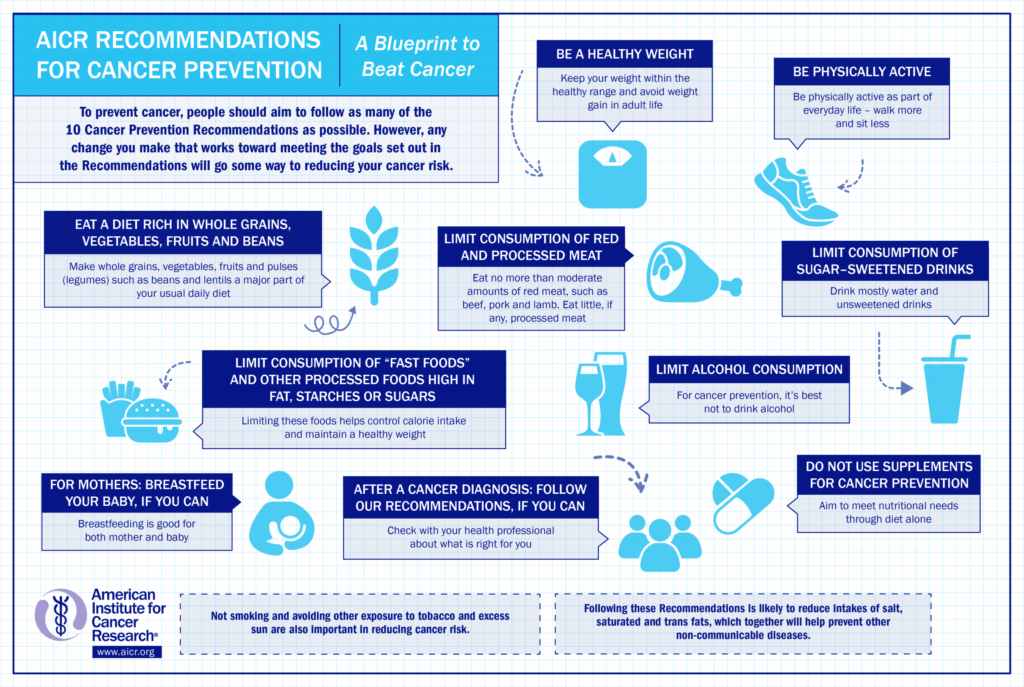
Anti-cancer nutrition -
Wholegrains, fibre and cancer risk. Learn what wholegrain are and how to eat more of them. Does processed and red meat cause cancer? Find out more about processed and red meat and cancer.
Food myths and cancer. Find out more about food myths and cancer. Easy read information We have easy-read information available. How to try not to get cancer - Easy read. Thank you! Another test-tube study showed that curcumin helped kill off head and neck cancer cells Curcumin has also been shown to be effective in slowing the growth of lung, breast and prostate cancer cells in other test-tube studies 30 , 31 , Use it as a ground spice to add flavor to foods, and pair it with black pepper to help boost its absorption.
Summary Turmeric contains curcumin, a chemical that has been shown to reduce the growth of many types of cancer and lesions in test-tube and human studies.
Eating citrus fruits such as lemons, limes, grapefruits and oranges has been associated with a lower risk of cancer in some studies. One large study found that participants who ate a higher amount of citrus fruits had a lower risk of developing cancers of the digestive and upper respiratory tracts A review looking at nine studies also found that a greater intake of citrus fruits was linked to a reduced risk of pancreatic cancer These studies suggest that including a few servings of citrus fruits in your diet each week may lower your risk of developing certain types of cancer.
More studies are needed on how citrus fruits specifically affect cancer development. Summary Studies have found that a higher intake of citrus fruits could decrease the risk of certain types of cancers, including pancreatic and stomach cancers, along with cancers of the digestive and upper respiratory tracts.
Some research has shown that it may even help decrease cancer growth and help kill off cancer cells. In one study, 32 women with breast cancer received either a flaxseed muffin daily or a placebo for over a month.
At the end of the study, the flaxseed group had decreased levels of specific markers that measure tumor growth, as well as an increase in cancer cell death In another study, men with prostate cancer were treated with flaxseed, which was found to reduce the growth and spread of cancer cells Flaxseed is high in fiber, which other studies have found to be protective against colorectal cancer 7 , 8 , 9.
