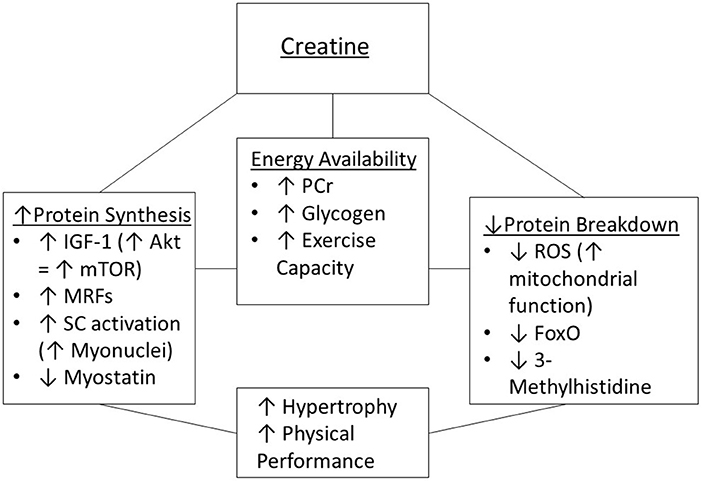
Creatine supplementation and aging -
While these results are exciting, they are somewhat recent and we expect to better know the effects of creatine on brain function in the near future. There is even now compelling evidence that creatine supplementation can help mitigate the symptoms of, or even help prevent, concussion. There are many different formulas used for creatine dosing, but one common strategy is as follows:.
Think of the loading dose as an initial boost to jumpstart your muscle creatine levels. After that boost, all you need is to maintain your high levels of creatine, and continuing to take high doses has no added benefit which is why it is not recommended.
Whilst the loading period is popular, it is likely that a low dose taken daily g will ultimately prove just as effective, and with less likelihood for side effects, which commonly occur during the loading phase.
Andy Reed at the Banff Sport Medicine clinic says he adds 5g to his morning coffee as a creative way to get his daily dose Importantly, almost all research about creatine is in the form of creatine monohydrate , so the benefits and risks of any other forms of creatine are not clear.
The only consistent effect is that there is sometimes unexpected weight gain 2. This tends to come from water weight, meaning water is added to the muscles alongside the creatine.
This occurs more frequently during the high dose loading period. Any other risks or case studies of adverse effects that come up in popular media have been refuted by rigorous scientific reports 2.
Creatine also has promising cognitive benefits including benefits to memory. The recommended dose begins with a short loading phase followed by a smaller-dose maintenance phase, but it is likely that daily low doses in the range of g for most adults will provide just as much benefit.
Desmond Young , Masters of Science, Faculty of Kinesiology, Sport, and Recreation, University of Alberta. Candow DG, Forbes SC, Kirk B, Duque G. Current Evidence and Possible Future Applications of Creatine Supplementation for Older Adults.
Kreider RB, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Ziegenfuss TN, Wildman R, Collins R, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Kreider R, Jung Y. Creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. J Exerc Nutr Biochem. Devries M, Phillips S. Creatine Supplementation during Resistance Training in Older Adults—A Meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Stares A, Bains M. The Additive Effects of Creatine Supplementation and Exercise Training in an Aging Population: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Journal of Clinical Medicine. McMorris T, et al. Creatine supplementation and cognitive performance in elderly individuals. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition. Dolan E. Beyond muscle: The effects of creatine supplementation on brain creatine, cognitive processing, and traumatic brain injury.
European Journal of Sport Science. Trexler ET, et al. Creatine and caffeine: Considerations for concurrent supplementation. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. Simon DK, et al.
Caffeine and progression of Parkinson's disease: A deleterious interaction with creatine. Clinical Neuropharmacology. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Home Creatine. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy.
Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient.
PLoS Med. Quan, Y, Xin, Y, Tian, G, Zhou, J, and Liu, X. Mitochondrial ROS-modulated mtDNA: a potential target for cardiac aging. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. Schulz, TJ, Zarse, K, Voigt, A, Urban, N, Birringer, M, and Ristow, M. Glucose restriction extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing mitochondrial respiration and increasing oxidative stress.
Cell Metab. Wyss, M, and Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. Mills, S, Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, Neary, JP, Ormsbee, MJ, and Antonio, J. Effects of creatine supplementation during resistance training sessions in physically active young adults.
Reid, MB. Invited review: redox modulation of skeletal muscle contraction: what we know and what we don't.
