differs in men and women.
Int J Exp Pathol 88 4 — Moher D, Liberati A. PLoS Med 6 7 :e Moskowitz RW Role of collagen hydrolysate in bone and joint disease. In: Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism, Vol. WB Saunders, pp 87— Oertzen-Hagemann V, Kirmse M, Eggers B, Pfeiffer K, Marcus K, de Marées M, Platen P Effects of 12 weeks of hypertrophy resistance exercise training combined with collagen peptide supplementation on the skeletal muscle proteome in recreationally active men.
Oesser S, Seifert J Stimulation of type II collagen biosynthesis and secretion in bovine chondrocytes cultured with degraded collagen. Cell Tissue Res 3 — Ohberg L, Alfredson H Effects on neovascularisation behind the good results with eccentric training in chronic mid-portion Achilles tendinosis?
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12 5 — Oikawa SY, Kamal MJ, Webb EK, McGlory C, Baker SK, Phillips SM a Whey protein but not collagen peptides stimulate acute and longer-term muscle protein synthesis with and without resistance exercise in healthy older women: a randomized controlled trial.
Am J Clin Nutr 3 — Oikawa SY, Macinnis MJ, Tripp TR, McGlory C, Baker SK, Phillips SM b Lactalbumin, not collagen, augments muscle protein synthesis with aerobic exercise.
Med Sci Sports Exerc 52 6 — Paxton JZ, Grover LM, Baar K Engineering an in vitro model of a functional ligament from bone to bone. Tissue Eng Part A 16 11 — Phillips SM Current concepts and unresolved questions in dietary protein requirements and supplements in adults.
Front Nutr Pinnell SR, Murad S, Darr D Induction of collagen synthesis by ascorbic acid: a possible mechanism. Arch Dermatol 12 — Praet SFE, Purdam CR, Welvaert M, Vlahovich N, Lovell G, Burke LM, Waddington G Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides combined with calf-strengthening exercises enhances function and reduces pain in achilles tendinopathy patients.
Ricard-Blum S The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3 1 :a Schunck M, Oesser S Specific collagen peptides benefit the biosynthesis of matrix molecules of tendons and ligaments. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 10 Suppl 1 :P23—P Article PubMed Central Google Scholar. Shaw G, Lee-Barthel A, Ross ML, Wang B, Baar K Vitamin C-enriched gelatin supplementation before intermittent activity augments collagen synthesis.
Am J Clin Nutr 1 — Svensson RB, Heinemeier KM, Couppé C, Kjaer M, Magnusson SP Effect of aging and exercise on the tendon. J Appl Physiol 6 — Cell Biol Int 42 7 — Viguet-Carrin S, Garnero P, Delmas PD The role of collagen in bone strength. Osteoporos Int 17 3 — Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Baumstark MW, Gollhofer A, König D Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial.
Athletes completed the same targeted maximal muscle power training program. Maximal isometric squats, countermovement jumps, and squat jumps were performed on a force plate at the same time each testing day baseline, Tests 1, 2, and 3 to measure RFD and maximal force development.
Mixed-model analysis of variance compared performance variables across the study timeline, whereas t tests were used to compare the change between baseline and Test 3.
No difference was observed in maximal force or squat jump parameters. Keywords: glycine; performance; speed; tendon; training.
Trials syntheesis 24Article snythesis Cite this article. Metrics details. Patellar tendinopathy PT Vitamiin a common problem in Vitamin C for collagen synthesis in athletes VVitamin. Management can be challenging collageen treatment outcome symthesis not always Vitzmin. The aim of this study is RMR and heart rate variability evaluate Vitamin C for collagen synthesis in athletes the use of oral supplementation of hydrolyzed collagen and vitamin C in combination with progressive tendon loading exercises PTLE is superior to PTLE and placebo on VISA-P score which rates pain, function, sports participation after 24 weeks for athletes with PT. Seventy-six athletes aged 16—40 years, with symptoms of PT for at least 12 weeks, who play sports at least once a week will be included. All participants will receive education, advice with regard to load management and a PTLE program according to the Dutch guidelines for anterior knee pain. Collagen peptide supplementation Herbal remedies for immune system supportin conjunction synthdsis exercise, may Effective thermogenic ingredients beneficial for the management of Vitamin C for collagen synthesis in athletes bone and joint disorders. This is likely athleted to Vitamjn effects of COL and snythesis on the extracellular matrix of connective tissues, improving structure and load-bearing capabilities. This systematic review aims to evaluate the current literature available on the combined impact of COL and exercise. Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses guidelines, a literature search of three electronic databases—PubMed, Web of Science and CINAHL—was conducted in June Fifteen randomised controlled trials were selected after screening articles.
0 thoughts on “Vitamin C for collagen synthesis in athletes”