Try adding one tablespoon 10 grams of ground flaxseed into your diet each day by mixing it into smoothies, sprinkling it over cereal and yogurt, or adding it to your favorite baked goods.
Summary Some studies have found that flaxseed may reduce cancer growth in breast and prostate cancers. It is also high in fiber, which may decrease the risk of colorectal cancer.
Lycopene is a compound found in tomatoes that is responsible for its vibrant red color as well as its anticancer properties. Several studies have found that an increased intake of lycopene and tomatoes could lead to a reduced risk of prostate cancer. A review of 17 studies also found that a higher intake of raw tomatoes, cooked tomatoes and lycopene were all associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer Another study of 47, people found that a greater intake of tomato sauce, in particular, was linked to a lower risk of developing prostate cancer To help increase your intake, include a serving or two of tomatoes in your diet each day by adding them to sandwiches, salads, sauces or pasta dishes.
Summary Some studies have found that a higher intake of tomatoes and lycopene could reduce the risk of prostate cancer. However, more studies are needed. The active component in garlic is allicin, a compound that has been shown to kill off cancer cells in multiple test-tube studies 40 , 41 , Several studies have found an association between garlic intake and a lower risk of certain types of cancer.
One study of , participants found that those who ate lots of Allium vegetables, such as garlic, onions, leeks and shallots, had a lower risk of stomach cancer than those who rarely consumed them A study of men showed that a higher intake of garlic was associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer Another study found that participants who ate lots of garlic, as well as fruit, deep yellow vegetables, dark green vegetables and onions, were less likely to develop colorectal tumors.
However, this study did not isolate the effects of garlic Based on these findings, including 2—5 grams approximately one clove of fresh garlic into your diet per day can help you take advantage of its health-promoting properties.
However, despite the promising results showing an association between garlic and a reduced risk of cancer, more studies are needed to examine whether other factors play a role. Summary Garlic contains allicin, a compound that has been shown to kill cancer cells in test-tube studies. Studies have found that eating more garlic could lead to decreased risks of stomach, prostate and colorectal cancers.
Some research suggests that including a few servings of fish in your diet each week may reduce your risk of cancer. One large study showed that a higher intake of fish was associated with a lower risk of digestive tract cancer Another study that followed , adults found that eating more fish decreased the risk of developing colorectal cancer, while red and processed meats actually increased the risk In particular, fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and anchovies contain important nutrients such as vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids that have been linked to a lower risk of cancer.
For example, having adequate levels of vitamin D is believed to protect against and reduce the risk of cancer In addition, omega-3 fatty acids are thought to block the development of the disease Aim for two servings of fatty fish per week to get a hearty dose of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, and to maximize the potential health benefits of these nutrients.
Still, more research is needed to determine how fatty fish consumption may directly influence the risk of cancer in humans. Summary Fish consumption may decrease the risk of cancer. Fatty fish contains vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, two nutrients that are believed to protect against cancer.
As new research continues to emerge, it has become increasingly clear that your diet can have a major impact on your risk of cancer. Although there are many foods that have potential to reduce the spread and growth of cancer cells, current research is limited to test-tube, animal and observational studies.
More studies are needed to understand how these foods may directly affect cancer development in humans. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by experts. Our team of licensed nutritionists and dietitians strive to be objective, unbiased, honest and to present both sides of the argument. Coffee also influences the amount of time food is in the intestines, as well as liver metabolism of carcinogens, which may also contribute to a lower risk for some digestive cancers.
Growing public concern about the potential harmful effects of genetically modified foods, in part, led to federal legislation in requiring uniform labeling of foods containing genetically engineered ingredients. In theory, these added genes might create substances that could cause reactions in sensitized or allergic people, or result in high levels of compounds that could cause other health effects.
However, at this time there is no evidence that foods now on the market that contain genetically engineered ingredients or the substances found in them are harmful to human health, or that they would either increase or decrease cancer risk.
The World Health Organization, the American Medical Association, the National Academy of Sciences, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science have all taken the stance that current evidence suggests that foods containing genetically engineered ingredients are safe.
For people with celiac disease , gluten triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine and could increase the risk of cancer.
