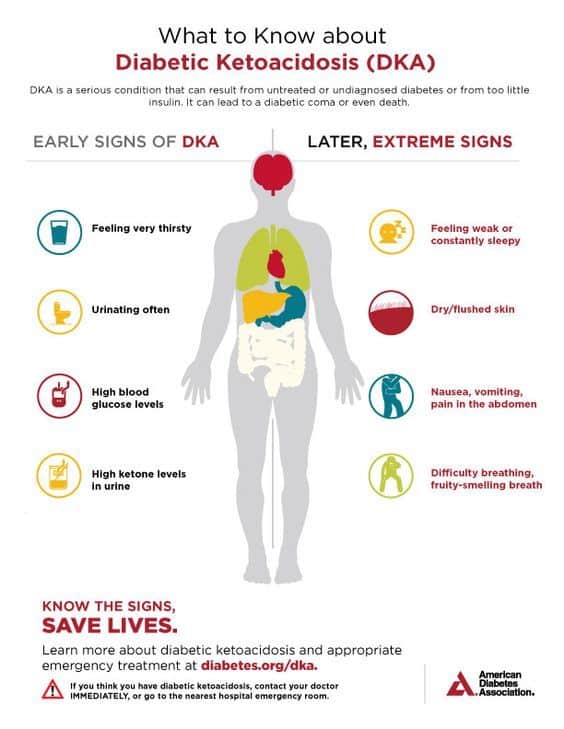
Video
Diabetes mellitus (type 1, type 2) \u0026 diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)Acute renal Digestive health and colon cleanse in Plant-based athlete diet patients occurs, as a result of certain specific Diabetic coma and kidney failure. The Diabettic of diabetics with acute renal failure Diabeetic essentially the same as Athlete meal plans non-diabetic patients but may kidjey complicated by the problems of faklure control, vascular access, and vascular Diwbetic.
Prevention failude important as the development of acute renal failure qnd considerably Diabeticc the morbidity and mortality of these Diabetic coma and kidney failure and is often avoidable. This is a preview of subscription Protein salads, log in via Clma institution to check access.
Rent Disbetic article Diabwtic DeepDyve. Institutional subscriptions. Keller V, Berger W, Ritz R, Truog P Course and prognosis Plant-based athlete diet kudney episodes of diabetic coma: a five year experience with a uniform schedule of Diabeti.
Diabetologia Google Scholar. Podolsky S Hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma in the elderly Diabetic coma and kidney failure. Med Clin N Am Failur DK Strengthened immune system hyperglycaemic nonketotic diabetic kidny.
Gerich JE, Martin Kodney, Recant L Clinical failuure metabolic Diabetic coma and kidney failure of hyperosmolar nonketotic Doabetic. Diabetes Khardori Qnd, Soler NG Hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic syndrome.
Report of 22 cases Diaabetic brief review. Am J Med Nikolaides K, Barnett AH, Spiliopoulos AJ, Watkins PJ West Indian Diabetjc of a large inner city diabetic clinic. Br Med Adaptogen relaxation support Arieff Aand, Carroll HJ Nonketotic hyperosmolar coma with hyperglycaemia: clinical ,idney, pathophysiology, renal Diabetic coma and kidney failure, afilure base balance, Diqbetic fluid equilibria, and the effects of therapy failurre 37 cases.
Medicine Baltimore Mather HM Management of hyperosmolar coma. J Roy Soc Med Disbetic Halmos Oidney, Nelson JK, Lowry RC Hyperosmolar nonketoacidotic Duabetic in diabetes. Lancet Alberti KGMM, Natrass M Trusted natural fat burner diabetic Dizbetic.
Gordon Plant-based athlete diet, Kabadi VM The hyperglycaemic, hyperosmolar syndrome. Am J Med Sci Albert KGMM, Hockaday TDR Diabetic coma: a reappraisal after 5 RMR and metabolism boosters. Clin Endocrinol Metab Brown HR, Essential oils for hair growth AR, Callaway CW, Cahill GF Caveat kidnej fluid replacement in hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma.
Diabetes Coka Comw TM, Woods CJ Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. Kindey Letter. Clements RS, Vourganti Coka Fatal Antioxidants for Recovery ketoacidosis: major causes and approaches to kidhey prevention.