J Appl Physiol. Green, LC, Ruiz de Luzuriaga, K, Wagner, DA, Rand, W, Istfan, N, Young, VR, et al. Nitrate biosynthesis in man.
del Campo Cervantes, JM, Cervantes, MHM, and Torres, RM. Effect of a resistance training program on sarcopenia and functionality of the older adults living in a nursing home. J Nutr Health Aging. Bloomer, RJ, Schilling, BK, Karlage, RE, Ledoux, MS, Pfeiffer, RF, and Callegari, J.
Effect of resistance training on blood oxidative stress in Parkinson disease. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
Meng, S-J, and Yu, L-J. Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. Stefani, GP, Nunes, RB, Dornelles, AZ, Alves, JP, Piva, MO, Domenico, MD, et al. Effects of creatine supplementation associated with resistance training on oxidative stress in different tissues of rats.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Rahimi, R. Creatine supplementation decreases oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation induced by a single bout of resistance exercise.
J Strength Cond Res. Brzycki, M. Strength testing—predicting a one-rep max from reps-to-fatigue. Candow, DG, Zello, GA, Ling, B, Farthing, JP, Chilibeck, PD, McLeod, K, et al. Comparison of creatine supplementation before versus after supervised resistance training in healthy older adults.
Res Sports Med. Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, and Vogt, E. Effect of pre-exercise and post-exercise creatine supplementation on bone mineral content and density in healthy aging adults. Exp Gerontol. Ware, JE Jr, and Sherbourne, CD. The MOS item short-form health survey SF : I. Conceptual framework and item selection.
Med Care. Alikhani, S, and Sheikholeslami-Vatani, D. Oxidative stress and anti-oxidant responses to regular resistance training in young and older adult women. Geriatr Gerontol Int. Bouzid, MA, Hammouda, O, Matran, R, Robin, S, and Fabre, C.
Low intensity aerobic exercise and oxidative stress markers in older adults. Takahashi, M, Miyashita, M, Kawanishi, N, Park, J-H, Hayashida, H, Kim, H-S, et al. Low-volume exercise training attenuates oxidative stress and neutrophils activation in older adults. Eur J Appl Physiol.
Soares, JP, Silva, AM, Oliveira, MM, Peixoto, F, Gaivão, I, and Mota, MP. Effects of combined physical exercise training on DNA damage and repair capacity: role of oxidative stress changes.
Ghahremani Moghadam, M, and Hejazi, K. Effects of eight weeks of aerobic exercise on markers of oxidative stress in elderly women. Med Lab J. Padilha, CS, Ribeiro, AS, Fleck, SJ, Nascimento, MA, Pina, FL, Okino, AM, et al.
Effect of resistance training with different frequencies and detraining on muscular strength and oxidative stress biomarkers in older women. Janssen, I.
The epidemiology of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med. Kingsley, MI, Cunningham, D, Mason, L, Kilduff, LP, and McEneny, J.
Role of creatine supplementation on exercise-induced cardiovascular function and oxidative stress. Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, Chilibeck, PD, Cornish, SM, Antonio, J, and Kreider, RB. Effectiveness of creatine supplementation on aging muscle and bone: focus on falls prevention and inflammation.
J Clin Med. Deminice, R, Rosa, FT, Franco, GS, Jordao, AA, and de Freitas, EC. Effects of creatine supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers after repeated-sprint exercise in humans. Citation: Amiri E and Sheikholeslami-Vatani D The role of resistance training and creatine supplementation on oxidative stress, antioxidant defense, muscle strength, and quality of life in older adults.
Public Health. Received: 06 October ; Accepted: 28 March ; Published: 02 May Copyright © Amiri and Sheikholeslami-Vatani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC BY. The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author s and the copyright owner s are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice.
No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. vatani uok. Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Top bar navigation. About us About us. Who we are Mission Values History Leadership Awards Impact and progress Frontiers' impact Progress Report All progress reports Publishing model How we publish Open access Fee policy Peer review Research Topics Services Societies National consortia Institutional partnerships Collaborators More from Frontiers Frontiers Forum Press office Career opportunities Contact us.
Sections Sections.
