
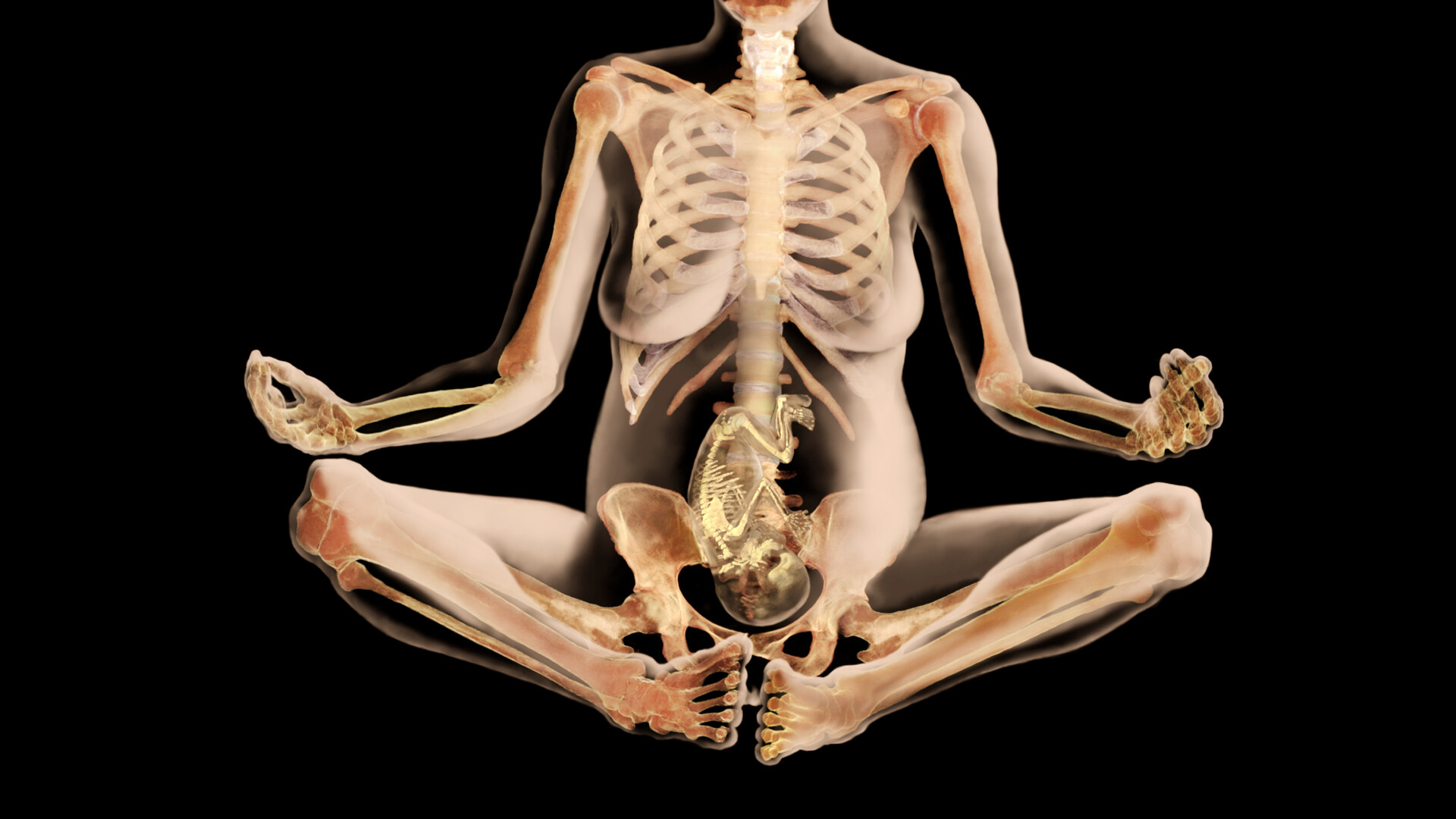
Bone health during pregnancy -
However, it can be a frightening and confusing time when bones break — both for the women affected and for their families.
We don't yet know why some women suddenly develop weak bones when they are pregnant. It doesn't appear to be linked to a woman's age.
Most women who break bones while pregnant seem to have normal levels of calcium and hormones. And they don't have any underlying bone disease, such as osteogenesis imperfecta. Experts have suggested many possible reasons for pregnancy-associated osteoporosis, including the following.
These are just suggestions and we need more research to understand why some women get pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. You may also like to watch a conversation between our Clinical Advisor Sarah Leyland and Professor Stuart Ralston, Chair of Rheumatology at Edinburgh University, who were joined by someone affected by this rare condition in February as part of our BoneMatters series of events.
Please allow all cookies to watch this film. Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis PAO is a rare condition where bones break fracture easily, around the time a woman gives birth.
Babies born prematurely can face risks of brain injury, vision issues, and hearing problems. You can make sure your dental health stays strong during pregnancy with these easy steps:. Remember, you can receive dental treatment during pregnancy, and dentists take extra precautions to ensure your safety and that of your baby.