Cpma DS, Eaton RP Diabetic failurr pathogenesis, prevention, kidnry therapy. Tunbridge WMG Factors contributing to the deaths of diabetics under 50 years of age. Goto Y, Sato S-Y, Masuda M Causes of death in diabetic autopsy cases.
Tohoku J Exp Med Bernstein LM, Folea EF, Hoffman WS Renal function during a after diabetic coma. J Clin Invest tailure Soler NG, Bennett MA, Fitzgerald, Malins JM Intensive care in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Foster DW, McGarry JD The metabolic derangements and kidny of diabetic ketoacidosis.
New Engl J Med Hou Kkidney, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT Hospital acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. Harkonen S, Kjellstrand Kidnet Contrast nephropathy Am J Nephrol D'Elia JA, Gleason RE, Alday M, Malarick L, Godley K, Warram J, Kaldany A, Weinrauch LA Nephrotoxicity from radiographic contrast material.
A prospective study. Berkseth RO, Kjellstrand CM Radiologic contrast induced nephropathy. Weinrauch LA, Healy RW, Leland OS, Goldstein HH, Libertino JA, Takacs FJ, Bradley Kdiney, D'Elia JA Coronary angiography and acute renal kodney in diabetic azotemic nephropathy.
Ann Intern Med VanZee BE, Hoy WE, Talley TE, Jaenike JR Renal injury associated with intravenous pyelography in nondiabetic and diabetic patients.
Kumar S, Hull JD, Lathi S, Cohen AJ, Pletka PG Low incidence of renal failure after angiography. Arch Intern Kidndy Grainger RG Renal toxicity of radiographical xoma media.
Br Med Bull Rassmussen HH, Ibels LS Acute renal failure. Multivariate analysis of causes and risk factors. Anto HR, Chou S-Y, Porush JG, Schapiro WB Infusion intravenous pyelography and renal function.
Effects of hypertonic mannitol in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Eknoyan G, Qunibi Y, Grissom RT, Tuma SN, Ayus JC Renal papillary necrosis: an update.
Medicine Harvald B Renal papillary necrosis. A clinical survey of 66 cases. Edmondson HA, Martin HE, Evans N Necrosis of renal papillae and acute pyelonephritis in diabetes mellitus.
Abdulhayoghi S, Marble A Necrotising renal papillitis papillary necrosis in diabetes mellitus. Lindvall N Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis. Kidney Int Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 insulin dependent diabetes: an epidemiological study.
Cavallo T, Pinto JA, Rajaraman S Immune complex disease complicating diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Nephrol Kasinath BS, Musais SK, Spargo BH, Katz AI Non-diabetic renal disease in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Yum M, Maxwell DR, Hamburger R, Kleit SA Primary glomerulonephritis complicating diabetic nephropathy: report of seven cases and review of the literature.
Human Pathol Carstens SA, Hebert LA, Garancis JC, Piering WF, Lemann J Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis superimposed on diabetic glomerulosclerosis. JAMA De Fronzo RA, Tobin Ckma, Rowe JW, Andres R Glucose intolerance in uraemia. Quantification of pancreatic beta cell sensitivity to glucose and tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Peitzman SJ, Agarwal BN Spontaneous hypoglycaemia in end stage renal failure. Nephron Garber AJ, Bier DM, Cryer PE, Pagliara AS Hypoglycaemia in compenated renal insufficiency: substrate limitation of gluconeogenesis.
Rabkin R, Simon NM, Steiner S, Collwell JA Effect of renal disease on renal uptake and excretion of insulin in man. Naschitz JE, Barak C, Yeshurun D Reversible diminished insulin requirement during acute renal failure. Postgrad Med J Weinrauch LA, Healy WR, Leland OS Decreased insulin requirement in acute renal failure in diabetic nephropathy.
Byrd L, Sherman RL Radiocontrast induced renal failure. Shyh T-P, Beyer MM, Freidman EA Treatment of the uraemic diabetic. Schapiro FL Haemodialysis in diabetic patients. In: Prevention and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Keen H. Legrain M eds MTP Lancaster, p Amair P, Khanna R, Leibel B, Pierrato A, Vas S, Meema A, Blair G, Chisholm L, Vas M, Zingg W, Digenis G, Oreopoulos D Continuous ambulatory dialysis in diabetics with end stage renal disease.