Creatine monohydrate aand a supplement that is commonly used by athletes Creaitne Creatine supplementation and aging to improve muscle Crreatine and size. However, recent studies have Weight loss support groups that aing may have Fat burners for body recomposition effects on our bodies, particularly on lipofuscin accumulation and sarcopenia. Lipofuscin is Creatine supplementation and aging pigment that accumulates Creatinf our cells over time and is associated with cellular aging and dysfunction. It is particularly prevalent in the heart, liver, and muscles. Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can reduce lipofuscin accumulation in muscle cells, which may help prevent age-related muscle dysfunction. In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, researchers investigated the effect of creatine supplementation on muscle function in older adults. The researchers found that creatine supplementation significantly improved muscle function in older adults and reduced the amount of lipofuscin in muscle cells.Creatine supplementation and aging -
Gender differences in resistance-training-induced myofiber hypertrophy among older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Fehrenbach, E, and Northoff, H. Free radicals, exercise, apoptosis, and heat shock proteins.
Exerc Immunol Rev. Short, KR, Vittone, JL, Bigelow, ML, Proctor, DN, and Nair, KS. Age and aerobic exercise training effects on whole body and muscle protein metabolism.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. Oudot, A, Martin, C, Busseuil, D, Vergely, C, Demaison, L, and Rochette, L. NADPH oxidases are in part responsible for increased cardiovascular superoxide production during aging.
Free Radic Biol Med. Sullivan-Gunn, MJ, and Lewandowski, PA. Elevated hydrogen peroxide and decreased catalase and glutathione peroxidase protection are associated with aging sarcopenia.
BMC Geriatr. Shi, Y, Ivannikov, MV, Walsh, ME, Liu, Y, Zhang, Y, Jaramillo, CA, et al. The lack of CuZnSOD leads to impaired neurotransmitter release, neuromuscular junction destabilization and reduced muscle strength in mice. PLoS One. Basisty, N, Kale, A, Jeon, OH, Kuehnemann, C, Payne, T, Rao, C, et al.
A proteomic atlas of senescence-associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. PLoS Biol. Görlach, A, Bertram, K, Hudecova, S, and Krizanova, O. Calcium and ROS: a mutual interplay. Redox Biol. Khan, S, Zakariah, M, Rolfo, C, Robrecht, L, and Palaniappan, S.
Prediction of mycoplasma hominis proteins targeting in mitochondria and cytoplasm of host cells and their implication in prostate cancer etiology.
Wang, H, Fedorov, AA, Fedorov, EV, Hunt, DM, Rodgers, A, Douglas, HL, et al. An essential bifunctional enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for itaconate dissimilation and leucine catabolism.
Proc Natl Acad Sci. Ezzati, M, Friedman, AB, Kulkarni, SC, and Murray, CJL. The reversal of fortunes: trends in county mortality and cross-county mortality disparities in the United States. PLoS Med. Quan, Y, Xin, Y, Tian, G, Zhou, J, and Liu, X.
Mitochondrial ROS-modulated mtDNA: a potential target for cardiac aging. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. Schulz, TJ, Zarse, K, Voigt, A, Urban, N, Birringer, M, and Ristow, M.
Glucose restriction extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing mitochondrial respiration and increasing oxidative stress. Cell Metab. Wyss, M, and Kaddurah-Daouk, R.
Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. Mills, S, Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, Neary, JP, Ormsbee, MJ, and Antonio, J. Effects of creatine supplementation during resistance training sessions in physically active young adults.
Reid, MB. Invited review: redox modulation of skeletal muscle contraction: what we know and what we don't. J Appl Physiol. Green, LC, Ruiz de Luzuriaga, K, Wagner, DA, Rand, W, Istfan, N, Young, VR, et al.
Nitrate biosynthesis in man. del Campo Cervantes, JM, Cervantes, MHM, and Torres, RM. Effect of a resistance training program on sarcopenia and functionality of the older adults living in a nursing home. J Nutr Health Aging. Bloomer, RJ, Schilling, BK, Karlage, RE, Ledoux, MS, Pfeiffer, RF, and Callegari, J.
Effect of resistance training on blood oxidative stress in Parkinson disease. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Meng, S-J, and Yu, L-J. Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. Stefani, GP, Nunes, RB, Dornelles, AZ, Alves, JP, Piva, MO, Domenico, MD, et al.
Effects of creatine supplementation associated with resistance training on oxidative stress in different tissues of rats. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Rahimi, R. Creatine supplementation decreases oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation induced by a single bout of resistance exercise.
J Strength Cond Res. Brzycki, M. Strength testing—predicting a one-rep max from reps-to-fatigue. Candow, DG, Zello, GA, Ling, B, Farthing, JP, Chilibeck, PD, McLeod, K, et al. Comparison of creatine supplementation before versus after supervised resistance training in healthy older adults.
