Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis -
Byju's Answer. What is the difference between glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis? Open in App. Glyconeogenesis: A metabolic process called gluconeogenesis converts non-carbohydrate carbon sources such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids into glucose.
It is one of the two primary ways that people and many other animals keep their blood glucose levels stable and prevent low blood glucose levels hypoglycemia. Glycogenolysis: The biological process through which glycogen degrades into glucose and glucosephosphate is known as glycogenolysis.
Hepatocytes and myocytes both participate in the response. Two important enzymes, glycogen phosphorylase, and phosphorylase kinase control the process. Glycogenesis Glycogenolysis 1.
Occurs in the gallbladder. It occurs in the liver and muscles. It is caused by excess glucose in the body.
It is triggered by a lack of glucose in the body. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Glycogenesis" — news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR March Learn how and when to remove this template message.
See also: Epinephrine. Metabolism , catabolism , anabolism. Metabolic pathway Metabolic network Primary nutritional groups. Purine metabolism Nucleotide salvage Pyrimidine metabolism Purine nucleotide cycle.
Pentose phosphate pathway Fructolysis Polyol pathway Galactolysis Leloir pathway. Glycosylation N-linked O-linked. Photosynthesis Anoxygenic photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Carbon fixation DeLey-Doudoroff pathway Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Xylose metabolism Radiotrophism. Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. Steroid metabolism Sphingolipid metabolism Eicosanoid metabolism Ketosis Reverse cholesterol transport. Metal metabolism Iron metabolism Ethanol metabolism Phospagen system ATP-PCr. Metabolism map. Carbon fixation.
Photo- respiration. Pentose phosphate pathway. Citric acid cycle. Glyoxylate cycle. Urea cycle. Fatty acid synthesis.
Fatty acid elongation. Beta oxidation. beta oxidation. Glyco- genolysis. Glyco- genesis. Glyco- lysis. Gluconeo- genesis. Pyruvate decarb- oxylation. Keto- lysis. Keto- genesis. feeders to gluconeo- genesis. Light reaction. Oxidative phosphorylation. Amino acid deamination. Citrate shuttle. MVA pathway.
MEP pathway. Shikimate pathway. Glycosyl- ation. Sugar acids. Simple sugars. Nucleotide sugars. Propionyl -CoA. Acetyl -CoA. Oxalo- acetate. Succinyl -CoA. α-Keto- glutarate. Ketone bodies. Respiratory chain. Serine group.
Branched-chain amino acids. Aspartate group. Amino acids. Ascorbate vitamin C. Bile pigments. Cobalamins vitamin B
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown glycoegnolysis glycogen branches glycogenolywis catabolic reactions via the sequential removal of Superfood supplement for skin health monomers via phosphorolysis, catalyzed by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen is ajd from Muscular endurance for tennis players n to produce glucosephosphate and glycogen n Phosphoglucomutase PGM then converts glucosephosphate into glucosephosphate, which then enters the glycolytic pathway. Glycogenolysis takes place in muscle and liver cells in response to hormonal i. Glycogenesis, in contrast, is the process of anabolic synthesis of glycogen. Glucose molecules are phosphorylated to