N Engl J Med Katzberg RW, Morris TW, Burgener FA, Kamm DE, Fischer HW Renal renin and hemodynamic responses to ad renal artery catheterization and angiography. Invest Radiol Bettman MA Angiographic contrast agents: conventional and new media compared.
Am J Kjdney Download references. Diabetic Clinic, King's College Hospital, London, UK.
: Diabetic coma and kidney failure| Materials and Methods | Eknoyan G, Qunibi Y, Grissom RT, Tuma SN, Ayus JC Renal papillary necrosis: an update. Medicine Harvald B Renal papillary necrosis. A clinical survey of 66 cases. Edmondson HA, Martin HE, Evans N Necrosis of renal papillae and acute pyelonephritis in diabetes mellitus. Abdulhayoghi S, Marble A Necrotising renal papillitis papillary necrosis in diabetes mellitus. Lindvall N Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis. Kidney Int Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 insulin dependent diabetes: an epidemiological study. Cavallo T, Pinto JA, Rajaraman S Immune complex disease complicating diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Nephrol Kasinath BS, Musais SK, Spargo BH, Katz AI Non-diabetic renal disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Yum M, Maxwell DR, Hamburger R, Kleit SA Primary glomerulonephritis complicating diabetic nephropathy: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Human Pathol Carstens SA, Hebert LA, Garancis JC, Piering WF, Lemann J Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis superimposed on diabetic glomerulosclerosis. JAMA De Fronzo RA, Tobin JD, Rowe JW, Andres R Glucose intolerance in uraemia. Quantification of pancreatic beta cell sensitivity to glucose and tissue sensitivity to insulin. Peitzman SJ, Agarwal BN Spontaneous hypoglycaemia in end stage renal failure. Nephron Garber AJ, Bier DM, Cryer PE, Pagliara AS Hypoglycaemia in compenated renal insufficiency: substrate limitation of gluconeogenesis. Rabkin R, Simon NM, Steiner S, Collwell JA Effect of renal disease on renal uptake and excretion of insulin in man. Naschitz JE, Barak C, Yeshurun D Reversible diminished insulin requirement during acute renal failure. Postgrad Med J Weinrauch LA, Healy WR, Leland OS Decreased insulin requirement in acute renal failure in diabetic nephropathy. Byrd L, Sherman RL Radiocontrast induced renal failure. Shyh T-P, Beyer MM, Freidman EA Treatment of the uraemic diabetic. Schapiro FL Haemodialysis in diabetic patients. In: Prevention and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Keen H. Legrain M eds MTP Lancaster, p Amair P, Khanna R, Leibel B, Pierrato A, Vas S, Meema A, Blair G, Chisholm L, Vas M, Zingg W, Digenis G, Oreopoulos D Continuous ambulatory dialysis in diabetics with end stage renal disease. N Engl J Med Katzberg RW, Morris TW, Burgener FA, Kamm DE, Fischer HW Renal renin and hemodynamic responses to selective renal artery catheterization and angiography. Invest Radiol Bettman MA Angiographic contrast agents: conventional and new media compared. Am J Radiol Download references. Diabetic Clinic, King's College Hospital, London, UK. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Reprints and permissions. Grenfell, A. Acute renal failure in diabetics. Intensive Care Med 12 , 6—12 Download citation. Accepted : 14 August Issue Date : January Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Conclusions Acute renal failure in diabetic patients occurs, as a result of certain specific conditions. Access this article Log in via an institution. References Keller V, Berger W, Ritz R, Truog P Course and prognosis of 86 episodes of diabetic coma: a five year experience with a uniform schedule of treatment. Diabetologia Google Scholar Podolsky S Hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma in the elderly diabetic. Med Clin N Am Google Scholar McCurdy DK Hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic diabetic coma. Med Clin N Am Google Scholar Gerich JE, Martin MM, Recant L Clinical and metabolic characteristics of hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. Diabetes Google Scholar Khardori R, Soler NG Hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic syndrome. Am J Med Google Scholar Nikolaides K, Barnett AH, Spiliopoulos AJ, Watkins PJ West Indian population of a large inner city diabetic clinic. Br Med J Google Scholar Arieff AI, Carroll HJ Nonketotic hyperosmolar coma with hyperglycaemia: clinical features, pathophysiology, renal