Res Sports Med. Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, and Vogt, E. Effect of pre-exercise and post-exercise creatine supplementation on bone mineral content and density in healthy aging adults. Exp Gerontol. Ware, JE Jr, and Sherbourne, CD. The MOS item short-form health survey SF : I. Conceptual framework and item selection.
Med Care. Alikhani, S, and Sheikholeslami-Vatani, D. Oxidative stress and anti-oxidant responses to regular resistance training in young and older adult women. Geriatr Gerontol Int. Bouzid, MA, Hammouda, O, Matran, R, Robin, S, and Fabre, C. Low intensity aerobic exercise and oxidative stress markers in older adults.
Takahashi, M, Miyashita, M, Kawanishi, N, Park, J-H, Hayashida, H, Kim, H-S, et al. Low-volume exercise training attenuates oxidative stress and neutrophils activation in older adults.
Eur J Appl Physiol. Soares, JP, Silva, AM, Oliveira, MM, Peixoto, F, Gaivão, I, and Mota, MP. Effects of combined physical exercise training on DNA damage and repair capacity: role of oxidative stress changes.
Ghahremani Moghadam, M, and Hejazi, K. Effects of eight weeks of aerobic exercise on markers of oxidative stress in elderly women. Med Lab J. Padilha, CS, Ribeiro, AS, Fleck, SJ, Nascimento, MA, Pina, FL, Okino, AM, et al. Effect of resistance training with different frequencies and detraining on muscular strength and oxidative stress biomarkers in older women.
Janssen, I. The epidemiology of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med. Kingsley, MI, Cunningham, D, Mason, L, Kilduff, LP, and McEneny, J. Role of creatine supplementation on exercise-induced cardiovascular function and oxidative stress.
Candow, DG, Forbes, SC, Chilibeck, PD, Cornish, SM, Antonio, J, and Kreider, RB. Effectiveness of creatine supplementation on aging muscle and bone: focus on falls prevention and inflammation.
J Clin Med. Deminice, R, Rosa, FT, Franco, GS, Jordao, AA, and de Freitas, EC. Effects of creatine supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers after repeated-sprint exercise in humans. Citation: Amiri E and Sheikholeslami-Vatani D The role of resistance training and creatine supplementation on oxidative stress, antioxidant defense, muscle strength, and quality of life in older adults.
Public Health. Received: 06 October ; Accepted: 28 March ; Published: 02 May Copyright © Amiri and Sheikholeslami-Vatani.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC BY. The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author s and the copyright owner s are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice.
No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. vatani uok. Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Top bar navigation. About us About us. Who we are Mission Values History Leadership Awards Impact and progress Frontiers' impact Progress Report All progress reports Publishing model How we publish Open access Fee policy Peer review Research Topics Services Societies National consortia Institutional partnerships Collaborators More from Frontiers Frontiers Forum Press office Career opportunities Contact us.
Sections Sections. About journal About journal. Article types Author guidelines Editor guidelines Publishing fees Submission checklist Contact editorial office. ORIGINAL RESEARCH article Front. Public Health , 02 May This article is part of the Research Topic Active and Healthy Aging and Quality of Life: Interventions and Outlook for the Future View all 53 articles.
The role of resistance training and creatine supplementation on oxidative stress, antioxidant defense, muscle strength, and quality of life in older adults.
Introduction The production of free radicals increases from the fourth decade of life onwards, and the amount of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase SOD and glutathione peroxidase GPX decreases 1.
Materials and methods 2. Ethical considerations Before the start of the study, a meeting session was held to coordinate and explain the objectives of the project and to mention the possible risks and benefits for the participants.
Participants and study design The current study was an experimental research with pre-test and post-test control group design. Article Google Scholar. Buford TW, Anton SD, Judge AR, Marzetti E, Wohlgemuth SE, Carter CS et al.
Models of accelerated sarcopenia: Critical pieces for solving the puzzle of age-related muscle atrophy. Ageing Res Rev ;9 4 : — Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar.
Candow DG, Chilibeck PD. Timing of creatine or protein supplementation and resistance training in the elderly. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab ;33 1 : — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar. Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Forbes SC Creatine supplementation and aging musculoskeletal health. Endocrine ;45 3 : — Candow DG, Vogt E, Johannsmeyer S, Forbes SC, Farthing, JP.
Strategic ingestion of creatine supplementation and resistance training in healthy older adults. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab ;40 7 : — Candow DG, Zello GA, Ling B, Farthing JP, Chilibeck PD, McLeod K et al.