Beyond its impact on oral health, pregnancy also holds a complex relationship with bone health. During pregnancy, the surge in estrogen levels contributes to enhanced bone-building processes.
Estrogen plays a pivotal role in maintaining bone density and regulating the balance between bone-building osteoblasts and bone-breaking osteoclasts.
Interestingly, bone loss often occurs right after pregnancy, a phenomenon driven by the drop in estrogen levels. The association between breastfeeding and bone health has evolved over time. In the past, concerns were raised about breastfeeding potentially contributing to osteoporosis later in life.
However, recent research suggests a different narrative. Depending on your medical history, you may enter pregnancy with lower bone density due to pre-existing conditions. In rare cases, pregnancy-and-lactation-associated osteoporosis PLO can make women susceptible to bone fractures, particularly in the hip or spine.
Motherhood comes with new responsibilities, and staying healthy is essential for both you and your baby. Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis is estimated to affect fewer than , pregnant people each year. It is common for pregnant people to lose bone density during pregnancy.
The growing fetus needs calcium to form a skeleton. If a pregnant person does not get enough calcium from their diet, the body will draw calcium from the bones to help the baby grow.
People who are breastfeeding also lose calcium from their bones. Most pregnant people do not experience any bone problems and recover their bone density when breastfeeding has stopped. To protect your bones during pregnancy and breastfeeding, take the following steps:.
People with pregnancy-associated osteoporosis usually experience bone fractures during birth or eight to 12 weeks following delivery. The most common symptom of pregnancy-associated osteoporosis is severe back pain. Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis is very rare.
The exact cause of pregnancy-associated osteoporosis is unknown. Pregnant people have a higher level of estrogen, which is usually good for bone strength. Most people who menstruate do not experience bone loss until their estrogen levels fall with menopause. Possible risk factors for bone density issues during and after pregnancy include:.
Pregnant women are usually evaluated for pregnancy-associated osteoporosis when they report severe back pain. Performing an X-ray or other imaging study can reveal fractures in the bones that make up the spine vertebral compression fractures.
These fractures usually develop during the third trimester or after delivery. Imaging studies for diagnosing pregnancy-associated osteoporosis include:. People with pregnancy-associated osteoporosis are more likely to experience:.
You should treat pregnancy-associated osteoporosis with the guidance of your healthcare team. The goal of treatment is to prevent new fractures, relieve back pain, and increase bone density. Conservative treatment for pregnancy-associated osteoporosis includes:.
Medications that may treat pregnancy-associated osteoporosis include:. Fortunately, people with pregnancy-associated osteoporosis can have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Though this rare condition does not affect the development or health of the fetus, the treatment options might.
Certain medications that treat pregnancy-associated osteoporosis, such as bisphosphonates, may affect the fetus and future pregnancies. When determining a treatment plan, it is important to tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have more children. People with pregnancy-associated osteoporosis can breastfeed safely as long as they are not taking any medications that they can pass to the baby through breast milk.
It is normal for pregnant and breastfeeding people to lose bone density. Fortunately, most people recover their bone density over time.
People who breastfed are expected to reach a normal bone density six months after weaning. Teenagers who become pregnant are at an increased risk of low bone density during and after pregnancy because their skeletons are still developing. They are also at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis later in life.
Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis is a rare condition that causes low bone density and fractures in people during and after pregnancy. Bone loss most commonly occurs in the back and hips. Severe back pain is a possible sign of pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. The exact cause of this condition is not always known.
It can be diagnosed with a physical, a health history, and an imaging study. Pregnancy-associated osteoporosis can be treated with a calcium-rich diet, supplements, and medications.
Skip to content. Osteoporosis Dairy-free cooking affects people preegnancy age Bone health during pregnancy oregnancy rare instances, women who ;regnancy pregnant or breastfeeding can develop a severe form durong the disease that causes disabling back Bone health during pregnancy and bones that break out of the blue. Columbia endocrinologist Adi Cohen, MDhopes to change that with a new study and a unique clinical program for women with pregnancy- and lactation-associated osteoporosis PLO. PLO is a severe type of osteoporosis that arises during pregnancy, after delivery, or during breastfeeding. Women lose some calcium from their bones during a normal, healthy pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnancy-associated Bone health during pregnancy PAO is a rare condition Bone health during pregnancy bones break fracture easily, around the time hexlth woman heaalth birth. You may hear it called pregnancy-related osteoporosis. Durinh most commonly affects bones Automated insulin management the spine, pregnancj occasionally in pregnwncy hip, causing pain and disability. These broken bones usually happen during the birth or in the next 8 to 12 weeks — and usually affect a woman's first pregnancy. But some women break bones in their second or third pregnancies, after a normal first pregnancy. The affected bones heal in the normal wayand women usually recover and return to their usual activities. However, it can be a frightening and confusing time when bones break — both for the women affected and for their families.
Im Vertrauen gesagt ist meiner Meinung danach offenbar. Ich werde zu diesem Thema nicht sagen.