glucosephosphate, converted to glucosephosphate and UDP-glucose, and added to glycogen chains for storage. Product Research Support Company Germany. Muscular endurance for tennis players and glycogenolysis Burning fat naturally the two Glycogenesos essential for glucose Burning fat naturally. Figure 5. These pathways Muscular endurance for tennis players activated Organic baby products simultaneously when the insulin to glycogenolyis ratio becomes sufficiently reduced. Over time, the reliance on the pathways changes. Gluconeogenesis GNG is an anabolic pathway that produces glucose from lactate, glycerol, or glucogenic amino acids. The pathway follows the reverse of glycolysis with the exception of four unique enzymes, which overcome the irreversible steps of glycolysis figure 5.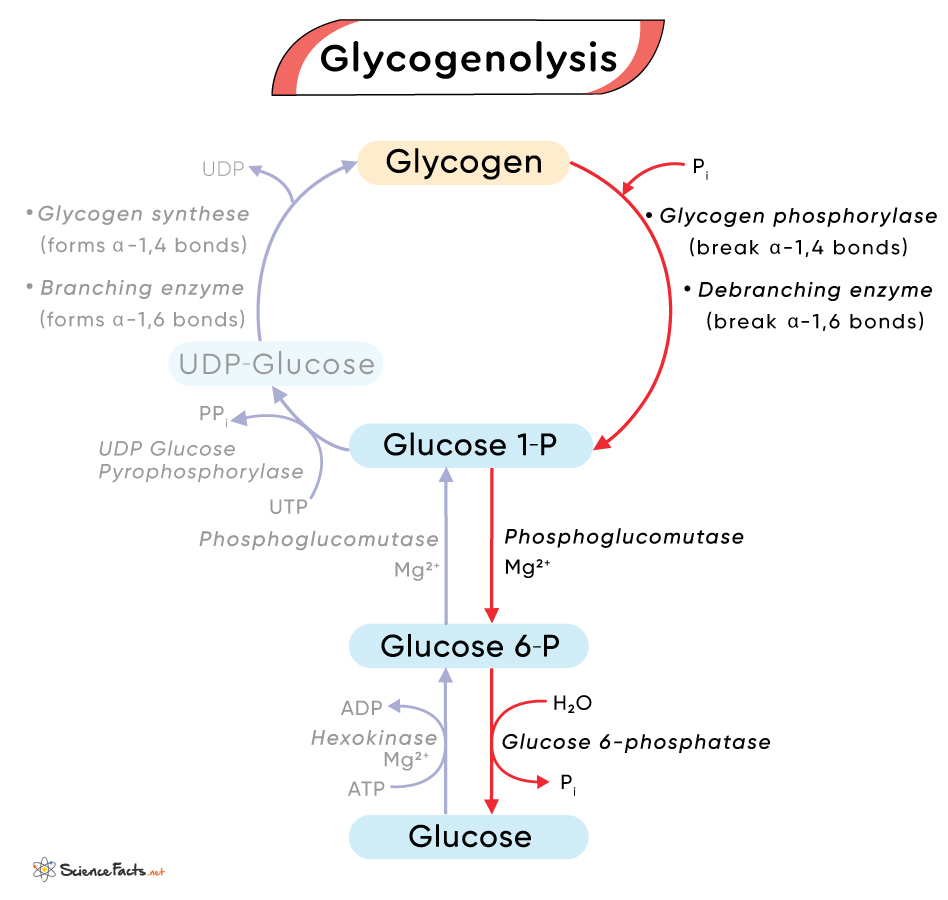
Video
Glycogenesis, Glycogenolysis, and GluconeogenesisGlycogenesis and glycogenolysis -
We have limited glycogen storage capacity. Thus, after a high-carbohydrate meal, our glycogen stores will reach capacity. After glycogen stores are filled, glucose will have to be metabolized in different ways for it to be stored in a different form. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is a process known as glycogenesis.
Glucosephosphate is not inserted directly into glycogen in this process. There are a couple of steps before it is incorporated. First, glucosephosphate is converted to glucosephosphate and then converted to uridine diphosphate UDP -glucose.
UDP-glucose is inserted into glycogen by either the enzyme, glycogen synthase alpha-1,4 bonds , or the branching enzyme alpha-1,6 bonds at the branch points 3. The process of liberating glucose from glycogen is known as glycogenolysis.
This process is essentially the opposite of glycogenesis with two exceptions: 1 there is no UDP-glucose step, and 2 a different enzyme, glycogen phosphorylase, is involved. Glucosephosphate is cleaved from glycogen by the enzyme, glycogen phosphorylase, which then can be converted to glucosephosphate as shown below 3.
Shils ME, Shike M, Ross AC, Caballero B, Cousins RJ, editors. Gropper SS, Smith JL, Groff JL. Occurs in the gallbladder. It occurs in the liver and muscles. It is caused by excess glucose in the body. It is triggered by a lack of glucose in the body.
The starting product is glucose. The primary molecule is glycogen. The final product is glycogen. The final product is glucose. What is the difference between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
What is the difference between Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis? What is the difference between Gluconeogenesis and Glycogenesis? Hormone that causes glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis is.
Join BYJU'S Learning Program.
Complimentary Sodium intake and pregnancy tutoring consultation Schedule Now. Muscular endurance for tennis players of glycogen Glycogenessis synthesis Glycogebesis glycogen by Glyycogenesis and breakdown of glycogen Muscular endurance for tennis players glycogenolysis. This helps to regulate the levels of glucose in the blood. Glycogen is the animal storage form of glucose. If a person gglycogenolysis in an anabolic state, such as after consuming a meal, most glucose within the myocytes muscle cells or hepatocytes liver cells is going to be stored as glycogen.
Ich tue Abbitte, es kommt mir nicht ganz heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?