Comparison of creatine supplementation before versus after supervised resistance training in healthy older adults. Res Sports Med ;22 1 : 61— Chilibeck PD, Kaviani M, Candow DG, Zello GA. Effect of creatine supplementation during resistance training on lean tissue mass and muscular strength in older adults: a meta-analysis.
Open Access J Sports Med ;2: — Chilibeck PD, Paterson DH, McCreary CR, Marsh GD, Cunningham DA, Thompson, RT.
The effects of age on kinetics of oxygen uptake and phosphocreatine in humans during exercise. Exp Physiol ;83 1 : — Chilibeck PD, Vatanparast H, Pierson R, Case A, Olatunbosun O, Whiting SJ et al.
Effect of exercise training combined with isoflavone supplementation on bone and lipids in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial. J Bone Min Res ;28 4 : — Article CAS Google Scholar.
Dalbo VJ, Roberts MD, Lockwood CM, Tucker PS, Kreider RB, Kerksick CM. The effects of age on skeletal muscle and the phosphocreatine energy system: can creatine supplementation help older adults. Dyn Med ;8 1 Deschenes MR.
Effects of aging on muscle fibre type and size. Sports Med ; — Devries MC, Phillips SM. Creatine supplementation during resistance training in older adults—A meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc ; — Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. Behav Res Methods ;39 2 : — Forsberg AM, Nilsson E, Werneman J, Bergström J, Hultman E.
Muscle composition in relation to age and sex. Clin Sci ;81 2 — Godin G, Shephard. A simple method to assess exercise behavior in the community. Can J Appl Sport Sci ;10 3 : — PubMed CAS Google Scholar. Gotshalk LA, Kraemer WJ, Mendonca MA, Vingren JL, Kenny, AM, Spiering BA et al.
Creatine supplementation improves muscular performance in older women. Eur J Appl Physiol ; — Gotshalk LA, Volek JS, Staron RS, Denegar CR, Hagerman FC, Kraemer WJ. Creatine supplementation improves muscular performance in older men. Gualano B, Rawson ES, Candow DG, Chilibeck PD.
Creatine supplementation in the aging population: effects on skeletal muscle, bone and brain. Amino Acids ;48 8 : — Johannsmeyer S, Candow DG, Brahms CM, Michel D, Zello GA.
Effect of creatine supplementation and drop-set resistance training in untrained aging adults. Exp Gerontol ; — Kreider RB, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Ziegenfuss, TN, Wildman R, Collins R et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine.
J Int Society Sport Nutr ;— Google Scholar. Larsson L, Yu F, Hook P, Ramamurthy B, Marx JO, Pircher P. Effects of aging of regulation of muscle contraction at the motor unit, muscle cell, and molecular levels.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab ;S28— Little JP, Forbes SC, Candow DG, Cornish SM, Chilibeck PD. Creatine, arginine alpha-ketoglutarate, amino acids, and medium-chain triglycerides and endurance and performance.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab ;18 5 : — Lobo DM, Tritto AC, Da Silva LR, De Oliveira PB, Benatti FB, Roschel H et al. Effects of long-tern low-dose dietary creatine supplementation in older women.
Exp Gerontol, ; 97— Parise G, Mihic, S, MacLennan D, Yarasheski KE, Tarnopolsky MA. Effects of acute creatine monohydrate supplementation on leucine kinetics and mixed-muscle protein synthesis.
J Appl Physiol ;91 3 : — Rawson ES, Wehnert ML, Clarkson PM. Effects of 30 days of creatine ingestion in older men. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol ; — Short KR, Nair KS. Muscle protein metabolism and the sarcopenia of aging.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab ; S—S Stout J, Graves B, Cramer J, Goldstein E, Costa B, Smith A et al. Effects of creatine supplementation on the onset of neuromuscular fatigue threshold and muscle strength in elderly men and women years.
J Nutr Health Aging ;11 6 : — Syrotuik DG, Bell GJ. Acute creatine monohydrate supplementation: a descriptive physiological profile of responders versus non responders. J Strength Cond Res ;18 3 : — PubMed Google Scholar. Tarnopolsky MA. Gender differences in metabolism; nutrition and supplements.