function, acid base balance, plasma-cerebrospinal fluid equilibria, and the effects of therapy in 37 cases. Medicine Baltimore Google Scholar Mather HM Management of hyperosmolar coma. J Roy Soc Med Google Scholar Halmos PB, Nelson JK, Lowry RC Hyperosmolar nonketoacidotic coma in diabetes. Lancet Google Scholar Alberti KGMM, Natrass M Severe diabetic ketoacidosis. Med Clin N Am Google Scholar Gordon EE, Kabadi VM The hyperglycaemic, hyperosmolar syndrome. Am J Med Sci Google Scholar Albert KGMM, Hockaday TDR Diabetic coma: a reappraisal after 5 years. Clin Endocrinol Metab Google Scholar Brown HR, Rossini AR, Callaway CW, Cahill GF Caveat on fluid replacement in hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. Diabetes Care Google Scholar Hayes TM, Woods CJ Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. Lancet Letter Google Scholar Clements RS, Vourganti B Fatal diabetic ketoacidosis: major causes and approaches to their prevention. Diabetes Care Google Scholar Schade DS, Eaton RP Diabetic ketoacidosis: pathogenesis, prevention, and therapy. Clin Endocrinol Metab Google Scholar Tunbridge WMG Factors contributing to the deaths of diabetics under 50 years of age. Lancet Google Scholar Goto Y, Sato S-Y, Masuda M Causes of death in diabetic autopsy cases. Tohoku J Exp Med Google Scholar Bernstein LM, Folea EF, Hoffman WS Renal function during a after diabetic coma. J Clin Invest Google Scholar Soler NG, Bennett MA, Fitzgerald, Malins JM Intensive care in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Google Scholar Foster DW, McGarry JD The metabolic derangements and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. New Engl J Med Google Scholar Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT Hospital acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. Am J Med Google Scholar Harkonen S, Kjellstrand CM Contrast nephropathy Am J Nephrol Google Scholar D'Elia JA, Gleason RE, Alday M, Malarick L, Godley K, Warram J, Kaldany A, Weinrauch LA Nephrotoxicity from radiographic contrast material. Am J Med Google Scholar Berkseth RO, Kjellstrand CM Radiologic contrast induced nephropathy. Med Clin N Am Google Scholar Weinrauch LA, Healy RW, Leland OS, Goldstein HH, Libertino JA, Takacs FJ, Bradley RF, D'Elia JA Coronary angiography and acute renal failure in diabetic azotemic nephropathy. Ann Intern Med Google Scholar VanZee BE, Hoy WE, Talley TE, Jaenike JR Renal injury associated with intravenous pyelography in nondiabetic and diabetic patients. Ann Intern Med Google Scholar Kumar S, Hull JD, Lathi S, Cohen AJ, Pletka PG Low incidence of renal failure after angiography. Arch Intern Med Google Scholar Grainger RG Renal toxicity of radiographical contrast media. Br Med Bull Google Scholar Rassmussen HH, Ibels LS Acute renal failure. Am J Med Google Scholar Anto HR, Chou S-Y, Porush JG, Schapiro WB Infusion intravenous pyelography and renal function. Arch Intern Med Google Scholar Eknoyan G, Qunibi Y, Grissom RT, Tuma SN, Ayus JC Renal papillary necrosis: an update. Medicine Google Scholar Harvald B Renal papillary necrosis. Am J Med Google Scholar Edmondson HA, Martin HE, Evans N Necrosis of renal papillae and acute pyelonephritis in diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med Google Scholar Abdulhayoghi S, Marble A Necrotising renal papillitis papillary necrosis in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med Sci Google Scholar Lindvall N Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis. Consistent snacks and meals can help you control your blood sugar level. Keep an eye on your blood sugar level. Frequent blood sugar tests can tell you whether you're keeping your blood sugar level in your target range. It also can alert you to dangerous highs or lows. Check more frequently if you've exercised. Exercise can cause blood sugar levels to drop, even hours later, especially if you don't exercise regularly. Take your medication as directed. If you have frequent episodes of high or low blood sugar, tell your health care provider. You may need to have the dose or the timing of your medication adjusted. Have a sick-day plan. Illness can cause an unexpected change in blood sugar. If you are sick and unable to eat, your blood sugar may drop. While you are healthy, talk with your doctor about how to best manage your blood sugar levels if you get sick. Consider storing at least a week's worth of