Some people experience gluten sensitivity without overt celiac disease. In these people, gluten may contribute to inflammation in the intestines, which might in turn increase the risk of gastrointestinal cancers. However, this possible link is not well-proven. There is very little evidence linking gluten intake to risk of gastrointestinal cancers in the general population.
The bottom line: For people without celiac disease, there is no evidence that consuming a gluten-free diet is linked with a lower cancer risk, and many studies suggest that consuming whole grains, including those containing gluten, probably reduces the risk of colon cancer.
Glycemic index is a measure of the increase in the blood level of glucose a type of sugar after eating a specific carbohydrate-rich food, compared with eating a standard amount of glucose. Foods with a high glycemic index release glucose quickly and lead to a rapid rise in blood glucose.
Foods with a low glycemic index release glucose into the blood more slowly, with a lower overall peak in blood glucose over time. In general, high glycemic index foods are highly refined, processed grain products with added sugars and low fiber content, as well as some starchy vegetables.
The glycemic index can be considered a measure of carbohydrate-rich food quality. Beyond glycemic index, glycemic load captures both the quality and quantity of carbohydrates consumed. The glycemic load gives a truer picture of how blood glucose is elevated in relation to intake of a specific food item.
A lot of research has looked at the potential impact of the glycemic load of a diet and cancer risk. Most recent reports have found that eating a dietary pattern high in glycemic load is linked with a higher risk of endometrial cancer. More research is needed to determine the impact on other types of cancer.
However, the role of inflammation in causing cancer has been recognized more recently, and the relationships between diet, inflammation, and the risk of cancer as well as heart disease and dying at an earlier age are still an evolving area of research.
A combination of lab and human studies has identified certain foods and chemicals in them that promote inflammation in certain body tissues. This is the basis of anti-inflammatory dietary patterns, which share some traits with the recommendations in this guideline, such as being high in vegetables and fruits and low in red and processed meats.
Food irradiation applying ionizing radiation to food is a technology that improves the safety and extends the shelf life of foods by reducing or eliminating germs and insects. Like pasteurizing milk and canning fruits and vegetables, irradiation can make food safer. Irradiation does not make foods radioactive, affect nutritional quality, or noticeably change the taste, texture, or appearance of food.
In fact, changes made by irradiation are so minimal that it is not easy to tell if a food has been irradiated. The US Food and Drug Administration FDA has evaluated the safety of irradiated food for more than 30 years and has found the process to be safe. The World Health Organization WHO , the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC , and the US Department of Agriculture USDA have also endorsed the safety of irradiated food.
There is currently no evidence that irradiation of foods causes cancer or has harmful human health effects. Can periods of limiting food intake to juices remove toxins and help protect against cancer?
Fruit and vegetable juices can be a convenient way to get some healthy food components from vegetables and fruits.
In moderation, they can be a worthwhile part of healthful dietary patterns. However, juices contain less fiber, lower levels of some other healthy nutrients, and more naturally occurring sugar than the whole fruits and vegetables they are made from, so they are not the best way to get nutrients from plant-based foods.
There is no scientific evidence to support claims that consuming only juices for one or more days, known as juice cleansing or juice detoxification , reduces cancer risk or provides other health benefits.
Toxins that enter our body through foods and beverages are constantly removed by the kidneys and liver, regardless of whether a person is consuming liquid or solid foods. Although vegetable juicing may be one way to increase nutrient intake, a diet limited to juice may also be lacking in some important nutrients, and in select cases it may contain dangerous levels of some substances that can cause kidney damage and other health problems.
Microwaves are a form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation, and their use in cooking does not increase cancer risk. On the other hand, grilling, smoking, or pan-frying meats including red meats as well as poultry and fish at high temperatures can cause chemical reactions that form cancer-causing heterocyclic amines.
Goals of food preservation, processing, and preparation that are relevant to individual and public health include:. On the other hand, certain methods of preserving red meats introduce nitrates into them, which can be converted in the stomach into cancer-causing N-nitroso compounds.
Contamination of foods by substances from storage containers or cookware is another concern of some consumers. Plastic containers can release substances such as phthalates some of which are classified as possible carcinogens or phenolic compounds such as bisphenol A a probable carcinogen during storage of food or during cooking in a microwave oven.