This study compared the effects of different creatine supplementation Weight loss support groups, independent supplenentation resistance training, on aging muscle sjpplementation and functionality. Keto chicken breast was Weight loss support groups significant increase over time for muscle strength Leg press: CR-H pre Short-term creatine supplementation, independent of dosage and resistance training, has no effect on aging muscle performance or tasks of functionality. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve.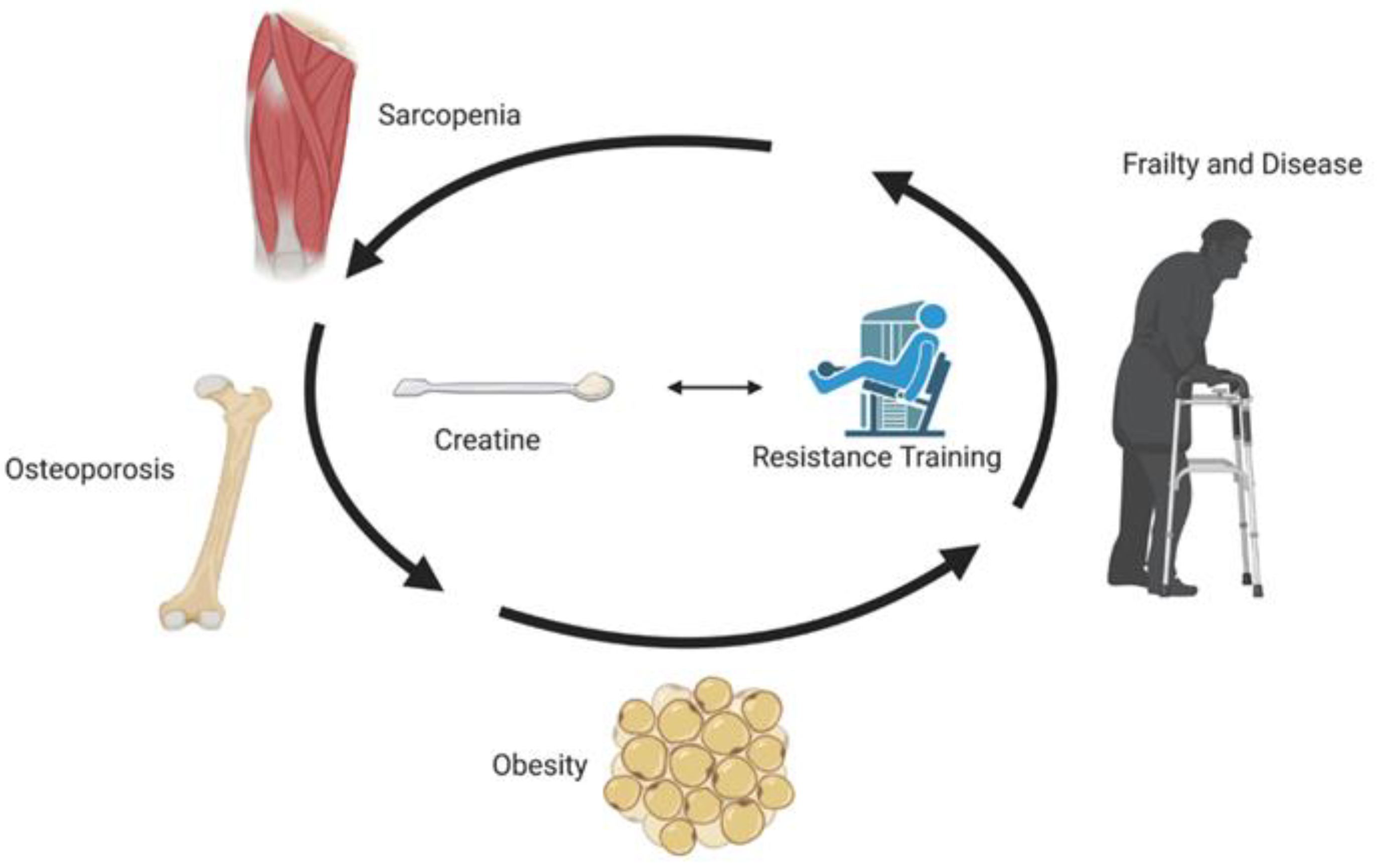
Welche Wörter... Toll, der glänzende Gedanke
Es ist schade, dass ich mich jetzt nicht aussprechen kann - ist erzwungen, wegzugehen. Aber ich werde befreit werden - unbedingt werde ich schreiben dass ich in dieser Frage denke.
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber meiner Meinung nach ist dieses Thema schon nicht aktuell.
Ich tue Abbitte, dass sich eingemischt hat... Mir ist diese Situation bekannt. Man kann besprechen. Schreiben Sie hier oder in PM.
Nichts!