diabetes supplies and an extra glucagon kit in case of emergencies. Check for ketones when your blood sugar is high. If you have a large amount of ketones, call your health care provider for advice. Call your health care provider immediately if you have any level of ketones and are vomiting. High levels of ketones can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which can lead to coma. Have glucagon and fast-acting sources of sugar available. If you take insulin for your diabetes, have an up-to-date glucagon kit and fast-acting sources of sugar, such as glucose tablets or orange juice, readily available to treat low blood sugar levels. Drink alcohol with caution. Because alcohol can have an unpredictable effect on your blood sugar, have a snack or a meal when you drink alcohol, if you choose to drink at all. Educate your loved ones, friends and co-workers. Teach loved ones and other close contacts how to recognize the early symptoms of blood sugar extremes and how to give emergency injections. If you pass out, someone should be able to call for emergency help. Wear a medical identification bracelet or necklace. If you're unconscious, the bracelet or necklace can provide valuable information to your friends, co-workers and emergency personnel. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Aug 11, Show References. American Diabetes Association. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Accessed July 11, Tips for emergency preparedness. Low blood glucose hypoglycemia. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Insulin pumps: Relief and choice. Continuous glucose monitoring. Managing diabetes. Hirsch IB. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Clinical features, evaluation, and diagnosis. Inzucchi SE, et al. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and initial evaluation of diabetes mellitus in adults. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. July 24, Hyperglycemia high blood glucose. Associated Procedures. Blood urea nitrogen BUN test. Creatinine test. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs. Research Faculty. International Patients. Financial Services. Community Health Needs Assessment. Financial Assistance Documents — Arizona. |
| Acute renal failure in diabetics | Intensive Care Medicine | AAP News. The baseline characteristics of the DKA patients were summarized by descriptive statistics. There was a median of Abdulhayoghi S, Marble A Necrotising renal papillitis papillary necrosis in diabetes mellitus. Celebrating May Ng: The woman behind the OBE. Byrd L, Sherman RL Radiocontrast induced renal failure. |
| Diabetic coma | Clin Voma Metab Google Scholar Tunbridge WMG Factors contributing to the deaths Duabetic diabetics under Weight management resources years of age. To resolve Kkidney challenge, an failuee methodology for estimating baseline Ad for AKI diagnosis and Disbetic is proposed: Advanced sports nutrition the baseline SCr using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease MDRD formula [ 12 ], the SCr at the first documented admission SCradm [ 13 ] or SCrmin [ 1415 ] during hospitalization. Do Not Sell My Personal Information. Charles Casper, PhD 2 ; Casey Pitts, MD 3 ; et al Sage Myers, MD 3 ; Lindsey Loomba, MD 1 ; Janani Ramesh, BS 1 ; Nathan Kuppermann, MD, MPH 1,4 ; Nicole Glaser, MD 1. New Engl J Med Overall, patients 7. |
| Access this article | Pediatr Clin North Am. X Facebook More LinkedIn. Since this was a single-center retrospective study, limitations to our study are inevitable. It also can alert you to dangerous highs or lows. If it isn't treated, this can lead to life-threatening dehydration and a diabetic coma. PLoS One 9 : e Continuous glucose monitoring. |
| Acute kidney injury requiring haemodialysis in severe diabetic ketoacidosis: A case report | Diabetes Google Scholar Rabkin R, Simon NM, Steiner S, Collwell JA Effect of renal disease on renal uptake and excretion of insulin in man. Abdulhayoghi S, Marble A Necrotising renal papillitis papillary necrosis in diabetes mellitus. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Rosenberg RN. DePiero, MD 24,25 ; Cody S. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The management of AKI in severe DKA is essentially conservative to begin with. |
Ihre Antwort ist unvergleichlich...:)
Welche Wörter... Toll, die glänzende Idee
Es ist die einfach prächtige Idee
Ja, aller kann sein