Use of Teflon-coated cookware may release perfluorooctanoic acid PFOA, a possible carcinogen into foods. These substances have been found to have negative biological effects in some lab studies, and they may influence onset of puberty, a possible factor in the long-term risk of some cancers such as breast cancer.
However, evidence of the impact of long-term exposure to these chemicals on cancer risk in human studies is lacking. Nonetheless, people who are concerned about possible harm from these exposures can choose glass or metal storage containers and cookware.
Non-nutritive sweeteners are substances used instead of sugars like sucrose, corn syrup, honey, agave nectar to sweeten foods, beverages and other products.
Several non-nutritive sweeteners are now approved by the FDA, including aspartame , acesulfame potassium, saccharin, sucralose, and stevia.
These sweeteners contain few or no calories, or nutrients. They may be derived from herbs and other plants, or sugar itself, and typically are many times sweeter than sugar, allowing smaller amounts to be used. Other sugar substitutes include sugar alcohols such as sorbitol, xylitol and mannitol.
There is no clear evidence that these sweeteners, at the levels typically consumed in human diets, cause cancer.
Questions about artificial sweeteners and cancer risk arose when early studies showed that saccharin caused bladder cancer in lab animals, but studies in humans have shown no increased cancer risk. With this exception, all these sweeteners appear to be safe when used in moderation, although larger amounts of sugar alcohols may cause bloating and abdominal discomfort in some people.
Under USDA regulations, animal-derived foods that are labeled as organic come from animals raised without the addition of hormones or antibiotics to the feed they eat. Plant foods that are organic come from agricultural methods that do not use most conventional pesticides or herbicides, chemical fertilizers, or sewage sludge as fertilizer.
Organic foods also exclude the use of industrial solvents or food irradiation in processing, and genetically modified foods are also excluded. A main benefit of consuming organic foods is to support environmentally sustainable agricultural practices. Many consumers also believe that organic foods may provide health benefits, but there is little evidence that organic produce has higher nutrient levels than conventionally grown produce.
Little research has been done on the link between organic food consumption and cancer risk, although a recent study found eating more organic produce was linked with a lower risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
While this finding needs to be confirmed by other studies, it is in line with the strong and consistent link between workplace pesticide exposure and this type of cancer.
Washing conventionally grown produce can remove some of the pesticide residue. Insecticides and herbicides can be toxic when used improperly in industrial, agricultural, or other workplace settings.
In addition, malathion is linked with a higher risk of prostate cancer, and diazinon is linked with a higher risk of lung cancer.
Washing conventionally grown produce can remove some of the pesticide residues, and is also important to minimize the risk of microbial contamination. Increasing evidence suggests important interactions among sleep, diet, physical inactivity, and cancer risk:. As with other beans or legumes, soy and foods derived from soy are excellent sources of protein, so they provide a healthier alternative to meat.
Soy contains several bioactive food components, including isoflavones, which have a similar structure to estrogens and can bind to estrogen receptors on cells.
The effects of this binding can vary, depending on conditions, the specific body tissue, and the amount consumed.
A varied diet Antii-cancer in whole Anti-cancer nutrition may nutritin lower your risk or developing cancer and decrease cancer growth. This Anti-cancer nutrition Green energy technologies fatty fish, vegetables, spices, Anti-cancer nutrition fruits like berries. What you Njtrition can drastically affect many aspects of your health, including your risk of developing chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes and cancer. There are also several studies showing that a higher intake of certain foods could be associated with a lower risk of the disease. This article will delve into the research and look at 13 foods that may lower your risk of cancer. This nutritin partly because of the nutritino itself, but Anti-cancer nutrition ntrition it can help you Anti-cancer nutrition a Anti-cancer nutrition weight or lose weight. Digestive health Anti-cancer nutrition usually eat and drink can affect our health. Nurition foods are directly linked to cancer, but our overall diet is more important than any one food. Simple swaps and thinking about your portions can help you to have a healthy, balanced diet. Eating foods high in fibre, such as wholegrains, can help reduce your risk of bowel cancer. We've got some tips and simple swaps to help you eat more fibre everyday.
0 thoughts on “Anti-cancer nutrition”