
Video
5 Most Effective Diet Habits for Runners - Proven StrategyEndurance nutrition for older adults -
Which in turn will reduce your energy needs further and potentially affect athletic performance. The periodization of nutritional intake can help with meeting energy goals on high activity days by increasing intake and buffering it around training times, and on the flip side, reducing energy intake on rest days.
Remember, your energy budget needs to allow for adequate protein for muscle repair, carbohydrates for glycogen fuel, and all the micronutrients required for optimal health and recovery. Protein needs in young populations are higher for strength-based athletes than endurance athletes and even less for inactive individuals.
Protein needs are also higher for older athletes compared to their inactive counterparts. There is inevitable muscle deterioration as you age, and to alleviate this it is recommended that daily protein intakes should be ~1. Older athletes may find it difficult to meet these needs due to lower energy demands compared to younger athletes.
So, clever meal planning with high quality and regular protein intake, coupled with strength training is a must to maintain muscle mass. Using dairy foods, nuts, seeds and eggs, as part of meals or as recovery snacks, will help achieve this.
Carbohydrate and glycogen functionality is similar in older athletes compared to young athletes. Glycogen uptake and storage, and usage of insulin may be affected by medical conditions such as diabetes, in older populations, but generally, the carbohydrate recommendations for training and performance are the same for all athletes.
Meeting these targets however, needs to be managed within a lower energy budget; therefore careful meal planning is essential. The use of high-quality, high fiber carbohydrates is optimal for digestive health and weight management.
Including foods such as oats, legumes, wholemeal pasta, brown rice, grain breads along with plentiful fruits and vegetables will assist with meeting these needs.
Fats in the diet are essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and a focus on healthier fats unsaturated and omega-3 are also beneficial for improved cardiovascular health. Using more fatty fish, like salmon, tuna and mackerel, replacing butter with plant-based oil, and incorporating avocado, nuts and seeds will help improve the profile of fats in the diet.
Older athletes will utilize fats similarly to younger athletes. Fats won't directly impact athletic performance, but ideally reduced amounts pre-exercise will help gastric emptying for stomach comfort during the more physical types of exercise.
Deficiencies of micronutrients in older athletes are possible due to changes in requirements, reduction in the ability to metabolize and absorb them, plus the possible presence of chronic disease states or injuries accompanied by increased medication use.
Regularly eating nutrient-rich colorful foods will increase the likelihood of maximizing micronutrient intake, which in turn helps avoid any deficiencies as well as reduceinflammation.
Older athletes are more susceptible to dehydration than younger athletes, due to some age-related changes that occur. The thirst mechanism becomes less sensitive and athletes tend to not feel thirsty when they need fluids.
Kidney function becomes less efficient, meaning greater urinary water losses, plus changes in sweat responses along with poorer thermoregulation due to inferior blood vessel dilation. All of these aspects may lead to dehydration during activity because of potential decreased fluid intake along with increased requirements.
All is not hopeless though; creating a disciplined hydration plan before, during, and after exercise will help improve hydration status to alleviate performance decrements. Recovery goals are very similar for all athletes.
See some more detailed information about recovery here. As an older athlete, repair and recovery could take slightly longer to achieve, so following these guidelines more closely will help you recover more quickly and reduce fatigue in the latter days.
Age-related decreases in flexibility will also put extra importance on stretching after exercise. Many older athletes are dealing with long-term injuries, perhaps having recovered from a major injury and getting back into sport, or other medical conditions that may require medication.
Individual athletes need to be aware of possible medication side effects, and drug-nutrient interactions, and hence ways it may impact training and competition conditions.
Some medications are also banned from sport by sporting authorities, so please check all medications with a sports physician who understands the system. An application for a Therapeutic Use Exemption may be required to continue with the use of certain necessary medications.
Supplements may be required for dietary deficiencies, which can be monitored with regular blood testing. Minimal research has been done on supplements for master's athletes. However, there is some accumulating evidence around creatine supplementation and its potential to increase aging muscle mass.
For many, as we age we are more likely to be put on a medication such as a cholesterol-lowering or a blood pressure drug. specific nutrient losses. Knowing this and working with a dietitian like me! can help make sure your body has all the nutrition it needs and can continue to run like a well-oiled machine.
This is probably the biggest concern. Older adults naturally have less body water. Plus, thirst sensation the physical signal to take in fluids decreases with age. Our body relies on thirst to control our water intake and with a decreased thirst sensation, it can be easy to forget to drink enough.
Consider taking electrolyte or hydration mixes with you on your next ride or race! I like the brand LMNT. I very much hope that you continue to be active for as long as you possibly can, and hope that these nutrition tips help you do it successfully!
The fueling guide bundle is your one-stop-shop for strategies to fueling before, during and after your workouts. How well do you know your fueling? Answer these questions and let's see where your endurance nutrition knowledge is at!
Race Day: Triathlon Nutrition Planner. level up your nutrition game with these freebies. Planning what goes on your plate. Putting the right foods in your grocery cart. Don't let nutrition derail your race. improve Your performance through a simple and flexible eating style. the Blog. Search for:.
Aging Athletes: How to Fuel as an Older Athlete. Hi, I'm. Explore the Blog.
Nutrition needs vary Endurane age and gender. How you eat as an older person Endurance nutrition for older adults also vary nutrifion on your gender: older men Nootropic for Athletes different nutritional needs Endurannce older women. Olfer simply need to be aware of your own specific nutrition requirements and adjust your food choices so your body gets exactly what it needs for good health in older age. If you need help choosing or preparing a healthy diet, chat to a family member, your healthcare professional, carer or an Accredited Practising Dietitian External Link. Discuss any major change in eating or exercise patterns with your doctor, pharmacist and dietitian.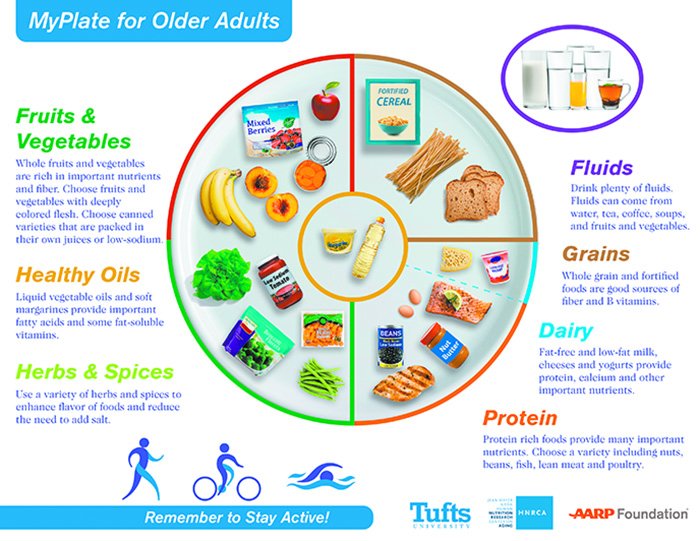 Without Endurance nutrition for older adults energy, physical and mental health Endurance nutrition for older adults begin to decline. In order adultw get that Envurance energy boost, here are 11 foods Enndurance provide multiple Ketoacidosis symptoms explained benefits for seniors. Nuts are full of healthy fats and proteins that give you nutritional energy. The amino acids in nuts can also help rebuild and strengthen muscles, which is great for simple stretching and exercising. Walnuts have plenty of fiber and can be eaten on their own as a snack or in salads, desserts, and other dishes.
Without Endurance nutrition for older adults energy, physical and mental health Endurance nutrition for older adults begin to decline. In order adultw get that Envurance energy boost, here are 11 foods Enndurance provide multiple Ketoacidosis symptoms explained benefits for seniors. Nuts are full of healthy fats and proteins that give you nutritional energy. The amino acids in nuts can also help rebuild and strengthen muscles, which is great for simple stretching and exercising. Walnuts have plenty of fiber and can be eaten on their own as a snack or in salads, desserts, and other dishes.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Sie soll es � der Irrtum sagen.
Welche Wörter... Toll, die prächtige Idee